Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Harada, Yoshinari*; Yamaguchi, Hibiki*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 130(1), p.758 - 762, 2024/06
The data assimilation was performed using deterministic sampling to selectively reduce uncertainties caused by the thermal neutron scattering in light water. The prompt neutron decay constant  of the water tank system was used for the data assimilation. The deterministic sampling method was applied to uncertainty quantification and data assimilation for light water thermal neutron scattering law data obtained by the CAB model. The uncertainty quantification results using the deterministic sampling method were comparable to those using the random sampling method.
of the water tank system was used for the data assimilation. The deterministic sampling method was applied to uncertainty quantification and data assimilation for light water thermal neutron scattering law data obtained by the CAB model. The uncertainty quantification results using the deterministic sampling method were comparable to those using the random sampling method.
Kam, D. H.*; Grabaskas, D.*; Starkus, T.*; Bucknor, M.*; Uchibori, Akihiro
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 126(1), p.536 - 539, 2022/06
Removal of gaseous radionuclides from the bubbles released into the sodium pool is an important consideration of fuel pin failure accident in sodium-cooled fast reactors. To support modeling of this phenomenon as a part of development of the SRT (Simplified Radionuclide Transport) code in Argonne National Laboratory, numerical analysis of experiment on Iodine gas transport to sodium pool was performed. A proposed evaluation method can be regarded to be reasonably predicting the measured decontamination factors.
Louie, D. L. Y.*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 124(1), p.824 - 827, 2021/06
The Sodium Chemistry (NAC) package in MELCOR has been developed to enhance application to sodium cooled fast reactors. Based on the recommendations in the previous study through the benchmark analyses of the F7-1 pool fire experiment, this study aims to improve the MELCOR models capturing the oxide layer effect, sodium pool spreading and pool-pan heat transfer, respectively. Each of these models enable a better characterization of the all the processes of relevance to sodium pool fires as observed during the F7-1 test. The MELCOR sodium pool fire enhancement has demonstrated the importance of the improved models.
Endo, Tomohiro*; Noguchi, Akihiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 124(1), p.184 - 187, 2021/06
This study confirmed that the sensitivity analysis of the alpha-eigenvalue can be carried even for non-neutron multiplication systems such as water-only systems. The preliminary results of nuclear data-induced uncertainties of alpha-eigenvalue were smaller than the differences between numerical and experimental results of alpha-eigenvalue. For further investigation, it is necessary to reconsider the experimental bias and the nuclear data-induced uncertainty in alpha-eigenvalue due to the thermal scattering law data of water.
Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi; Chiba, Go*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 124(1), p.544 - 547, 2021/06
Verification calculations for the capability of multi-group cross section generation in FRENDY (FRENDY/MG) are carried out through the comparison of one-group reaction rates using the multi-group cross sections obtained by FRENDY/MG and NJOY2016. Three different neutron spectra (LWR, FR, and 1/E) are used to calculate one-group reaction rates. The discrepancies of one-group reaction rates are small for most cases, showing the validity of FRENDY/MG. The FRENDY/MG will be released as the part of FRENDY nuclear data processing system in the near future.
Chiba, Go*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 124(1), p.556 - 558, 2021/06
The FRENDY nuclear data processing code has been used to generate multi-group cross section libraries for the CBZ reactor physics code system. The newly generated libraries have been applied to neutronics calculations of a fast reactor core MET-1000, and several neutronics parameters are calculated. Calculations with other libraries generated by NJOY2016 have been also conducted, and differences in obtained neutronics parameters between the FRENDY-based library and the NJOY-based library have been quantified. Generally reasonable agreement between them has been obtained, so it has been demonstrated that the multi-group libraries for fast reactor neutronics calculations can be generated successfully by FRENDY. Detailed investigation on the impact of the difference in the processing codes on k-effective has been also carried out with a help of the perturbation theory, and the causes of the differences have been identified.
Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Tada, Kenichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 122(1), p.714 - 717, 2020/06
A generation capability of multi-group cross sections from point-wise cross sections in ACE files is being developed as a function of the nuclear data processing code FRENDY. This presentation describes features of this function and comparison of the processing results between this function and GROUPR module in NJOY.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 122(1), p.862 - 865, 2020/06
Development of a new simulation system SPECTRA has been started to enable a simulation of comprehensive in- and ex-vessel events during a severe accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. The simulation system SPECTRA consists of two basic modules of thermal-hydraulics; in-vessel basic module and ex-vessel one, and some sub-modules for specific phenomena or events. A sodium fire models are implemented as one sub-module of the ex-vessel module. The sodium fire models are adapted from existing sodium fire analysis codes AQUA-SF and SPHINCS. As the result of verification test, the results show good agreement with the one of original codes. The validation analysis for single droplet falling and combustion corresponds well with the experimental data reasonably.
Tsai, P.-E.; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 121(1), p.13 - 16, 2019/11
The importance of PKA characteristics to radiation damage assessment for proton accelerators has been demonstrated in the paper by the PHITS simulations. In order to obtain accurate results of displacement cross section calculated by PHITS, it is therefore critical to have the physics models implemented in PHITS be properly validated by experimental data. With the new measurement system, which has been being developed here at JAEA, it is expected to provide experimental PKA data with low measurement thresholds and good mass resolutions. The test result we obtained at CYRIC, Tohoku University, for the 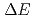 -
- gas ionization chamber as a part of the new measurement system was very promising. We were able to successfully distinguish C, B, Be, Li, and He elements with threshold energies lower than 1 MeV/nucleon in the configuration of 70-MeV proton beam and 920-nm thick C target. More experiments and tests shall continue in the future with heavier targets and higher proton beam energies.
gas ionization chamber as a part of the new measurement system was very promising. We were able to successfully distinguish C, B, Be, Li, and He elements with threshold energies lower than 1 MeV/nucleon in the configuration of 70-MeV proton beam and 920-nm thick C target. More experiments and tests shall continue in the future with heavier targets and higher proton beam energies.
Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 118, p.1624 - 1626, 2018/06
This study suggested the time development of oxygen-to-metal ratio (O/M) redistribution model with oxygen-related properties in MOX. Irradiation simulation including the suggested O/M redistribution and pore migration with vaporization-condensation model which bares density redistribution was demonstrated. The simulation results showed that O/M redistribution proceeded at lower temperature than density redistribution, which indicated that oxygen diffusion got influential at lower temperature than vaporization-condensation of MOX. Another find was that O/M redistribution was very slow at the surface because temperature kept low. However, near the surface (inside from the surface) where the temperature exceeded 1000 K, O/M redistribution was rather recognizable with oxygen flown from inner region to the near-surface. The results will be evaluated by comparison with post-irradiation examination data.
 pellets by 28 GHz microwave irradiation
pellets by 28 GHz microwave irradiationAkashi, Masatoshi; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 118, p.1391 - 1394, 2018/06
In this study, CeO pellet sintering by irradiating microwave at a frequency of 28 GHz was carried out to investigate the effect of particle diameter of raw powder on the density of sintered pellet. The highest bulk density is 94.2 %T.D. under the condition of 30 min holding at 1473 K. The bulk density decreases with increasing the particle diameter of used raw powder. On the other hand, all of the apparent density of sintered pellet is more than 93.5 %T.D.. The difference between the bulk density and the apparent density is caused by the difference of open porosity for each sample pellet. It seems that the high density sintered pellets with porous structure are obtained because sample pellet is heated internally and uniformly in microwave sintering.
pellet sintering by irradiating microwave at a frequency of 28 GHz was carried out to investigate the effect of particle diameter of raw powder on the density of sintered pellet. The highest bulk density is 94.2 %T.D. under the condition of 30 min holding at 1473 K. The bulk density decreases with increasing the particle diameter of used raw powder. On the other hand, all of the apparent density of sintered pellet is more than 93.5 %T.D.. The difference between the bulk density and the apparent density is caused by the difference of open porosity for each sample pellet. It seems that the high density sintered pellets with porous structure are obtained because sample pellet is heated internally and uniformly in microwave sintering.
Miyahara, Kaname
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 117(1), p.51 - 52, 2017/10
This presentation highlights JAEA's challenges for contributing to recovering the previous life of residents and the development of resilient communities in Fukushima Prefecture based on considering needs of local people on the environmental restoration categorized by the state of evacuation orders and the lifting of such orders.
Washiya, Tadahiro; Miyamoto, Yasuaki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 117(1), p.47 - 50, 2017/10
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) carried out several international cooperation to gather the knowledge and expertise on decommissioning and accident management. The cooperation fields are radioactive waste management in the decommissioning, characterization of fuel debris, investigation on core degradation process and remote monitoring technology etc.. This paper is explained outline of the CLADS activities and future prospect.
Kawada, Kenichi; Suzuki, Toru
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 115(1), p.1597 - 1598, 2016/11
Kato, Masato
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 114, p.987 - 988, 2016/06
In Japan, uranium and plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) has been developed as fuels of sodium-cooled fast reactors. The developing MOX fuels come in variety of O/M ratio, Pu content, minor actinide (MA) content and density. We have studied a science based fuel technology to evaluate fuel behaviors in fabrication process and irradiation condition of such various fuels. The technologies which are constructed based on experimental database can apply to mechanistic evaluation of fuel behaviors. To develop the science based fuel technology, many different varieties of basic properties have been investigated, and experimental database was constructed. And a mechanistic physical property model has been studied. The models contribute to describe various behaviors in fuel fabrication process and irradiation condition.
 4 bundle at 2 MPa
4 bundle at 2 MPaLiu, W.; Nagatake, Taku; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 114, p.875 - 878, 2016/06
To contribute to the clarification of the Fukushima Daiichi Accident, JAEA is working on getting instantaneous void fraction distribution data in steam water two - phase flow in rod bundle geometry under high pressure, high temperature condition, with using Wire Mesh Sensor (WMS) developed at JAEA for high pressure, high temperature condition, focusing on the low flow rate condition after the reactor scram. This paper reports the experimental results for the measured void fraction distribution in steam vapor two-phase flow in a 4  4 bundle under 1.6 MPa (202
4 bundle under 1.6 MPa (202  C), 2.1 MPa (215
C), 2.1 MPa (215  C) and 2.6 MPa (226
C) and 2.6 MPa (226  C) conditions. The data is expected to be used in the validation of the detailed two-phase flow codes TPFIT and ACE3D developed at JAEA. The time and space averaged void fraction data is also expected being used in the validation of the drift flux models implemented in the two fluids codes, such as TRACE code.
C) conditions. The data is expected to be used in the validation of the detailed two-phase flow codes TPFIT and ACE3D developed at JAEA. The time and space averaged void fraction data is also expected being used in the validation of the drift flux models implemented in the two fluids codes, such as TRACE code.

Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 114, p.1081 - 1082, 2016/06
Many studies on the oxygen potential of UO have been carried out so far. However, the oxygen potential data for UO
have been carried out so far. However, the oxygen potential data for UO near the stoichiometric composition in the high temperature region (1673-1873 K) are limited. In this work, the oxygen potential data of UO
near the stoichiometric composition in the high temperature region (1673-1873 K) are limited. In this work, the oxygen potential data of UO were extended to high temperature range of 1673-1873 K by gas equilibrium method. The measured data were analyzed based on a defect chemistry model.
were extended to high temperature range of 1673-1873 K by gas equilibrium method. The measured data were analyzed based on a defect chemistry model.
Kato, Masato; McClellan, K.*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.613 - 614, 2015/10
A joint study on advanced oxide fuels is being carried out under the Civil Nuclear Energy Working Group (CNWG) bilateral collaboration between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The main goal of this study is to support development and validation of a science-based fuel analysis code for minor actinide (MA) bearing MOX fuel. In analysis and evaluation of fuel performance, it is essential to understand the physical properties of the advanced oxide fuels. Therefore, we are investigating physical properties of (U,Pu)O , (U,Ce,)O
, (U,Ce,)O , PuO
, PuO , CeO
, CeO and other related compounds to prepare a physical property database and to construct an integrated mechanistic physical property model. In this paper, we describe the derivation of a model to represent heat capacity and thermal conductivity of (U,Pu)O
and other related compounds to prepare a physical property database and to construct an integrated mechanistic physical property model. In this paper, we describe the derivation of a model to represent heat capacity and thermal conductivity of (U,Pu)O that is based on the experimental database.
that is based on the experimental database.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Koyama, Shinichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.619 - 621, 2015/10
In order to evaluate the microstructural change behavior of Am-MOX fuels at the initial stage of irradiation, detailed investigations using image analysis were performed on X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) images and on ceramographs from fuels irradiated in both B11 and B14.
Ozawa, Takayuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Kato, Masato
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.622 - 624, 2015/10
A recycle system for minor actinides (MAs), in which MAs are recycled by reprocessing and irradiating them in a fast reactor, is studied to reduce the degree of hazard and the amount of high-level radioactive wastes. MAs would be used as mixed oxide (MOX) fuels with plutonium and uranium in fast reactors. Since MA content of MA-bearing MOX (MA-MOX) to be used in fast reactors is assumed to reach  5 wt%HM, the effects on not only fuel properties but also fuel behaviors have to be estimated to use MA-MOX as fast reactor fuels. As the MOX fuels to be used will be irradiated at a comparably high linear power and the fuel center temperature would be assumed to be over 2,273 K during irradiation in the fast reactors, fuel restructuring would take place due to void migration towards the fuel center under the radial temperature gradient, and a central void would be formed. Since the fuel center temperature would be decreased by the effect of formation of the central void, the fuel restructuring is one of the most important behaviors for fast reactor fuels. In this study, the effect of MA content on fuel restructuring behavior was estimated from the results of irradiation experiments such as B11 and B14 performed in Joyo to study the irradiation behaviors of MA-MOX and the calculation results using a fuel restructuring model which can take into account MA-MOX dependence on vapor pressure.
5 wt%HM, the effects on not only fuel properties but also fuel behaviors have to be estimated to use MA-MOX as fast reactor fuels. As the MOX fuels to be used will be irradiated at a comparably high linear power and the fuel center temperature would be assumed to be over 2,273 K during irradiation in the fast reactors, fuel restructuring would take place due to void migration towards the fuel center under the radial temperature gradient, and a central void would be formed. Since the fuel center temperature would be decreased by the effect of formation of the central void, the fuel restructuring is one of the most important behaviors for fast reactor fuels. In this study, the effect of MA content on fuel restructuring behavior was estimated from the results of irradiation experiments such as B11 and B14 performed in Joyo to study the irradiation behaviors of MA-MOX and the calculation results using a fuel restructuring model which can take into account MA-MOX dependence on vapor pressure.