Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
R.M.Lambrecht*; Sekine, Toshiaki; H.Vera-Ruiz*
IAEA-TECDOC-1065, p.75 - 85, 1999/02
no abstracts in English
R.M.Lambrecht*; Sekine, Toshiaki; H.V.Ruiz*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 51(2), p.177 - 182, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.31(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
T.V.Hung*
JAERI-Research 98-037, 14 Pages, 1998/07
no abstracts in English
 Tc generator using a new adsorbent
Tc generator using a new adsorbentTanase, Masakazu; ;
Isotope News, 0(509), p.6 - 9, 1996/10
no abstracts in English
Isotope News, 0(508), p.12 - 15, 1996/09
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki
Nihon Kagakkai-Shi, 0(10), p.888 - 894, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Isotope News, 0(483), p.38 - 39, 1994/09
no abstracts in English
 Tc(n,p)
Tc(n,p) Mo,
Mo,  Tc(n,
Tc(n, )
)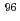 Nb,
Nb,  Tc(n,n
Tc(n,n )
) Nb, and
Nb, and  Tc(n,n)
Tc(n,n) Tc reactions at 13.5 and 14.8MeV
Tc reactions at 13.5 and 14.8MeVIkeda, Yujiro; E.T.Cheng*; Konno, Chikara; Maekawa, Hiroshi
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 116, p.28 - 34, 1994/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Mo adsorption/
Mo adsorption/ Tc elution property
Tc elution propertyFujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Hori, Junichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*; Ide, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 for production of
for production of  Tc by neutron irradiation
Tc by neutron irradiationSuematsu, Hisayuki*; Sato, Soma*; Nanko, Makoto*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Nishikata, Kaori; Suzuki, Tsuneo*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Niihara, Koichi*
no journal, ,
Spark plasma sintering of MoO was carried out for production of
was carried out for production of  Tc from
Tc from  Mo by the (n,
Mo by the (n, ) method in a nuclear reactor. Powder of MoO
) method in a nuclear reactor. Powder of MoO with an average grain size of 0.8
with an average grain size of 0.8 m and a purity of 99.99% was pressed in a graphite die with a diameter of 20 mm. Then, the green compact was heated in a spark plasma sintering apparatus with heating rates of 100
m and a purity of 99.99% was pressed in a graphite die with a diameter of 20 mm. Then, the green compact was heated in a spark plasma sintering apparatus with heating rates of 100  200
200 C/min to 500
C/min to 500  600
600 C in vacuum. After holding the temperature for 5 min, the sample was quenched. The sintered samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction for phase identifications, electron energy loss spectroscopy for compositional analyses and scanning electron microscopy for grain size measurements. After sintering at 550
C in vacuum. After holding the temperature for 5 min, the sample was quenched. The sintered samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction for phase identifications, electron energy loss spectroscopy for compositional analyses and scanning electron microscopy for grain size measurements. After sintering at 550 C, a sintered bulk of MoO
C, a sintered bulk of MoO with a relative density of 98% was obtained. These properties are good enough for separation of
with a relative density of 98% was obtained. These properties are good enough for separation of  Tc and recycle of Mo.
Tc and recycle of Mo.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc production development by (n,
Tc production development by (n, ) reaction in JMTR
) reaction in JMTRTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sozawa, Shizuo; Takeuchi, Nobuhiro*; Suzuki, Yasuaki*; Hasegawa, Yoshio*; Kakei, Sadanori*; Araki, Masanori
no journal, ,
Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of commonly used radioisotopes in the field of nuclear medicine. JAEA has a plan to produce
Tc) is one of commonly used radioisotopes in the field of nuclear medicine. JAEA has a plan to produce  Mo by (n,
Mo by (n, ) method, a parent nuclide of
) method, a parent nuclide of  Tc in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). In case of Japan, all of
Tc in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). In case of Japan, all of  Mo are imported from foreign countries, therefore JAEA has been performed the R&D on production of
Mo are imported from foreign countries, therefore JAEA has been performed the R&D on production of  Mo/
Mo/ Tc in JMTR with Japanese industrial users under the cooperation programs. The R&D on
Tc in JMTR with Japanese industrial users under the cooperation programs. The R&D on  Mo/
Mo/ Tc production was adopted as new project in Tsukuba International Strategic Zone, last year. In this project, various devices for production of
Tc production was adopted as new project in Tsukuba International Strategic Zone, last year. In this project, various devices for production of  Tc solution will be equipped the hot cell in the JMTR Hot laboratory and the following R&D items will be carried out for the production improvement. (1) Fabrication of irradiation target such as the sintered MoO
Tc solution will be equipped the hot cell in the JMTR Hot laboratory and the following R&D items will be carried out for the production improvement. (1) Fabrication of irradiation target such as the sintered MoO pellets, (2) Separation and concentration of
pellets, (2) Separation and concentration of  Tc by the solvent extraction from Mo solution, (3) Examination of
Tc by the solvent extraction from Mo solution, (3) Examination of  Tc solution for a medicine, and (4) Mo recycling from Mo generator and solution. In this symposium, the status of the R&D and construction of the PIE devices under this project will be introduced for the production of
Tc solution for a medicine, and (4) Mo recycling from Mo generator and solution. In this symposium, the status of the R&D and construction of the PIE devices under this project will be introduced for the production of  Mo/
Mo/ Tc production improvement.
Tc production improvement.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc production by activation method
Tc production by activation methodTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Nishikata, Kaori; Kimura, Akihiro; Ishida, Takuya; Takeuchi, Nobuhiro*; Kobayashi, Masaaki*; Kawamura, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Tc isolated from
Tc isolated from  MoO
MoO 3 using a thermal separation technique
3 using a thermal separation techniqueKawabata, Masako*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Motoishi, Shoji*; Saeki, Hideya*; Shiina, Takayuki*; Ota, Akio*; Takeuchi, Nobuhiro*; Nagai, Yasuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English