Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Yuki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf046_1 - ncaf046_11, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0Takahara, Shogo; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Takayuki*; Kawabata, Masako*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 50(1), p.1 - 9, 2025/03
The Health Physics Society of Japan established a working group to obtain insights and findings from articles related to the 1F accident, published in the Japanese Journal of Health Physics. This study describes the review results of 47 articles classified into the field without risk communication, environmental measurement and monitoring, radiation dose measurement and assessment, radiation medicine, and radioactive waste. The reviewed articles contain various insights and issues depending on the authors' standpoints and relevant social interests. As a result, the 1F accident relevant articles offer various discussion points depending on the authors' awareness of the issues, which give an opportunity to make reconsiderations on what kind of academic system health physics or radiation protection should be on the basis of the experiences from the 1F accident. Note that this is an English translation of an article published in Japanese Journal of Health Physics.
Kowatari, Munehiko*; Nakagami, Koichi*; Hijikata, Yasukazu*; Yamashita, Kazuta*; Hirai, Yuta*; Matsuzaki, Satoru*; Moritake, Takashi*; Tsuji, Tomoya; Zutz, H.*; Ketelhut, S.*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf061_1 - ncaf061_9, 2025/00
Tsuji, Tomoya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Sato, Fuminobu*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf060_1 - ncaf060_15, 2025/00
Kowatari, Munehiko*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tani, Kotaro*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Kurihara, Osamu*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1574 - 1579, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Kujiraoka, Ikuo; Noguchi, Yoshihiro*; Shimada, Kazumasa; Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1561 - 1567, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Lifetime Attributable Risk (LAR) of cancer induced by radiation exposures is one of the important factors for deciding about radiological protection measures or protective actions for nuclear emergency preparedness and response. In Japan, while a model for estimating LAR for the Japanese population has been developed based on epidemiological data from A-bomb survivors, a flexible projection code implementing this model needs to be developed. This study investigated the existing codes to contribute to the development of the projection code. Based on these investigations, we compared their LAR calculation results, and explored the cause of their differences.
Seito, Hajime*; Yokozuka, Eri*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1656 - 1659, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)We have examined dosimetric characteristics of bio-inspired carbonated hydroxyapatite (CO HAp), which is a main component of calcified tissues like tooth enamel. CO
HAp), which is a main component of calcified tissues like tooth enamel. CO HAp powder samples were exposed to gamma-ray with radiation doses ranging from 1 Gy to 1000 Gy at room temperature, and ESR spectra were measured immediately after irradiation and subsequently measured each 1 day during 90 days. The post-irradiation fading resulted in significant 20% decay of the signal amplitude, which stabilised within 7 days after irradiation, and the intensity approached a constant. The sample has good linear dose response in the experiment range of 10 Gy - 1000 Gy. Our results indicate that the CO
HAp powder samples were exposed to gamma-ray with radiation doses ranging from 1 Gy to 1000 Gy at room temperature, and ESR spectra were measured immediately after irradiation and subsequently measured each 1 day during 90 days. The post-irradiation fading resulted in significant 20% decay of the signal amplitude, which stabilised within 7 days after irradiation, and the intensity approached a constant. The sample has good linear dose response in the experiment range of 10 Gy - 1000 Gy. Our results indicate that the CO HAp materials is suitable for chemical dosimetry.
HAp materials is suitable for chemical dosimetry.
 -ray visualization survey meter in high gamma and neutron background environment
-ray visualization survey meter in high gamma and neutron background environmentTsubota, Yoichi; Kobayashi, Kenji; Ishii, Tatsuya; Hirato, Misaki; Shioya, Satoshi; Nakagawa, Takahiro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1676 - 1680, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)In the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS, 1F), workers are removing structures from inside the buildings, monitoring radioactive contamination, and decontaminating inside the buildings. For the measurement of contamination of suit surfaces of workers, we have developed a hand-held survey meter that can measure and visualize surface radioactive contamination of  -nuclides in a high
-nuclides in a high  /
/  -ray background environment. In order to selectively measure
-ray background environment. In order to selectively measure  -nuclides, we designed and built a prototype hand-held survey meter for
-nuclides, we designed and built a prototype hand-held survey meter for  -rays, which consists of a thin-film ZnS:Ag scintillator, a multi-anode photomultiplier tube (MA-PMT), individual amplification and counting circuits for each channel of the MA-PMT. Based on the result of
-rays, which consists of a thin-film ZnS:Ag scintillator, a multi-anode photomultiplier tube (MA-PMT), individual amplification and counting circuits for each channel of the MA-PMT. Based on the result of  -ray counting, the developed device is capable of counting the
-ray counting, the developed device is capable of counting the  -radiation beyond 2.1
-radiation beyond 2.1 10
10 cpm. In the
cpm. In the  -ray response test, there was no
-ray response test, there was no  -ray response even when the detector was in close proximity to a high intensity source; The dose rate was estimated to be more than 1 Sv/h. In the future, we plan to reduce the weight and size of the device, as well as improve the usability of the device through actual testing in contaminated environments.
-ray response even when the detector was in close proximity to a high intensity source; The dose rate was estimated to be more than 1 Sv/h. In the future, we plan to reduce the weight and size of the device, as well as improve the usability of the device through actual testing in contaminated environments.
Kitamura, Yoshimasa; Oka, Toshitaka; Seito, Hajime*; Yokozuka, Eri*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1660 - 1665, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)In this work, we evaluated the applicability of hydroxyapatite, which is a main component of tooth enamel, as individual dosimeters that can detect from less than 1 Gy to several tens Gy. Commercially available hydroxyapatite was irradiated by  Co gamma-ray up to 75 Gy and ESR spectrum of the irradiated sample was observed. The relationship between the intensity of produced carbonated radical and the absorbed dose shows a good linearity (
Co gamma-ray up to 75 Gy and ESR spectrum of the irradiated sample was observed. The relationship between the intensity of produced carbonated radical and the absorbed dose shows a good linearity (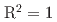 ) from 0 to 75 Gy. The detection limit of this samples was estimated to be 99.7 mGy, and the radical intensity do not change for eight month from the irradiation. These results suggest that this sample can be used as a candidate of the individual dosimeter.
) from 0 to 75 Gy. The detection limit of this samples was estimated to be 99.7 mGy, and the radical intensity do not change for eight month from the irradiation. These results suggest that this sample can be used as a candidate of the individual dosimeter.
 Am gamma calibration field based on international standards and its conversion coefficients
Am gamma calibration field based on international standards and its conversion coefficientsTsuji, Tomoya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(15), p.1416 - 1424, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Endo, Akira
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(13), p.1266 - 1273, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)This study examines the relationship between ambient dose  , ambient dose equivalent
, ambient dose equivalent  , and effective dose for external neutron irradiation over 163 operational spectra from different workplaces. The results show that
, and effective dose for external neutron irradiation over 163 operational spectra from different workplaces. The results show that  provides a reasonable estimate with a controlled margin, even if overestimated, to assess effective dose compared with
provides a reasonable estimate with a controlled margin, even if overestimated, to assess effective dose compared with  , which can lead to a significant overestimation or underestimation of effective dose depending on the neutron spectra. The results highlight the limitations of
, which can lead to a significant overestimation or underestimation of effective dose depending on the neutron spectra. The results highlight the limitations of  and the superiority of
and the superiority of  in estimating effective dose according to the requirements of the operational quantity, especially in environments with high-energy neutrons.
in estimating effective dose according to the requirements of the operational quantity, especially in environments with high-energy neutrons.
Watabe, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yamaya, Taiga*; Kawachi, Naoki*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(2), p.130 - 142, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Environmental Sciences)Previously, we have developed DynamicMC for modelling relative movement of ORNL phantom in a radiation field for MCNP. Using this software, 3-dimensional dose distributions in a phantom irradiated by a certain mono-energetic source can be deduced through its graphical user interface (GUI). In this study, we extended DynamicMC to be used in combination with the PHITS by providing it with a higher flexibility for dynamic movement for a less sophisticated anthropomorphic phantom. We anticipate that the present work and the developed open-source tools will be in the interest of nuclear radiation physics community for research and teaching purposes.
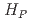 (0.07) for extremity dose monitoring of medical personnel
(0.07) for extremity dose monitoring of medical personnelKowatari, Munehiko*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nagamoto, Keisuke*; Nakagami, Koichi*; Moritake, Takashi*; Kunugita, Naoki*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(15-16), p.1807 - 1812, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Toyoda, Shin*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Yamaguchi, Ichiro*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Hirota, Seiko*; Oka, Toshitaka; Shimazaki, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Hideyuki*; Tani, Atsushi*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Environmental Sciences)Interlaboratory comparison studies are important for radiation dosimetry in order to demonstrate how the technique is universally available. The set of standard samples are examined in each participating laboratory in the present study. After a set of standard samples together with the samples with unknown doses, which were prepared in the same laboratory as the standard samples, are measured at a participating laboratory, those samples are sent to another participating laboratory for next measurement. There is some small difference observed in the sensitivity (the slope of the dose response line) of the standard samples while the differences in the obtained doses for the samples with unknown doses are rather systematic, implying that the difference is mostly due to the samples but not to measurements.
Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1620 - 1625, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Environmental Sciences)We have been conducting dose assessments for Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima to reveal radiobiological effects on the low-dose expose animals. To accurately determine the external exposure dose, it is desirable to examine the analysis of the CO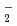 radical intensity. We examined ESR spectra of teeth of 10 macaques captured in Fukushima by two spectrum-decomposition algorithms.
radical intensity. We examined ESR spectra of teeth of 10 macaques captured in Fukushima by two spectrum-decomposition algorithms.
 particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detectorMorishita, Yuki; Sagawa, Naoki; Takada, Chie; Momose, Takumaro; Takasaki, Koji
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(13), p.1376 - 1383, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Environmental Sciences)It is very important to evaluate the diameters (activity median aerodynamic diameter) of Plutonium dioxide (PuO ) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO
) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of
particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of  PuO
PuO and the case of PuO
and the case of PuO (including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO
(including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
Kowatari, Munehiko*; Kubota, Takumi*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kunugita, Naoki*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(11), p.1239 - 1247, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Sasaki, Michiya*; Furukawa, Kyoji*; Satoh, Daiki; Shimada, Kazumasa; Kudo, Shinichi*; Takagi, Shunji*; Takahara, Shogo; Kai, Michiaki*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 48(2), p.90 - 99, 2023/06
This paper reports on the calculation code that is the result of the activities of the "Task Group for Development of Cancer Risk Estimation Codes Associated with Radiation Exposure (FY2020-2021)" established by the Japan Health Physics Society. In order to promote research on the estimation of cancer risk associated with radiation exposure, the Task Group decided to disclose the source code, including the algorithm and parameters used in the calculations, and to release the code under a license that permits modification and redistribution of the code. The computational code was named SUMRAY and coded in two computer languages, that is R and Python. The code is capable of calculating the accumulated excess risk using Monte Carlo methods with a 95% confidence interval. The results of SUMRAY were compared with the results of the existing codes whose source code is not publicly available, under the same calculation conditions. From the results, it was found that they were in reasonable agreement within the confidence interval. It is expected that SUMRAY, an open-source software, will be used as a common basis for cancer risk estimation studies associated with radiation exposure.
Miwa, Kazuji; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 48(2), p.68 - 76, 2023/06
In the process of discussion on possibility of using radionuclide-contaminated soil and debris generated by radiation disasters, strategy on the proper management of radiation exposure protection while considering the source of the contaminated materials is necessary. We proposed five interpretations of radiation protection to contribute the promotion of discussion on possibility of using a part of low-level-radionuclide-contaminated soil and debris in post-accident rehabilitation. Interpretations I to III are based on the idea of "using a reference level to protect the public in post-accident rehabilitation," whereas IV and V are based on the idea of "using the dose constraint to protect the public in post-accident rehabilitation when the sources are handled in a planned activity."
Sato, Yuki; Minemoto, Kojiro*; Nemoto, Makoto*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(8-9), p.1021 - 1028, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:62.75(Environmental Sciences)