Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebihara, Kenichi; Kaburaki, Hideo; Takai, Kenichi*
Zairyo To Purosesu (CD-ROM), 27(1), P. 418, 2014/03
In order to understand the mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement, identifying the state of hydrogen trapped by defects in steels is dispensable. In the identification of the hydrogen trapping state, thermal desorption profiles of hydrogen obtained in the thermal desorption analysis of steel specimens are widely used, and need to be analyzed using the numerical model because they include the effect of the specimen size and the experimental conditions as well as the effect of defects. The prefactor of detrap rate in the model is previously used as a fitting parameter. In the presentation, the influence of specimen size on the identification of the prefactor was examined numerically. As a result, in the specimens of pure iron and martensite steels whose size is larger than 0.3 mm, the accuracy of the identification rapidly drops. In addition, according to the influence of the prefactor on the desorption profile, it is possible to identify the order of magnitude of the prefactor.
Kasahara, Seiji; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
Zairyo To Purosesu (CD-ROM), 26(2), p.498 - 501, 2013/09
Outline was discussed for very high temperature reactors (VHTRs), IS process for hydrogen production and hydrogen steelmaking process integrated with them. Hydrogen of 7.07 10
10 Nm
Nm /d was produced and electricity of 497 MW was generated using 5 VHTRs of 600 MW thermal output to produce steel of 1
/d was produced and electricity of 497 MW was generated using 5 VHTRs of 600 MW thermal output to produce steel of 1 10
10 t/d, similar scale to a conventional blast furnace (BF) plant. A significant reduction of CO
t/d, similar scale to a conventional blast furnace (BF) plant. A significant reduction of CO emission to 13% of that from a BF plant was expected by the hydrogen steelmaking plant. Sensitivity analysis of steelmaking cost on hydrogen production cost showed that the hydrogen production cost of 3.0 US
emission to 13% of that from a BF plant was expected by the hydrogen steelmaking plant. Sensitivity analysis of steelmaking cost on hydrogen production cost showed that the hydrogen production cost of 3.0 US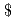 /kg-H
/kg-H was required for the lower steelmaking cost than conventional steelmaking processes.
was required for the lower steelmaking cost than conventional steelmaking processes.
Kasahara, Seiji; Sato, Hiroyuki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
Zairyo To Purosesu (CD-ROM), 25(2), p.647 - 650, 2012/09
Application of ACRES (Active Carbon Recycling Energy System) to steelmaking process is proposed for reduction of CO emission and security of fossil fuel supply. ACRES is the concept of reuse of carbon element in CO
emission and security of fossil fuel supply. ACRES is the concept of reuse of carbon element in CO from fossil fuel usage by reducting to CO using non-fosssil primary energy. Selection of the primary energy and CO
from fossil fuel usage by reducting to CO using non-fosssil primary energy. Selection of the primary energy and CO reduction technology is important for the usability evaluation. High temperature gas-cooled reactor is a candidate of the energy, which can supply electricity, hydrogen and high temperature heat usable for CO
reduction technology is important for the usability evaluation. High temperature gas-cooled reactor is a candidate of the energy, which can supply electricity, hydrogen and high temperature heat usable for CO reduction. Technical examination on high temperature gas-cooled reactor as energy source of ACRES for steelmaking was carried out. Renewable solar energy is an also promising energy source. Here, ability of HTGR to follow load change was investigated and validated for parallel use of HTGR and solar energy.
reduction. Technical examination on high temperature gas-cooled reactor as energy source of ACRES for steelmaking was carried out. Renewable solar energy is an also promising energy source. Here, ability of HTGR to follow load change was investigated and validated for parallel use of HTGR and solar energy.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionXu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi; Li, J.*; Tomota, Yo*
Zairyo To Purosesu (CD-ROM), 24, p.547 - 549, 2011/03