Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Nuryanthi, N.*; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Voss, K.-O.*; Severin, D.*; Tautmann, C.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 435, p.162 - 168, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)We used individual single-ion tracks in fluoropolymers with diameters of tens to hundreds of nanometers; chemical etching and ion-track grafting enabled us to develop ion-track and proton-conductive membranes, respectively. In the ion-track membranes of PVDF, strongly-LET-dependent etching was found, so the pore shape as well as the size was exclusively controlled by the track structures. We performed the ion-track grafting of styrene into ETFE to develop nanostructure-controlled proton exchange membranes (PEMs) for applications in PEM fuel cells. Our ion beam technology to develop fluoropolymer-based nanostructures has the potential to apply in the field of filtration processes and fuel cell devices. This would make it possible to provide new microfiltration technology for water treatment, sterilization, petroleum refining and dairy processing.
 -irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film
-irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) filmHiroki, Akihiro; Asano, Masaharu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Masaru
Chemical Physics Letters, 406(1-3), p.188 - 191, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.95(Chemistry, Physical)The pre-treatment effect of  -irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films bombarded with swift heavy ions was investigated by electric conductometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation. The Xe-ion bombarded PET films were etched for 6 hours in 0.2 M NaOH aqueous solution at 70
-irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films bombarded with swift heavy ions was investigated by electric conductometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation. The Xe-ion bombarded PET films were etched for 6 hours in 0.2 M NaOH aqueous solution at 70 C to prepare track-etched membranes. As
C to prepare track-etched membranes. As  -irradiation doses increased in the range of 0-160 kGy, the pore diameter obtained by SEM observation decreased while that obtained by conductometry became large. This inconsistent result between the two methods was due to an increase in the crosslinked region in the latent tracks caused by
-irradiation doses increased in the range of 0-160 kGy, the pore diameter obtained by SEM observation decreased while that obtained by conductometry became large. This inconsistent result between the two methods was due to an increase in the crosslinked region in the latent tracks caused by  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Asano, Masaharu; Yoshida, Masaru
Kogyo Zairyo, 52(12), p.65 - 69, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Maekawa, Yasunari; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshida, Masaru
Polymer, 45(7), p.2291 - 2295, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:27.92(Polymer Science)Ion track membranes of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) are applied to the production of anisotropically conducting films possessing copper wires of less than sub-micron in diameter. The membranes possessing cylindrical pores of 1.9  m and 200 nm in diameter were prepared by irradiation of
m and 200 nm in diameter were prepared by irradiation of  Xe
Xe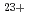 ion beams followed by etching in an aqueous NaOH. Copper wires were deposited into the pores by electrochemical plating in aqueous copper sulfate solution to prepare the PET/Cu hybrid membranes. The copper wires with 1.9
ion beams followed by etching in an aqueous NaOH. Copper wires were deposited into the pores by electrochemical plating in aqueous copper sulfate solution to prepare the PET/Cu hybrid membranes. The copper wires with 1.9  m in diameter showed wavelike surface roughness, resulting from the roughness of the pore side wall, whereas the copper wires with 200 nm in diameter showed smooth surfaces. The resistances of the membranes measured by a four terminal resistance method are in good agreement with the calculated values, indicating that the hybrid membranes possess conductivity perpendicular to the membrane surfaces but not parallel to the surfaces.
m in diameter showed wavelike surface roughness, resulting from the roughness of the pore side wall, whereas the copper wires with 200 nm in diameter showed smooth surfaces. The resistances of the membranes measured by a four terminal resistance method are in good agreement with the calculated values, indicating that the hybrid membranes possess conductivity perpendicular to the membrane surfaces but not parallel to the surfaces.
Apel, P. Y.*; Korchev, Y. E.*; Siwy, Z.*; Spohr, R.*; Yoshida, Masaru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 184(3), p.337 - 346, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:492 Percentile:99.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Peng, L.; Apel, P.*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 168(4), p.527 - 532, 2000/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.87 - 88, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
 -point temperature
-point temperatureHiroki, Akihiro*; Yoshida, Masaru; ; Asano, Masaharu; N.Reber*; R.Spohr*; Kubota, Hitoshi*; Katakai, Ryoichi*
Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids, 147, p.165 - 175, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masaru; Asano, Masaharu; Suwa, Takeshi; N.Reber*; R.Spohr*; Katakai, Ryoichi*
Advanced Materials, (9), p.757 - 758, 1997/09
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:97.96(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masaru; Nagaoka, Noiyasu*; Asano, Masaharu; Omichi, Hideki; Kubota, Hitoshi*; Ogura, K.*; Vetter, J.*; Spohr, R.*; Katakai, Ryoichi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 122(1), p.39 - 44, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masaru; Asano, Masaharu; Omichi, Hideki; Spohr, R.*; Katakai, Ryoichi*
Radiat. Meas., 28(1-6), p.799 - 810, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:67.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masaru; Asano, Masaharu; Safranj, A.; Omichi, Hideki; Spohr, R.*; Vetter, J.*; Katakai, Ryoichi*
Macromolecules, 29(27), p.8987 - 8989, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:87.01(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masaru
BEAMS 1995: Dai-6-Kai Ryushisen No Sentanteki Oyo Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, 0, p.139 - 154, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kitamura, Akane; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Chemical etching of polymer films irradiated with heavy ions leads to the formation of ion-track membranes with nanoscale pores in different shapes. Particularly, conically-shaped pores are expected to have a potential to create metallic nanoneedles by combination of vapor-deposition and electroplating methods. In this study, we prepared copper nanoneedles inside the conical pores of polyimide (PI)-based ion-track membranes and investigated their morphology. The PI films were irradiated with  Ar ions. The irradiated films were etched in a sodium hypochlorite solution at 60
Ar ions. The irradiated films were etched in a sodium hypochlorite solution at 60 C for 0.5 h, leading to the formation of conical pores with a surface diameter of ca. 500 nm. A very thin Au layer was deposited on this pore side of the ion-track membranes; then, it was used as a cathode for electroplating copper into the pores. After dissolving the PI templates, we obtained the copper needles ca. 500 nm in base diameter and 1.2
C for 0.5 h, leading to the formation of conical pores with a surface diameter of ca. 500 nm. A very thin Au layer was deposited on this pore side of the ion-track membranes; then, it was used as a cathode for electroplating copper into the pores. After dissolving the PI templates, we obtained the copper needles ca. 500 nm in base diameter and 1.2  m in height on copper plates.
m in height on copper plates.
Yamaki, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
My talk is devoted to the following two topics, both of which include the creation of fluoropolymer-based nanostructures with swift heavy ions mainly from the cyclotron of the Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application. (1) We have prepared the ion-track membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF), a type of fluoropolymer, by etching out latent tracks of MeV-GeV heavy ions in an alkaline solution. (2) The electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications have been prepared by the direct grafting of a styrene monomer into the ion tracks in a fluoropolymer substrate, poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film.
Yamaki, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
We have realized the importance of developing micro/nanofabrication techniques for fluoropolymers in order to further pursue the potential for their future applications. My talk is devoted to our recent research activities on (1) ion-track membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) and (2) proton-conductive membranes prepared by ion-track grafting into poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films. Both of them include the creation of fluoropolymer-based nanostructures with swift heavy ions mainly from the cyclotron of the Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA), JAEA.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu*; Sawada, Shinichi; Kitamura, Akane; Maekawa, Yasunari; Kay-Obbe, V.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Practically, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has been said to be the only fluoropolymer in which ion tracks can be developed by chemical etching. We thus investigated the possibility of varying the beam parameters and applying the effect of a pre-etching treatment for PVDF ion-track membranes with the goal of achieving enhanced track etching for effective control of the pore size and shape. Our activities also cover all types of fluoropolymers including PVDF. Compared to PVDF, poly(ethylene-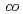 -tetrafluoroethylene) and a series of perfluoropolymers are known to be very stable in highly-concentrated acid or alkaline solutions or at higher temperatures. Although this property might make their ion-track etching very challenging, the ongoing research is expected to allow one to accumulate know-how on methods of chemical etching, which can be generalized for the chemical structures. These will give feedback to a guiding principle for effective ion-track etching in fluoropolymers.
-tetrafluoroethylene) and a series of perfluoropolymers are known to be very stable in highly-concentrated acid or alkaline solutions or at higher temperatures. Although this property might make their ion-track etching very challenging, the ongoing research is expected to allow one to accumulate know-how on methods of chemical etching, which can be generalized for the chemical structures. These will give feedback to a guiding principle for effective ion-track etching in fluoropolymers.
Kitamura, Akane; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Yuri, Yosuke*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yuyama, Takahiro*
no journal, ,
Ion track membranes of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are produced by chemical etching using a strong oxidant in an alkali solution after irradiation with an ion beam in vacuum. The oxidant erodes not only ion tracks but also a pristine surface of PVDF. Therefore, it causes serious deterioration in the quality of PVDF membranes. We have developed a track etching technique without any oxidant by irradiation with an ion beam in an oxygen atmosphere. PVDF films were irradiated with 330-MeV Ar ions in an oxygen atmosphere using a uniform-beam formation/irradiation system developed at the TIARA AVF-cyclotron facility. The maximum etching rate resulting from the present method was six times faster than that from the conventional method; furthermore, the maximum diameter of track-etched pores with the present method was more than twice as large as that in the conventional method. This suggests that the irradiation in oxygen can provide a useful technique of an oxidant-free track-etching process.
Kitamura, Akane; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Yuri, Yosuke*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yuyama, Takahiro*
no journal, ,
Ion track membranes of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are produced by chemical etching using a strong oxidant in an alkali solution after irradiation with an ion beam in vacuum. The oxidant erodes not only ion tracks but also a pristine surface of PVDF. Therefore, it causes serious deterioration in the quality of PVDF membranes. We have developed a track etching technique without any oxidant by irradiation with an ion beam in an oxygen atmosphere. PVDF films were irradiated with 330-MeV Ar ions in an oxygen atmosphere using a uniform-beam formation/irradiation system developed at the AVF-cyclotron of the TIARA facility. The maximum etching rate was six times faster than that from the conventional method; furthermore, the maximum diameter of track-etched pores was more than twice as large as that in the conventional method. FT-IR results showed that more oxygen-containing functional groups were formed on the surface irradiated in an oxygen atmosphere. Those were both caused by oxidation of ion tracks and the oxidation of ion tracks widened the size of etchable ion tracks. This suggests that the irradiation in oxygen can provide a useful technique of an oxidant-free track-etching process.