Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shindo, Manami*; Ueoku, Aya*; Okamura, Wakana*; Kikuchi, Shin; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Koga, Nobuyoshi*
Thermochimica Acta, 749, p.180021_1 - 180021_14, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Fukuda, Takanari
Proceedings of 13th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS13) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/11
Deepening the understanding of the molten core-concrete interaction (MCCI) is of the great importance for the sake of the severe accident managements as well as the fuel debris retrieval. Due to the difficulty to perform the experimental study with the extremely hot corium, the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is expected to provide physical insights on the thermal-hydraulics taken place in the corium. The particle method are one of the CFDs that have advantages on seamless tracking of the multi-phase multi-component flow, typically involved in the MCCI. However, the adequacy of the modelling methods for the interfacial tension has not yet well investigated, especially for the general multi-phase flow with more than three phases. Hence, in this study, a simple liquid-liquid-gas three phase flow is analyzed with the existing two types of the interfacial tension models: the continuum surface force (CSF) model and the potential model. Through the comparison, it has been implied that the CSF model gives more accurate result with the satisfactory resolution, whereas the stability is strongly dependent on the resolution of the bulk fluid. On the other hand, the potential model outperforms in terms of the stability, presumably because it does not require the numerical estimation of the geometrical information. However the inter-particle potential force seems to induces locally unphysical pressure distribution, which can be especially detrimental on the multiple interface junctions.
Shindo, Manami*; Ueoku, Aya*; Okamura, Wakana*; Kikuchi, Shin; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Koga, Nobuyoshi*
Thermochimica Acta, 738, p.179801_1 - 179801_12, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:34.56(Thermodynamics)Maeda, Masaki*; Tanabe, Tadao*; Nishiwaki, Tomoya*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Dozaki, Koji*; Nishimura, Koshiro*; Fujii, Sho*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tanaka, Akio*; Suzuki, Yusuke*; et al.
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
Yasue, Ayumu*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Yoshioka, Masahiro*; Noma, Takashi*; Okuno, Koichi*; Tanaka, Seiichiro*; Hirata, Yoshikazu*; Ooka, Tokunao*; Kimura, Yoshiharu*; Nagai, Tomoya*; et al.
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 21(5), p.337 - 350, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)The purpose of this study was to evaluate the use of resin injection to repair cracks in ultra-high-strength concrete (UHSC) members. As a preliminary step, the applicability of the neutron diffraction method (NDM) to investigate the effect of repairs in UHSC specimens was examined. The experimental results showed that the NDM can measure stresses in rebars in UHSC and normal concrete specimens. Therefore, in this experiment, the NDM was used to measure the bond performance of repairs with epoxy resin around the slit in normal concrete and UHSC specimens and examine the effect of repair on the UHSC specimens. Displacement around the slit was measured using a PI-shape displacement transducer. The evaluation confirmed that the bond performance of the repaired area was recovered by resin injection regardless of the concrete strength. In addition, the displacement around the slit was smaller for the injected specimens than the noninjected specimens. These experimental results clarified that by injecting resin, the same bond repair effect could be obtained in UHSC and normal concrete specimens.
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ohashi, Yusuke
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 175, p.109240_1 - 109240_7, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Decommissioning is planned at nuclear facilities that have been discontinued. We examined the evaluation method of uranium radioactivity for concrete waste generated by the decommissioning of nuclear facilities. Since the peaks of Ac-228, Tl-208, and K- 40 are derived from concrete waste, it is difficult to distinguish the 1001 keV peak emitted from the uranium source. We have derived a formula to correct gamma rays from concrete and the environment, and the amount of uranium was quantified. When the weight of concrete waste is about 300 kg, if the weight of uranium is 3 g or more, it can be quantified within a relative error of about 30%. Measurement tests were performed using homogeneous simulated concrete waste. Since uranium contamination is on the concrete surface at the uranium processing facility and small chunks generated by scraping the concrete surface will be stored in a drum and measured, it seems that the test of homogeneous concrete reflects the actual waste.
Takai, Shizuka; Namekawa, Masakazu*; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 69(7), p.1789 - 1798, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To reduce a large amount of contaminated concrete rubble stored in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station site, recycling low-radioactivity rubble within the site is a possible remedy. To promote recycling while ensuring safety, not only the average radioactivity but also the radioactivity distribution of concrete rubble should be efficiently evaluated because the details of rubble contamination caused by the accident remain unclear and likely include hotspots. However, evaluating inhomogeneous contamination of thick and/or dense materials is difficult using previous measurement systems, such as clearance monitors. This study experimentally confirmed the potential applicability of image reconstruction algorithms for radioactivity distribution evaluation in concrete rubble filled in a chamber. Radiation was measured using plastic scintillation fiber around the chamber (50  50
50  40 cm
40 cm ). Localized hotspots were simulated using standard sources of
). Localized hotspots were simulated using standard sources of  Cs, which is one of the main nuclides of contaminated rubble. The radioactivity distribution was calculated for 100 or 50 voxels (voxel size: (10 cm)
Cs, which is one of the main nuclides of contaminated rubble. The radioactivity distribution was calculated for 100 or 50 voxels (voxel size: (10 cm) or 10
or 10  10
10  20 cm
20 cm ) constituting the chamber. For 100 voxels, inner hotspots were undetected, whereas, for 50 voxels, both inner and surface hotspots were reconstructible. The distribution evaluated using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm was the most accurate; the average radioactivity was estimated within 70% accuracy in all seven cases.
) constituting the chamber. For 100 voxels, inner hotspots were undetected, whereas, for 50 voxels, both inner and surface hotspots were reconstructible. The distribution evaluated using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm was the most accurate; the average radioactivity was estimated within 70% accuracy in all seven cases.
Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Yasue, Ayumu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kogaku Nenji Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 44(1), p.208 - 213, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Nishio, Yuhei*; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Nihon Kenchiku Gakkai Kozokei Rombunshu, 86(785), p.1026 - 1035, 2021/07
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Computational Materials Science, 188, p.110173_1 - 110173_14, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:75.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ueno, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Takamura, Masato*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kozobutsu No Hoshu, Hokyo, Appuguredo Rombun Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 20, p.273 - 278, 2020/10
no abstracts in English
Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Oda, Chie; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Crystals (Internet), 10(9), p.767_1 - 767_33, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.76(Crystallography)Details are presented of the development of a coupled modeling simulator for assessing the evolution in the near-field of a geological repository for radioactive waste disposal where concrete is used as a backfill. The simulator uses OpenMI, a standard for exchanging data between simulation software programs at run-time, to form a coupled chemical-mechanical-hydrogeological model of the system. The approach combines a tunnel scale stress analysis finite element model, a discrete element model for accurately modeling the patterns of emerging cracks in the concrete, and a finite element and finite volume model of the chemical processes and alteration in the porous matrix and cracks in the concrete, to produce a fully coupled model of the system. Combining existing detailed simulation software in this way with OpenMI has the benefit of not relying on simplifications that might be necessary to combine all of the modeled processes in a single piece of software.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 6(2), p.021305_1 - 021305_9, 2020/04
Sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) is one of the important phenomena during severe accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) owing to the generation of large sources of hydrogen and aerosols in the containment vessel. In this study, SCR experiments with an internal heater were performed to investigate the chemical reaction beneath the internal heater (800 C), which was used to simulate the obstacle and heating effect on SCR. Furthermore, the effects of the internal heater on the self-termination mechanism were discussed. The internal heater on the concrete hindered the transport of Na into the concrete. Therefore, Na could start to react with the concrete at the periphery of the internal heater, and the concrete ablation depth at the periphery was larger than under the internal heater. The high Na pool temperature of 800
C), which was used to simulate the obstacle and heating effect on SCR. Furthermore, the effects of the internal heater on the self-termination mechanism were discussed. The internal heater on the concrete hindered the transport of Na into the concrete. Therefore, Na could start to react with the concrete at the periphery of the internal heater, and the concrete ablation depth at the periphery was larger than under the internal heater. The high Na pool temperature of 800 C increased largely the Na aerosol release rate, which was explained by Na evaporation and hydrogen bubbling, and formed the porous reaction product layer, whose porosity was 0.54-0.59 from the mass balance of Si and image analyzing EPMA mapping. They had good agreement with each other. The porous reaction products decreased the amount of Na transport into the reaction front. The Na concentration around the reaction front became about 30wt.% despite the position of the internal heater. It was found that the Na concentration condition was one of the dominant parameters for the self-termination of SCR, even in the presence of the internal heater.
C increased largely the Na aerosol release rate, which was explained by Na evaporation and hydrogen bubbling, and formed the porous reaction product layer, whose porosity was 0.54-0.59 from the mass balance of Si and image analyzing EPMA mapping. They had good agreement with each other. The porous reaction products decreased the amount of Na transport into the reaction front. The Na concentration around the reaction front became about 30wt.% despite the position of the internal heater. It was found that the Na concentration condition was one of the dominant parameters for the self-termination of SCR, even in the presence of the internal heater.
Miyabe, Azusa*; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kozobutsu No Hoshu, Hokyo, Appuguredo Rombun Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 19, p.59 - 64, 2019/10
no abstracts in English
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sakurai, Akitaka; Miyara, Nobukatsu; Sugita, Yutaka; Tanai, Kenji
Shigen, Sozai Koenshu (Internet), 6(2), 7 Pages, 2019/09
no abstracts in English
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.513 - 520, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study revealed melting points and thermal conductivities of four samples generated by sodium-concrete reaction (SCR). We prepared the samples using two methods such as firing mixtures of sodium and grinded concrete powder, and sampling depositions after the SCR experiments. In the former, the mixing ratios were determined from the past experiment. The latter simulated the more realistic conditions such as the temperature history and the distribution of Na and concrete. The thermogravimetry-differential thermal analyzer (TG-DTA) measurement showed the melting points were 865-942 C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840
C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840 C and the melting point was 840-850
C and the melting point was 840-850 C, which was 10-20
C, which was 10-20 C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na
C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na SiO
SiO and/or Na
and/or Na SiO
SiO . Moreover, the thermal conductivity was
. Moreover, the thermal conductivity was  =1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa
=1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa O-1-xSiO
O-1-xSiO (x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700
(x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700 C were explained by the equation of
C were explained by the equation of 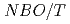 .
.
Hidaka, Akihide; Himi, Masashi*; Addad, Y.*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR 2019) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/05
no abstracts in English
Ueno, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kozobutsu No Hoshu, Hokyo, Appuguredo Rombun Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 18, p.647 - 650, 2018/10
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Kusunoki, Koichi*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Mukai, Tomohisa*
Konkurito Kozobutsu No Hihakai Kensa Shimpojiumu Hobunshu, 6, p.343 - 348, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
Sekine, Mariko*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kogaku Nenji Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 40(1), p.1545 - 1550, 2018/07
no abstracts in English