Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kamiya, Junichiro
Shinku Janaru, (189), p.6 - 11, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Junichiro
Saishin Jikken Shinku Gijutsu Soran, p.908 - 917, 2019/02
Vacuum is a core technology in accelerators, and the latest accelerator is full of next generation vacuum technologies. In order to solve the problem at each stage of the high intensity proton accelerator, such as stable beam supply from the ion source, suppression of discharge in the acceleration cavity, reduction in beam loss, suppression of pressure increase due to particle desorption from the surface, the vacuum is a key technology. In this manuscript, we will explain the vacuum technology in the high-intensity proton accelerator with J-PARC Linac and 3 GeV synchrotron as examples.
Sano, Yuichi; Ambai, Hiromu; Takahatake, Yoko
Aichi Shinkurotoron Hikari Senta 2017-Nendo Kokyoto Riyo Seika Hokokusho (Internet), 1 Pages, 2018/00
In order to elucidate the mechanism of corrosion in the reprocessing process and propose a method for suppressing corrosion, the effect of coexisting substances on the chemical form of Ru in nitric acid solution containing seawater components was evaluated. The result of XAFS measurement for Ru showed the structural change around a Ru atom due to the interaction with chloride ion, which will suppress the corrosion promoting action of Ru in nitric acid solution.
 binding site of a
binding site of a  -lactamase from the halophile by anomalous X-ray diffraction
-lactamase from the halophile by anomalous X-ray diffractionArai, Shigeki; Shibazaki, Chie; Shimizu, Rumi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Tokunaga, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
Kyushu Shinkurotoronko Kenkyu Senta Nempo, 2014, p.17 - 19, 2016/03
no abstracts in English
Teraoka, Yuden
Shinku Janaru, (143), p.22 - 23, 2013/01
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Shinku, 50(9), p.564 - 568, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Junichiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Ogiwara, Norio; Kuramochi, Masaya; Ueno, Tomoaki; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Takeda, Osamu; Watanabe, Masao; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Shinku, 50(5), p.371 - 377, 2007/05
Kicker magnets in Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) are now under construction. The kicker magnets are short pulse magnets with high charging voltage of 60 kV or more which is installing in vacuum chambers. The kicker magnet mainly consists of aluminum alloy as electric plates and ferrite as magnetic cores. The outgas reduction from those components is very important to prevent not only electrical discharge but also interaction between the proton beam and residual gas in the vacuum. We thoroughly reduced the outgas from the components. Surface of the aluminum alloy was finished by pit-free electropolishing. Aluminum and ferrites were baked in vacuum before construction of the magnet. They were baked each other until water, which was the main component of outgas, was reduced. We will discuss the effects of above processes on the discharge in the vacuum.
Kinsho, Michikazu; Saito, Yoshio*; Kabeya, Zenzaburo*; Ogiwara, Norio
Shinku, 49(12), p.728 - 733, 2006/12
It was success to develop alumina ceramics vacuum duct for the 3GeV-RCS of J-PARC at JAERI. This duct has titanium flanges and the exterior RF shield to reduce duct impedance. The production process of the alumina ceramics vacuum duct could be established, and mass production has been performing.
 molecular beams
molecular beamsOgawa, Shuichi*; Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mizuno, Yoshiyuki*
Shinku, 49(12), p.775 - 779, 2006/12
Nitridation on a Ti(0001)-1 1 surface using a supersonic N
1 surface using a supersonic N molecular beam was investigated by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy to clarify the adsorption reaction dynamics of N
molecular beam was investigated by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy to clarify the adsorption reaction dynamics of N molecule on the Ti surface. In a whole N
molecule on the Ti surface. In a whole N dosage region examined, N 1s spectra can be fitted well with two chemically-shifted components, the binding energies of which are 396.9 and 396.6 eV, respectively. For both the components, the initial sticking probability S
dosage region examined, N 1s spectra can be fitted well with two chemically-shifted components, the binding energies of which are 396.9 and 396.6 eV, respectively. For both the components, the initial sticking probability S shows a decrease with increasing incident energy in the overall trend, while has significant minima at 0.3 and 1.5 eV. Such incident energy dependences of S
shows a decrease with increasing incident energy in the overall trend, while has significant minima at 0.3 and 1.5 eV. Such incident energy dependences of S suggest that the chemisorbed states are similarly caused by a trapping-mediated adsorption process through a physisorption state at lower incident energy than 0.3 eV and an activated adsorption process becomes dominant at higher incident energy than 0.3 eV.
suggest that the chemisorbed states are similarly caused by a trapping-mediated adsorption process through a physisorption state at lower incident energy than 0.3 eV and an activated adsorption process becomes dominant at higher incident energy than 0.3 eV.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Higashijima, Satoru
Shinku, 49(2), p.62 - 68, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
 /Si(001) by N
/Si(001) by N beam irradiation
beam irradiationHachiue, Shunsuke; Teraoka, Yuden
Shinku, 48(5), p.343 - 345, 2005/05
Silicon oxynitride layers were formed by irradiation of nitrogen ion beams at silicon substrates with ultrathin oxide layers. The nitrogen beam was mass-selected N ion beam. The translational kinetic energy was about 3 keV. The dose was 6.3
ion beam. The translational kinetic energy was about 3 keV. The dose was 6.3 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . This value is almost equal to the atom density at the Si(001) surface. Chemical bonding states of irradiated nitrogen atoms were analyzed by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Although the nitrogen dose was a low density, N-1s photoemission spectra could be deconvoluted into four peaks. The chemical bonding state of each peak was assigned with a reference of a oxide layer thickness dependence of the N-1s photoemission peak profile.
. This value is almost equal to the atom density at the Si(001) surface. Chemical bonding states of irradiated nitrogen atoms were analyzed by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Although the nitrogen dose was a low density, N-1s photoemission spectra could be deconvoluted into four peaks. The chemical bonding state of each peak was assigned with a reference of a oxide layer thickness dependence of the N-1s photoemission peak profile.
Kojima, Takuji
Shinku, 47(11), p.789 - 795, 2004/11
When flue gas/off gas is irradiated by EB, many free radicals such as OH and active oxygen atom are formed from major components of air: namely nitrogen, oxygen, water and carbon dioxide ecules. The similer reaction can be achieved using UV light and plasma-discharging, but ionizing radiations produce such free radicals at higher density. Such radiation-induced radicals react efficiently with air pollutants, SOx and NOx in coal/oil combustion flue gas at thermal power plants, dioxins in waste incineration flue gas and volatile organic compounds (VOC) even in very low concentration and decompose them into non-toxic substances or change them to removable substances. R & D on EB treatment of flue gas/off gas done in JAERI on the basis of this principle process, as an example, is described in the present paper.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Moritani, Kosuke; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Mizuno, Yoshiyuki*; Tonda, Hideki*; Homma, Teiichi*
Shinku, 47(6), p.457 - 461, 2004/06
The oxidation reaction of Ti(0001) surface by oxygen molecules was observed by real-time in-situ photoemission spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation in the conditions of 400 C and 3.7
C and 3.7 10
10 Pa. The uptake curve of oxygen showed a plateau at the dose of 45-85 L and then increased again. This re-growth of oxide film was attributed to the drastic change of Ti oxidation state from TiO to TiO
Pa. The uptake curve of oxygen showed a plateau at the dose of 45-85 L and then increased again. This re-growth of oxide film was attributed to the drastic change of Ti oxidation state from TiO to TiO . Consequently, the characteristic change of the uptake curve was caused by the oxidation state change of Ti atoms.
. Consequently, the characteristic change of the uptake curve was caused by the oxidation state change of Ti atoms.
Tamura, Koji
Shinku, 47(6), p.477 - 479, 2004/06
The lateral distributions of the laser photoionized neodymium ion at the ion energy between 1400eV and 300eV were measured with a multi-channel Faraday cup. The obtained ions were collimated within these energy regions, and are considered to be useful for the applications of the laser photoionized ions.
Nishizawa, Daiji*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Kanazawa, Kenichiro; Ogiwara, Norio; Saito, Yoshio*; Kubo, Tomio*; Sato, Yoshihiro*
Shinku, 47(4), p.339 - 343, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Moritani, Kosuke
Shinku, 47(4), p.301 - 307, 2004/04
Recent research results on translational kinetic energy effects of incident oxygen molecules for Si(001) oxidation are summalized and introduced. The variation of surface temperature dependence of SiO desorption yield, oxygen uptake curves, and chemical bonding states depending on translational kinetic energy of oxygen molecules is described concretely. Eapecially, the translational kinetic energy effects on chemical reaction processes of concurrent oxide-layers formation and SiO desorption are discussed.
Nishizawa, Daiji*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Kanazawa, Kenichiro; Ogiwara, Norio; Saito, Yoshio*; Kubo, Tomio*; Sato, Yoshihiro*
Shinku, 47(4), p.339 - 343, 2004/02
Large aperture cylindrical beam ducts consisting of alumina ceramics will be used for the first time in the 3GeV-synchrotron of High Intensity Proton Accelerator Facility. It is necessary to evaluate roundness and straightness of ceramic ducts because we have to compensate contact area of the connected beam duct large as well as we have to compensate large enough beam aperture. We developed an apparatus of measuring roundness and straightness, and we completed data analysis method as well as measuring method. Then we are measuring and evaluating roundness and straightness of ceramic beam ducts. Now, we have newly made an ellipse ceramic duct for the 3GeV-synchrotron BM. This duct has ellipse cross-sections to satisfy with larger aperture that the beam dynamics requires. In this conference, we are going to present taken data and findings regarding form accuracy including roundness and straightness of the ellipse ceramic duct.
Yamaguchi, Kaoru*; Yamauchi, Yuji*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Hino, Tomoaki*; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro
Shinku, 46(5), p.449 - 452, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Moritani, Kosuke; Teraoka, Yuden
Shinku, 46(5), p.424 - 428, 2003/05
In order to study the reaction mechanism of the initial thermal Si(001) oxidation by O (1
(1 10
10 Pa) at the surface temperature region between 870K and 1120K, we have performed the
Pa) at the surface temperature region between 870K and 1120K, we have performed the 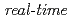 synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy of Si-2p and O-1s levels. The oxygen uptake curves as a function of the oxygen exposure time were analyzed on the basis of kinetics. The Si oxidation states corresponding to the adsorbed oxygen amount were well clarified by the time evolution of Si-2p photoemission spectra.
synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy of Si-2p and O-1s levels. The oxygen uptake curves as a function of the oxygen exposure time were analyzed on the basis of kinetics. The Si oxidation states corresponding to the adsorbed oxygen amount were well clarified by the time evolution of Si-2p photoemission spectra.
 /He mixed gas under room temperature
/He mixed gas under room temperatureTanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya
Shinku, 46(3), p.154 - 157, 2003/03
no abstracts in English