Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 gamma-ray imager using detector response patterns
gamma-ray imager using detector response patterns北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(7), p.076502_1 - 076502_8, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)三次元空間に無作為に配置した複数のガンマ線検出器の応答強度パターンから、ガンマ線源の入射方向を推定する新しいガンマ線イメージング技術の開発を行っている。本論文では、8個のGAGG (Ce)シンチレータキューブと18個の鉛キューブで構成されるガンマ線イメージャー、Coded Cube Camera for Gamma-ray (C3G)を製作し、 Cs線源の4
Cs線源の4 イメージング実験を実施した。実験の結果、3m先にある10MBqの
イメージング実験を実施した。実験の結果、3m先にある10MBqの Cs線源を10分間の測定で、angle uncertainty5度の精度でイメージングできることを確認した。一般にガンマ線イメージャーは数百から数千の読み出しチャンネル数が必要となるが、C3Gは僅か8チャンネルの読み出し回路で構成される。そのため回路や再構成アルゴリズムはシンプルにすることができ、安価かつ信頼性の高いイメージャーが実現する。C3Gは大きさ86mm
Cs線源を10分間の測定で、angle uncertainty5度の精度でイメージングできることを確認した。一般にガンマ線イメージャーは数百から数千の読み出しチャンネル数が必要となるが、C3Gは僅か8チャンネルの読み出し回路で構成される。そのため回路や再構成アルゴリズムはシンプルにすることができ、安価かつ信頼性の高いイメージャーが実現する。C3Gは大きさ86mm  86mm
86mm  86mmのハウジングに格納されており、重量は約600gである。小型軽量で4
86mmのハウジングに格納されており、重量は約600gである。小型軽量で4 視野を持ち、高角度分解能を持つ本技術は、天文学や医療、核セキュリティ、原子力発電所の廃止措置など広範な応用が期待される。
視野を持ち、高角度分解能を持つ本技術は、天文学や医療、核セキュリティ、原子力発電所の廃止措置など広範な応用が期待される。
 field-of-view gamma-ray imaging
field-of-view gamma-ray imaging北山 佳治
IEEE NPSS Newsletter (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/06
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station decommissioning site, there's a need for gamma-ray imaging technology that is compact and lightweight enough to be mounted on autonomous exploration robots, has a wide FOV and can operate in high-dose-rate environments. Coded masks and Compton cameras, although small and light, suffer from limitations such as a narrow FOV, susceptibility to background noise, or poor angular resolution and unsuitability for high-dose environments, respectively. Therefore, we developed a novel gamma-ray imaging technology that weighs about 600 g, has a cubic form measuring 8.6 cm on each side, offers a 4 FOV, has an angular resolution of approximately 5
FOV, has an angular resolution of approximately 5 , and is expected to operate in environments with radiation levels up to 100 mSv/h with only eight readout channels.
, and is expected to operate in environments with radiation levels up to 100 mSv/h with only eight readout channels.
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(3), p.032005_1 - 032005_6, 2024/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:40.97(Physics, Applied)検出器の応答パターンを利用した新しいガンマ線イメージング技術を紹介する。この方法では、三次元状にランダムに配置された複数の遮蔽体キューブを使用する。これらのキューブで定義された領域内では、ガンマ線の入射方向に基づいて固有のガンマ線フラックスパターンが形成される。このパターンは、複数のシンチレーターキューブの応答パターンとして測定される。ガンマ線の入射方向と対応する検出器応答パターンを事前に測定することで、アンフォールディング法を用いて入射方向を推定することができる。 Cs点線源を用いてシミュレーションを行った。その結果、10MBqの
Cs点線源を用いてシミュレーションを行った。その結果、10MBqの Cs線源をイメージャーから3m離れた位置に設置した場合、約10
Cs線源をイメージャーから3m離れた位置に設置した場合、約10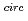 の角度分解能で撮像できることがわかった。これらの結果は、我々の新しい方法が既存のガンマ線イメージング技術と同等以上の性能を有することを示唆している。この撮像法の応用としては、原子力発電所の廃止措置、核医学、セキュリティ、天文学などが考えられる。
の角度分解能で撮像できることがわかった。これらの結果は、我々の新しい方法が既存のガンマ線イメージング技術と同等以上の性能を有することを示唆している。この撮像法の応用としては、原子力発電所の廃止措置、核医学、セキュリティ、天文学などが考えられる。
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
KEK Proceedings 2022-3, p.46 - 53, 2023/01
街灯の光で夜道に映し出された自分の影の向きや形から街灯の位置を予想することができる。この考えをガンマ線イメージャーに応用したものはCoded apertureとして知られている。今回、立体的な遮蔽とシンチレータ結晶配置を持ったCoded Cube Camera - POrtable (C3PO)を発案した。C3POは鉛、シンチレータ、空乏でできたキューブを3 3
3 3のルーリックキューブ状にランダムに配置したもので、各シンチレータの出力は3次元影模様を作り出す。三次元影からアンフォールディングによって線源方向分布にもどる。今回、Geant 4を用いたシミュレーションでその特性や実現可能性を検討した。
3のルーリックキューブ状にランダムに配置したもので、各シンチレータの出力は3次元影模様を作り出す。三次元影からアンフォールディングによって線源方向分布にもどる。今回、Geant 4を用いたシミュレーションでその特性や実現可能性を検討した。
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042006_1 - 042006_7, 2021/10
Gamma-ray imaging is a technique to visualize the spatial distribution of radioactive materials. Recently, gamma-ray imaging has been applied to research on decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident and environmental restoration, and active research has been conducted. This study is the elemental technology study of the new gamma-ray imager GISAS (Gamma-ray Imager using Small-Angle Scattering), which is assumed to be applied to the decommissioning site of FDNPS. GISAS consists of a set of directional gamma-ray detectors that do not require a shield. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of the shield free directional gamma-ray detector by simulation. The simulation result suggests that by measuring several keV of scattered electron energy by scatterer detector, gamma rays with ultra-small angle scattering could be selected. By using Compton scattering kinematics, a shield-free detector with directivity of about 10 could be feasible. By arranging the directional gamma-ray detectors in an array, it is expected to realize the GISAS, which is small, light, and capable of quantitative measurement.
could be feasible. By arranging the directional gamma-ray detectors in an array, it is expected to realize the GISAS, which is small, light, and capable of quantitative measurement.
佐藤 優樹; 峯本 浩二郎*; 根本 誠*; 鳥居 建男
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 976, p.164286_1 - 164286_6, 2020/10
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:89.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., experienced a meltdown as a result of a large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011. At that time, it was necessary to understand the aspects of the decommissioning working environment inside the FDNPS, such as establishing how the radioactive substances were distributed across the site, for work to be done efficiently without exposure to large amounts of radiation. Therefore, virtual reality (VR) emerged as a solution. There have been previous reports done on a technique for visualizing the distribution of radioactive substances in three dimensions utilizing a freely moving gamma-ray imager combined with simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology. In this paper, we introduce imaging technologies for the acquisition of image data from radioactive substances and three-dimensional (3D) structural models of the working environment, using a freely moving gamma-ray imager combined with SLAM technology. For this research, we also constructed a VR system and displayed the 3D data in a VR space, which enables users to experience the actual working environment without radiation exposure. In creating the VR system, any user can implement this method by donning an inexpensive head-mounted display apparatus and using a free, or low-cost, application software.
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)で働く作業員の安全確保のため、作業環境の放射性物質分布を測定できる技術が求められている。本研究では、既存のガンマ線イメージャーの欠点を補える新しいガンマ線イメージャーの開発に向けて、遮蔽体を必要としないガンマ線検出器の実現可能性をシミュレーションにより検討した。広範囲の放射性物質分布をイメージングする技術としてピンホールカメラとコンプトンカメラがある。ピンホールカメラは1イベントで線源方向を識別できるため、画像再構成が容易で今後定量測定に応用できる可能性がある。しかし遮蔽体を必要とするため総重量が重く遠隔測定には適さない。コンプトンカメラは遮蔽体を必要としないため小型軽量で遠隔測定が行える。しかし線源方向の推定に複数イベントが必要で、その際に描かれるコーンがノイズとなり画像のS/N比を下げている。我々は遮蔽体を必要としないピンホールカメラのような新しいガンマ線イメージャーを提案する。本研究では、その実現に必要となる遮蔽体を必要としない指向性ガンマ線検出器について、シミュレーションを用いて原理検証を行った。
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所の作業員の安全確保のため、建屋内に飛散した放射性物質分布を可視化するガンマ線イメージャーの研究が国内外で積極的に行われている。ガンマ線イメージャーの一つであるコンプトンカメラは遮蔽体を用いないため小型軽量で建屋内の遠隔測定に適している。しかし単一イベントで線源の方向を特定できないため画像が不鮮明になるといった課題がある。本研究は、検出が困難であるため今までイメージングに用いられることの無かった小角コンプトン散乱を利用し検出器に指向性を出すことで、既存のガンマ線イメージャーの欠点を克服した新しい技術の開発を目指す。これまでにシミュレーションベースでの原理検証を行い検出器のジオメトリや得られる指向性に関してのデータを取得した。その結果、軟X線用Si検出器を散乱体として用いることで必要な指向性を確保できることがわかった。また、マルチピクセル化についても検討した。
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹
no journal, ,
小角コンプトン散乱を利用しガンマ線検出器に指向性を持たせるというアイデアの実現可能性を、モンテカルロシミュレーションGEANT4を用いて検証した。検出器は散乱体と吸収体で構成され、散乱体で検出したエネルギーからガンマ線の散乱角を推定する。この指向性検出器は軽量かつ放射能の定量評価が可能なガンマ線イメージャーへ応用できる。散乱体にSi、吸収体にBGOシンチレータを用いそれぞれに2.5keV、662keV 32keVのエネルギー閾値を設け662keVのガンマ線を照射した。考慮する物理相互作用としてFTFP_BERT_LIV(標準的な電磁相互作用を網羅)を用いた。その結果、5度以下の散乱事象のみを選択的に検出することができ、約10度の指向性を得ることが可能であるとわかった。
32keVのエネルギー閾値を設け662keVのガンマ線を照射した。考慮する物理相互作用としてFTFP_BERT_LIV(標準的な電磁相互作用を網羅)を用いた。その結果、5度以下の散乱事象のみを選択的に検出することができ、約10度の指向性を得ることが可能であるとわかった。
北山 佳治
no journal, ,
医療や天文学、原子力施設など様々な分野で放射線イメージング技術は重要な役割を果たしている。本発表では、小型軽量、広視野、高空間分解能、低コストという相反する要素を高いレベルで実現した次世代の放射線イメージング技術を紹介する。小型ドローンから人工衛星まで対応可能なポテンシャルを持つこの要素技術について、具体的な技術概要とその応用可能性を説明する。
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
no journal, ,
We are developing a gamma-ray imager, the "Coded Cube Camera for Gamma-Ray" (C3G), which offers an omnidirectional field of view, and is compact and lightweight. The C3G consists of irregularly arranged shielding and detector cubes. The C3G has demonstrated the ability to image a  Cs source at a distance of 3 meters with an angular uncertainty of 5 degrees. In the current prototype, the arrangement of shielding and detectors has yet to be optimized. Since the imager geometry influences the angular resolution and accuracy of position estimation, identifying a metric for geometry optimization has become a pressing challenge. This study analyzed the relationship between imaging accuracy and detector response patterns. A simulation was conducted to search for parameters that affect imaging accuracy. As a result, it was found that the coefficient of variation (CV) of the detector's response patterns affects imaging accuracy, and the simulation confirmed that performance can be improved by changing the imager geometry to enhance the CV. The results obtained will be an essential indicator for future imager design. We plan to develop an algorithm that can select the optimal geometry.
Cs source at a distance of 3 meters with an angular uncertainty of 5 degrees. In the current prototype, the arrangement of shielding and detectors has yet to be optimized. Since the imager geometry influences the angular resolution and accuracy of position estimation, identifying a metric for geometry optimization has become a pressing challenge. This study analyzed the relationship between imaging accuracy and detector response patterns. A simulation was conducted to search for parameters that affect imaging accuracy. As a result, it was found that the coefficient of variation (CV) of the detector's response patterns affects imaging accuracy, and the simulation confirmed that performance can be improved by changing the imager geometry to enhance the CV. The results obtained will be an essential indicator for future imager design. We plan to develop an algorithm that can select the optimal geometry.