Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Kobata, Masaaki; Okane, Tetsuo; Satou, Yukihiko; Okochi, Takuo*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 23(1), p.16 - 21, 2025/02
Kamiya, Junichiro; Abe, Kazuhide; Fujimori, Shinichi; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kobata, Masaaki; Morohashi, Yuko; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yamada, Ippei; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 22(4), p.316 - 326, 2024/08
The activation and deterioration mechanisms of the Ti-Zr-V non-evaporable getter (NEG) coating have been investigated. Operando analysis of the surface chemical composition change of the Ti-Zr-V coating was performed by the synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy (SRPES) during the process of raising the sample temperature to 250 C, corresponding to the activation process of NEG coating. The surface oxidation process was also characterized by the SRPES during the injection of O_2 gas into the chamber while keeping the sample temperature at 250
C, corresponding to the activation process of NEG coating. The surface oxidation process was also characterized by the SRPES during the injection of O_2 gas into the chamber while keeping the sample temperature at 250 C, corresponding to the deterioration process of NEG coating, i.e. surface oxidation and oxygen diffusion to the coating interior. The depth profile of the oxidized sample was measured with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results shows, in the activation process, the surface Zr gets the oxygen from the oxides of Ti and V at the first stage, resulting in the metallic Ti and V on the surface, and the oxygen of the Zr-oxide and/or Zr sub-oxides diffuse to the interior of the coating in the continuous temperature rise, resulting in the metallic Zr on the surface. It is further suggested that the deterioration of the Ti-Zr-V NEG coating means the Zr and secondary Ti are oxidized deep into the coating, resulting in the restriction of the oxygen migration from the NEG compositions on the surface and consequently the lack of surface metallization.
C, corresponding to the deterioration process of NEG coating, i.e. surface oxidation and oxygen diffusion to the coating interior. The depth profile of the oxidized sample was measured with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results shows, in the activation process, the surface Zr gets the oxygen from the oxides of Ti and V at the first stage, resulting in the metallic Ti and V on the surface, and the oxygen of the Zr-oxide and/or Zr sub-oxides diffuse to the interior of the coating in the continuous temperature rise, resulting in the metallic Zr on the surface. It is further suggested that the deterioration of the Ti-Zr-V NEG coating means the Zr and secondary Ti are oxidized deep into the coating, resulting in the restriction of the oxygen migration from the NEG compositions on the surface and consequently the lack of surface metallization.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Ogiwara, Norio*; Kuramochi, Masaya*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(4), p.359 - 364, 2023/07
In recent years, durable target is required according to increase of the beam power. To solve this problem, a liquid film was formed in vacuum and tested it as a target. An ethanol and a mercury were selected as liquid target materials, and we investigated whether the liquid sheet could be formed stably in a vacuum and how about the vacuum pressure. As a result, it was confirmed that the liquid films were stably formed in both case and the pressures with the films were about the vapor pressure of the materials.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Takano, Kazuhiro*; Wada, Kaoru; Yanagibashi, Toru*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(3), p.144 - 153, 2023/06
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Junichiro; Nii, Keisuke*; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Harada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Yutaka; Matsuda, Makoto; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Ida, Yoshiaki*; et al.
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(4), p.344 - 349, 2023/05
no abstracts in English
 molecule at SiO
molecule at SiO /Si(001) interface during Si dry oxidation
/Si(001) interface during Si dry oxidationTsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Sakamoto, Tetsuya*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(1), p.30 - 39, 2022/11
Terasawa, Tomoo; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 20(4), p.196 - 201, 2022/07
Graphene is a perfect impermeable membrane for gases but permeable to hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ion permeation shows the isotope effect, i.e., deuteron is slower than proton when permeating graphene. However, the permeation mechanism and the origin of the isotope effect are still unclear. Here, we propose a strategy to discuss the hydrogen ion permeation mechanism of graphene by developing an ion source with ultraslow, monochromatic, and mass-selected hydrogen ion beam. We employed a hemispherical monochromator and a Wien filter for the ion source to achieve the energy and mass resolutions of 0.39 eV and 1 atomic mass unit, respectively. The energetically sharp ion beam is expected to allow us to directly measure the permeability of graphene with high accuracy.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 20(3), p.186 - 195, 2022/07
Cesium-135 having long life, 2.3 million y, that is contained in nuclear wastes may cause long-term pollution. Technology of isotopic separation of such long lived nuclide is indispensable not only for its volume reduction but also annihilation by nuclear transmutation. The recovery of atomic Cs from molecular CsI is mandatory. We have investigated fullerene C as a potential absorber for Cs. Angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, AR-XPS has been used to analyze the depth concentration distribution of Cs. Experiments were performed at soft X-ray beamline BL27A at KEK PF facility. We report on the annealing effect after deposition of Cs and the effect of heating substrate during deposition. For Cs/C
as a potential absorber for Cs. Angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, AR-XPS has been used to analyze the depth concentration distribution of Cs. Experiments were performed at soft X-ray beamline BL27A at KEK PF facility. We report on the annealing effect after deposition of Cs and the effect of heating substrate during deposition. For Cs/C sample, the intensity ratio of Cs-3d/C-1s increased in double at the high temperature. This suggests that Cs atoms remain in the material at high temperatures. On the other hand, for CsI/C
sample, the intensity ratio of Cs-3d/C-1s increased in double at the high temperature. This suggests that Cs atoms remain in the material at high temperatures. On the other hand, for CsI/C , the intensity ratio does not change much by elevating temperatures.
, the intensity ratio does not change much by elevating temperatures.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Takano, Kazuhiro*; Yuza, Hiromu*; Wada, Kaoru
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 20(2), p.107 - 118, 2022/05
no abstracts in English
 complex as a possible origin of localized electron behavior in hydrogen-irradiated SrTiO
complex as a possible origin of localized electron behavior in hydrogen-irradiated SrTiO
Ito, Takashi
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 20(3), p.128 - 134, 2022/05
 decomposition on Si(110)
decomposition on Si(110)Yano, Masahiro; Uozumi, Yuki*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 16, p.370 - 374, 2018/08
Fukaya, Yuki
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 16, p.111 - 114, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
 500
500 C) under electric field
C) under electric fieldBaba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 16, p.53 - 59, 2018/03
Surface ionization for cesium chloride and Cs-adsorbed soil has been investigated. For cesium chloride, neutral cesium was desorbed around 645 C which is close to the melting point of cesium. While Cs
C which is close to the melting point of cesium. While Cs ion was desorbed from 400
ion was desorbed from 400 C. The ratio of desorbed ions and neutrals (Cs
C. The ratio of desorbed ions and neutrals (Cs /Cs
/Cs ) has a maximum around 410
) has a maximum around 410  C. Temperature dependence of Cs
C. Temperature dependence of Cs /Cs
/Cs was analyzed using Saha-Langmuir equation, As a result, it was found that the temperature maximum is due to the changes of the surface work function induced by the phase transition of CsCl.
was analyzed using Saha-Langmuir equation, As a result, it was found that the temperature maximum is due to the changes of the surface work function induced by the phase transition of CsCl.
Honda, Mitsunori; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Suzuki, Shinichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 14, p.35 - 38, 2016/02
Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Okajima, Yuka*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 14, p.48 - 52, 2016/00
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Izumi, Toshinori
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.417 - 421, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1The interaction between alkali metals and oxides has attracted much attention as heterogeneous catalysis, chemical reaction promoters, and high intensity electron emitter. Also the interaction of cesium and oxides has become important subject, because radioactive cesium trapped in minerals such as clay and soil may cause health risks. In the present study, we analyzed chemical states of ultra-trace amount of cesium on oxide surfaces by total reflection X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (TR-XPS) exited by synchrotron radiation. For the adsorbed cesium thicker than 0.01 layer, cesium is weakly bound with oxide through Van-der-Waals force. On the other hand, for ultra-thin layer about 0.002 layer, the chemical bond changes to covalent bond. It is suggested that this change in the chemical bonding state is one of the reasons why radioactive cesium is hard to be released from minerals.
 Ce
Ce O
O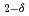 for electrolyte by Rietveld/ maximum entropy method
for electrolyte by Rietveld/ maximum entropy methodTaguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.339 - 342, 2015/06
Rare-earth doped ceria exhibits both ionic and electronic conductions, and those ceria with higher ratio of ionic conduction against electronic conduction is used as a solid electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells. The electron density distributions in crystals are closely related to the electron diffusing pathway which affects the electronic conduction. In this study, we investigated the electron density distribution of doped ceria as a function of the content of Nd O
O -dopant to deduce the ratio of the electronic to ionic conduction. The crystal structure was refined with the space group,
-dopant to deduce the ratio of the electronic to ionic conduction. The crystal structure was refined with the space group, 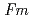 -3
-3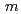 , which is the same as undoped ceria. Ce and Nd ions randomly occupied the 4
, which is the same as undoped ceria. Ce and Nd ions randomly occupied the 4 site and O ion the 8
site and O ion the 8 site. The electron conduction pathway was distributed through the 4
site. The electron conduction pathway was distributed through the 4 -8
-8 and 8
and 8 -8
-8 sites. The relationship between crystal structural change and electron density distribution as a function of the content of Nd
sites. The relationship between crystal structural change and electron density distribution as a function of the content of Nd O
O dopant will be discussed.
dopant will be discussed.
 O
O analyzed by combination of Rietveld/ maximum entropy method
analyzed by combination of Rietveld/ maximum entropy methodIgawa, Naoki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.247 - 252, 2015/05
The nuclear and electron density distributions of LiMn O
O which is one of the primitive cathode materials for secondary Li-ion batteries, were analyzed by applying Rietveld refinement and MEM to neutron and X-ray diffraction data, to estimate the Li diffusing pathway. The crystal structure of LiMn
which is one of the primitive cathode materials for secondary Li-ion batteries, were analyzed by applying Rietveld refinement and MEM to neutron and X-ray diffraction data, to estimate the Li diffusing pathway. The crystal structure of LiMn O
O could be refined with the space group,
could be refined with the space group, 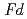 -3
-3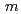 in the temperature range from 240 to 573 K. The structure was transformed to
in the temperature range from 240 to 573 K. The structure was transformed to 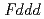 below 240 K. The isotropic thermal displacement parameter of Li was proportional to the temperature excluding 240 to 300 K. According to the MEM analyses it was indicated that the Li ions diffuse through 8
below 240 K. The isotropic thermal displacement parameter of Li was proportional to the temperature excluding 240 to 300 K. According to the MEM analyses it was indicated that the Li ions diffuse through 8 and 16
and 16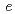 around 300 K.
around 300 K.
Honda, Mitsunori; Yanagida, Masatoshi*; Han, L.*; Miyano, Kenjiro*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 12, p.63 - 67, 2014/02
Tang, J.*; Nishimoto, Kiwamu*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Watanabe, Daiki*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 11, p.116 - 121, 2013/11