Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Takeda, Ryoma; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
Zairyo No Kagaku To Kogaku, 61(6), p.248 - 252, 2024/12
A comparative analysis of the 0.2 % yield stress in SUS304L stainless steel revealed that lower strain rates and higher temperatures significantly reduce yield stress. Grain refinement from 68.6  m to 0.59
m to 0.59  m minimally impacted the rate of yield stress reduction at slower strain rates. However, finer grains showed a decrease in yield stress at reactor operating temperature compared to room temperature. In slow strain rate tests under conditions promoting intragranular stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SUS304L with grain sizes of 28.4
m minimally impacted the rate of yield stress reduction at slower strain rates. However, finer grains showed a decrease in yield stress at reactor operating temperature compared to room temperature. In slow strain rate tests under conditions promoting intragranular stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SUS304L with grain sizes of 28.4  m or smaller exhibited similar fracture strains comparable to those at reactor operating temperatures, whereas coarse-grained SUS304L showed reduced fracture strain. Microstructural analysis showed that in smaller grains, over 87 % of the fracture surface was ductile. In particular, SUS304L with 0.59
m or smaller exhibited similar fracture strains comparable to those at reactor operating temperatures, whereas coarse-grained SUS304L showed reduced fracture strain. Microstructural analysis showed that in smaller grains, over 87 % of the fracture surface was ductile. In particular, SUS304L with 0.59  m grains exhibited a higher presence of {111} /
m grains exhibited a higher presence of {111} /  3 boundaries, which decreased with grain growth. These results indicate that grain refinement will suppress intragranular SCC by slowing corrosion progression through increased {111} /
3 boundaries, which decreased with grain growth. These results indicate that grain refinement will suppress intragranular SCC by slowing corrosion progression through increased {111} /  3 boundaries.
3 boundaries.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-71-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.253 - 256, 2024/11
In our previous study, we reported that Cl ions penetrating stainless steel crevices do not dissipate by diffusion, even in high-purity water (i.e., conductivity remains stable), likely due to electrochemical reactions inside and outside the crevice. This study further analyzes ion behavior by experimentally and computationally investigating ion concentration drivers in high-purity water. Results show that, at 50 C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100
C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100  S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm
S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm .
.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-58-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.51 - 54, 2024/07
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Kawasaki, Takuro
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-58-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.58 - 60, 2024/07
Wakui, Takashi; Takagishi, Yoichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Zairyo, 73(6), p.520 - 526, 2024/06
Cavitation damage is one of crucial issues to predict the structural endurability of the mercury targets for highly intensive pulsed neutron sources. Based on the comparison with numerical simulation on the pit shape and results of the basic test, the cavitation bubble collapsing was assumed to be resulted in the micro jet with the impact velocity of 160-200 m/s, imposing then impact pressure of 3-4 GPa at the input power simulating the operation condition in the mercury targets. It was statistically understandable that cavitation damage evolution was proportional to 4th power of the input power approximately, as taking the aggressivity of cavitation bubbles, the distribution of the maximum diameter of grown bubbles and the space of distribution of bubbles in the mercury into account.
Takahashi, Rieko*; Taniguchi, Naoki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 73(6), p.153 - 163, 2024/06
Carbon steel is one of the candidate materials for overpacks in geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, and is known to susceptible to stress corrosion cracking(SCC) depending on the condition in carbonate environment. In order to understand the influence of temperature on the SCC susceptibility of carbon steel, slow strain rate test (SSRT) of rolled steel were performed in NaHCO aqueous solution with varying temperature in the range of 303-393K for conditions of 0.1-0.5 mol/dm
aqueous solution with varying temperature in the range of 303-393K for conditions of 0.1-0.5 mol/dm , which is assumed to be the upper limit of carbonate concentration in groundwater in a geological disposal environment. As the results, no obvious influence of temperature on mechanical properties such as fracture strain ratio and reduction area ratio were observed, but SCC susceptibility based on SCC fracture ratio increased at relatively low temperatures of 303K and 323K. It was suggested that the reason for the higher SCC sensitivity at lower temperatures was due to slower repassivation at lower temperatures. Regarding the type of SCC, intergranular SCC was dominant at low temperatures and tended to transition to intergranular SCC at higher temperatures. Transgranular SCC tended to be observed at lower potentials than those at which intergranular SCC was observed.
, which is assumed to be the upper limit of carbonate concentration in groundwater in a geological disposal environment. As the results, no obvious influence of temperature on mechanical properties such as fracture strain ratio and reduction area ratio were observed, but SCC susceptibility based on SCC fracture ratio increased at relatively low temperatures of 303K and 323K. It was suggested that the reason for the higher SCC sensitivity at lower temperatures was due to slower repassivation at lower temperatures. Regarding the type of SCC, intergranular SCC was dominant at low temperatures and tended to transition to intergranular SCC at higher temperatures. Transgranular SCC tended to be observed at lower potentials than those at which intergranular SCC was observed.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 73(4), p.102 - 109, 2024/04
To evaluate the effects of dissolved oxygen concentration to water quality within SCC crack and the distribution of water quality in the depth direction under irradiation, immersion tests of stainless steel specimens given a gap and water radiolysis calculations for the water quality in the crevice gap were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that Fe O
O was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Oketani, Kazuki*; Fujii, Hirokazu*; Zhao, Y.*; Kato, Masaji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya; Kono, Masanori*
Zairyo, 73(3), p.220 - 225, 2024/03
The fractures in the rock are the main pass of groundwater flow and solute transport. The filling of fine-grained particle, such as clay minerals, was confirmed to decrease the permeability of rock by laboratory experiment. This research aimed to verify the occurrence of the phenomena in the field. The water containing the clay minerals was injected into the rock at the 200m stage of the Mizunami Underground research laboratory. The hydraulic conductivity decreased two order before and after the injection. This result suggested that the decrease of hydraulic conductivity by the filling of fine-grained particle in the fractures occurred in the real field.
Aoki, So; Sakai, Junichi*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 73(3), p.49 - 56, 2024/03
This paper briefly reviews the history of the development of duplex stainless steels and summarises the grades that are currently standardised in JIS and used industrially. The chemical composition, phase equilibrium and phase transformation of duplex stainless steels are described, showing the basic data. The physical and mechanical properties of the duplex stainless steels are touched upon, and in particular the resistance to uniform corrosion and localised corrosion such as pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion and stress corrosion cracking are outlined, citing previously published data. Finally, the main environments in which duplex stainless steels are used and the results of their use are mentioned.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Zairyo, 73(2), p.129 - 135, 2024/02
Body-centered-cubic transition metals, such as Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane. To find out the mechanism of this response, atomistic simulations of curved crack-fronts of bcc Fe were conducted at 0 K using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network (ANN) technique. We discovered that dislocations can be emitted from the curved crack fronts along the {110} crack plane, and this phenomenon explains why the cleavage is observed only along the {100} plane. In addition, the cleavage simulations along {100} at the elevated temperature were found to be accompanied by plasticity; namely, they represented more realistic fracture.
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steel
Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(11), p.284 - 288, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Soma, Yasutaka; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-70-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.199 - 202, 2023/10
Since an acidic corrosive environment (crevice environment) is formed inside the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel in high temperature water, it is important to understand the corrosion behavior in the crevice environment for the better understanding of crack growth behavior. In the previous study, the authors measured the electrical conductivity inside the crevice and obtained values of 380  S/cm and 1600
S/cm and 1600  S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH
S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH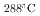 =4.41) and II (pH
=4.41) and II (pH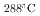 =3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
=3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
Arai, Taiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Motohashi, Mitsuya*
Zairyo No Kagaku To Kogaku, 60(5), p.153 - 158, 2023/10
Si oxide films are currently widely used as insulating materials in electronic devices and biomaterials. The atomic bonding state of these films significantly influences the properties of each device, thus it is particularly necessary to understand and control the chemical bonding state between Si and O in the films. In this study, the Si oxide films formed by anodic oxidation on Si substrate surfaces in extremely low concentrations of HF solutions were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy mainly focusing on Si2p and F1s spectra. Although the HF concentration is in the order of ppm, the films contain percent order of F atoms, suggesting the formation of Si-F and Si-O-F bonds in the films. It was also found that the different depth profiles for F and O atoms was observed, indicating that the surface reaction processes seem to be different depending on each element.
Noi, Hiromi*; Watanabe, Sota*; Kubo, Koji*; Okajima, Satoshi; Ando, Masanori
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2023 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.CL0712_1 - CL0712_5, 2023/09
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Kenji*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Morooka, Satoshi
Zairyo, 72(4), p.316 - 323, 2023/04
Hata, Kuniki; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Watanabe, Yutaka*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(4), p.126 - 130, 2023/04
Gamma-radiolysis experiments with gas-liquid coexistent samples were carried out to investigate effects of gas-phase radiolysis on corrosive environment for materials in solutions under irradiation. After gamma-ray irradiation, hydrogen peroxide, nitrate ion, nitrite ion were detected in the liquid phase. The production yields of nitrate ion and nitrite ion increased with increasing gas-phase volume and oxygen concentration. This result indicated that chemical reactions including oxygen and nitrogen in the gas phase were required for the production of nitrate ion and nitrite ion. To magnify the effects of gas-phase radiolysis in the gas-liquid coexistent samples, absorption dose rate in the liquid phase was reduced by one-hundredth using lead shield. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide and the pH in the shielded liquid phase were similar to those in the irradiated pure water, which did not contact with gas phase. This result indicated that the effects of nitrate ion and nitrite ion dissolved in the liquid phase on water radiolysis were not important in the current experimental system, in which the effects of gas-phase radiolysis were increased by 100-times.
Hirota, Noriaki; Funamoto, Kodai*; Tachibana, Yukio
Zairyo, 72(3), p.255 - 261, 2023/03
For the purpose of developing metallic materials with excellent corrosion resistance under boiling sulfuric acid environment, the coated materials were evaluated for their corrosion resistance and the differences in surface morphology were investigated. As a result, the corrosion resistance of SUS304 coated and sintered eight times by chemical densified coating method (S-ZAC) was maintained at the point after 12h corrosion test, but the corrosion rate rapidly increased after 100h corrosion test. The cross-sectional microstructural analysis of the specimens showed that only a small amount of SiO remained on the surface, while Cr
remained on the surface, while Cr O
O completely disappeared. The mechanism of film delamination in S-ZAC is assumed to be due to the thermal expansion caused by heating, which resulted in curvature of the thick film and cracks at the Cr
completely disappeared. The mechanism of film delamination in S-ZAC is assumed to be due to the thermal expansion caused by heating, which resulted in curvature of the thick film and cracks at the Cr O
O and SiO
and SiO interfaces. On the other hand, SUS304 coated with higher density of Cr
interfaces. On the other hand, SUS304 coated with higher density of Cr O
O by repeating the coating and sintering eleven times (MS-ZAC) showed excellent corrosion resistance as well as SiC even after 100h corrosion test. The results of cross-sectional microstructuCr
by repeating the coating and sintering eleven times (MS-ZAC) showed excellent corrosion resistance as well as SiC even after 100h corrosion test. The results of cross-sectional microstructuCr O
O particle layer, in addition to the thinning of the entire film.
particle layer, in addition to the thinning of the entire film.
Suzuki, Kenji*; Kura, Komoe*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa
Zairyo, 71(12), p.1005 - 1012, 2022/12
This paper describes a stress measurement from a welded part of an austenitic stainless steel using synchrotron X-rays. Difficulty measuring the X-ray stress of the welded part is caused by the broadening of the diffraction spot in the radial and circumferential directions. The bending strains of the rectangular bar made of the welded part were measured using synchrotron white X-rays and the double exposure method. To improve the energy resolution, monochromatic synchrotron X-ray of 70 keV was used. The diffraction pattern showed the sharp arc like a pattern from texture material. The diffraction profile was obtained from the integral of the diffraction intensity in the direction of the circumference. The diffraction angle was determined using the double exposure method. As a result, the distribution of the residual stresses of the welded part could be measured.
Shinohara, Masanori; Sumita, Junya; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Shibata, Taiju
Dai-59-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Toronkai Koen Rombunshu, p.22 - 28, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Tsuru, Tomohito
Zairyo, 71(8), p.660 - 665, 2022/08
The dynamic behavior of individual defects at the nanoscale plays an important role in understanding the mechanical properties of highly controlled materials and the nature of their mechanical functions. The purpose of this study is to reveal the origin of the mechanical properties from the electronic structure calculations of dislocation core. In this paper, we propose a modeling that describes the slip bahavior based on the kink mechanism for alloys with a body-centered cubic lattice structure (BCC) that shows a unusual temperature dependence on mechanical properties. In addition, we introduce analytical model to understand the role of alloying elements on dislocation motion from the electronic structure and predict mechanical properties.