Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nozaki, Yukio*; Sukegawa, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Shinichi*; Yunoki, Seiji*; Horaguchi, Taisuke*; Nakayama, Hayato*; Yamanoi, Kazuto*; Wen, Z.*; He, C.*; Song, J.*; et al.
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 26(1), p.2428153_1 - 2428153_39, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kiyohara, Shin*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Kumagai, Yu*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 25(1), p.2393567_1 - 2393567_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)While ceramic materials are widely used in our society, their understanding of the plasticity is not fully understood. MgO is one of the prototypical ceramics, extensively investigated experimentally and theoretically. However, there is still controversy over whether edge or screw dislocations glide more easily. In this study, we directly model the atomic structures of the dislocation cores in MgO based on the first-principles calculations and estimate the Peierls stresses. Our results reveal that the screw dislocation on the primary slip system exhibits a smaller Peierls stress than the edge dislocation. The tendency is not consistent with metals, but rather with TiN, suggesting a characteristic inherent to ceramics.
 temperature measurement for lamp-based heating device
temperature measurement for lamp-based heating deviceSumita, Takehiro; Sudo, Ayako; Takano, Masahide; Ikeda, Atsushi
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials; Methods (Internet), 2(1), p.50 - 54, 2022/02
 Co
Co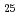 Ni
Ni Al
Al Ti
Ti Mo
Mo medium-entropy alloy; In situ neutron diffraction analysis
medium-entropy alloy; In situ neutron diffraction analysisKwon, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Jeong, S. G.*; Kim, E. S.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Kato, Hidemi*; Kim, H. S.*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.579 - 586, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O vapor on GaN surfaces
O vapor on GaN surfacesSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Sang, L.*; Harada, Yoshitomo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.189 - 198, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)GaN is an attracting material for power-electronic devices. Understanding the oxidation at GaN surface is important for improving metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices. In this study, the oxidation at GaN surfaces depending on the GaN crystal planes (+c, -c, and m-plane) was investigated by real time XPS and DFT-MD simulation. We found that H O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H
O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al
O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al Ga
Ga N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al
N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al O
O layer deposited by ALD using H
layer deposited by ALD using H O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H
O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H O and O
O and O should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al
should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al Ga
Ga N atomi layer deposition.
N atomi layer deposition.
Tremsin, A. S.*; Gao, Y.*; Dial, L. C.*; Grazzi, F.*; Shinohara, Takenao
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 17(1), p.324 - 336, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:53.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) (M: Ca, Ba) probed by muon spin relaxation and muon level-crossing resonance
(M: Ca, Ba) probed by muon spin relaxation and muon level-crossing resonanceKuroiwa, Sogo*; Takagiwa, Hiroyuki*; Yamazawa, Maki*; Akimitsu, Jun*; Koda, Akihiro*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Oishi, Kazuki; Higemoto, Wataru; Watanabe, Isao*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 7(1), p.12 - 16, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The temperature dependence of muon spin relaxation rate exhibits a significant increase below  130 K in CaB
130 K in CaB and
and  110 K in BaB
110 K in BaB , while no sigh of spontaneous muon precession signal under a zero field is observed. Moreover, the electric field gradient at the boron site measured by muon level-crossing resonance exhibits a step like change at
, while no sigh of spontaneous muon precession signal under a zero field is observed. Moreover, the electric field gradient at the boron site measured by muon level-crossing resonance exhibits a step like change at  110 K in CaB
110 K in CaB . These results suggest a change in electronic state and the associated emergence of weak random magnetism below 110-130 K in these alkaline earth hexaborides.
. These results suggest a change in electronic state and the associated emergence of weak random magnetism below 110-130 K in these alkaline earth hexaborides.