Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebihara, Kenichi; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Toda, Hiroyuki*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 136, p.751 - 756, 2025/06
It has been experimentally reported that adding tin (Sn) to high-strength aluminum-zinc-magnesium (Al-Zn-Mg) alloys effectively suppresses hydrogen (H) embrittlement, which may be attributed to H absorption by the second-phase particles of Sn. To verify this fact, a simulation of H entry into the Sn phase in Al was performed using a model based on the reaction-diffusion equation that incorporates the solid solution energy of H evaluated by first-principles calculations. The results showed that the H solid solution site concentration of the second-phase particles must be at least five times higher than that of the Al phase for H absorption by the Sn second-phase particles to suppress H embrittlement. Therefore, the actual H embrittlement suppression effect of Sn second-phase particles is limited, and other factors may influence the suppression of H embrittlement in the experiment.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Doda, Norihiro; Hamase, Erina; Kuwagaki, Kazuki; Mori, Takero; Okajima, Satoshi; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Matsushita, Kentaro; Hashidate, Ryuta; et al.
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 91(943), p.24-00229_1 - 24-00229_12, 2025/03
To assist conceptual studies of various reactor systems conducted by private sectors in nuclear power innovation, an innovative design system named ARKADIA (Advanced Reactor Knowledge- and AI-aided Design Integration Approach through the whole plant lifecycle) has been developed. In this paper, focusing on the ARKADIA-Design, achievements in the development of optimization processes in the fields of the core design, the plant structure design, and the maintenance schedule planning, as major function of ARKADIA-Design, and numerical analysis methods including coupled analysis to be used for the detailed analysis to confirm the plant performance after optimization are introduced at this point in time.
Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Kadowaki, Masanao; Nagai, Haruyasu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(2), p.113 - 117, 2025/02
, 67(2), p.113 - 117, 2025/02
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomohiro; Nagatake, Taku; Ono, Ayako; Tada, Kenichi; Kondo, Ryoichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/11
We have developed the JAEA Advances Multi-Physics Analysis platform for Nuclear systems (JAMPAN) to realize high-fidelity neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling simulations. We will perform MVP/JUPITER coupling simulation for a single BWR fuel assembly in order to confirm that the neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling through JAMPAN is feasible. This presentation explains how to send and receive data between MVP and JUPITER through JAMPAN and simulation results.
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Shobu, Takahisa; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 185, p.108336_1 - 108336_13, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:94.71(Engineering, Mechanical)Nagai, Haruyasu; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki; Tanimori, Toru*
Dai-52-Kai Kashika Joho Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/07
A novel monitoring method for the quantitative visualization of 3D distribution of a radioactive plume accidentally released from a nuclear facility is proposed, and the feasibility of its analysis method is demonstrated by preliminary test using hypothetical data. The proposed method is the combination of gamma-ray imaging spectroscopy with the electron tracking Compton camera (ETCC) and real-time high-resolution atmospheric dispersion simulation based on 3D wind observation with Doppler lidar. ETCC can acquire the angle distribution images of direct gamma-ray from a specific radionuclide in a target radioactive plume. The 3D distribution of radioactive plume is inversely reconstructed from direct gamma-ray images by several ETCCs located around the target by harmonizing with the air concentration distribution pattern of the plume predicted by real-time atmospheric dispersion simulation. Analysis methods were developed and tested by using hypothetical data generated by numerical simulations of atmospheric dispersion and radiation transport.
Watanabe, Tsutomu*; Ishikawa, Shuhei*; Kawashima, Masayuki*; Shimoyama, Ko*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Inagaki, Atsushi*
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 250, p.105783_1 - 105783_17, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.13(Engineering, Civil)This paper presents simulations of drifting snow using a Lagrangian particle dispersion model coupled with a large-eddy simulation code. The model accurately replicates observed features such as mass transport rate dependency on flow velocity and variations in particle size distribution. It also shows that the saltation layer height increases monotonically with flow velocity, contrary to conventional estimates. Additionally, the study confirms the transition from saltation to suspension near the estimated saltation layer height and finds that dense snow streamers are linked to small-scale low-speed streaks in near-surface flows.
Iimoto, Takeshi*; Shimada, Kazumasa; Hashimoto, Makoto; Nagai, Haruyasu; Hohara, Shinya*; Murakami, Kenta*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(7), p.356 - 360, 2024/07
, 66(7), p.356 - 360, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Shoma*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ohno, Shuji; Hayafune, Hiroki
Dai-28-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/06
A modified price-following model was developed to perform annual simulations, and case studies were performed for systems combining Solar power, wind, and SMR with thermal storage. The results show that, when comparing wind power and solar power as heat source, solar power is more effective in applying thermal energy storage technology because it allows for a larger price differential between heat charging and discharging. It was also found that a stable heat source such as SMRs allows a larger amount of electricity to be sold with the same amount of heat storage material.
Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi
Isotope News, (793), p.32 - 35, 2024/06
The design of a containment vessel in a sodium-cooled fast reactor was optimized from simulation on the hypothetical severe accident including sodium leakage and combustion. The simulation method is one of the base technologies of the design optimization system, ARKADIA. The simulation was performed on the different design conditions including volume of the containment vessel and the safety equipment as optimization parameters. The iterative simulation successfully found that the safety under this accident was kept even in the downsized containment vessel by selecting an effective safety equipment. This study demonstrated that the developed method has basic capability for design optimization in ARKADIA.
Abe, Shinichiro
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (138), p.24 - 31, 2024/06
Recently, muons are applied to various kinds of research fields, and the development of muon nuclear data is considered. The model for negative muon capture reaction implemented in PHITS has been underestimate the measured data for productions of secondary light particles. We applied the surface coalescence model (SCM) to the JQMD model and implemented the effect of meson exchange current (MEC) in the excitation function. The SCM improved productions of light complex particles, and the consideration of the MEC process in the excitation function improved productions of high energy nucleons. The improved model was applied to the soft error simulation. It was found that SEU event cross sections increase about 10  50% when the negative muon stop around the memory array.
50% when the negative muon stop around the memory array.
Ishikawa, Akihisa; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Hirai, Yuta*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Radiological Physics and Technology, 17(2), p.553 - 560, 2024/06
Shibata, Takanori*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nakano, Haruhisa*; Hoshino, Kazuo*; Miyamoto, Kenji*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Kawai, Isao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2743, p.012007_1 - 012007_5, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)Oscillation of the negative hydrogen ion (H ) beam phase space in Radio Frequency (RF) ion source is investigated by a simple 3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) model which takes into account the transport processes of electron, proton and H
) beam phase space in Radio Frequency (RF) ion source is investigated by a simple 3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) model which takes into account the transport processes of electron, proton and H in the extraction region. The calculation domain is in vicinity of the single beam aperture in J-PARC ion source configuration. In order to understand relation between the plasma density oscillation and the extracted H
in the extraction region. The calculation domain is in vicinity of the single beam aperture in J-PARC ion source configuration. In order to understand relation between the plasma density oscillation and the extracted H beam characteristics, the input electron and proton fluxes from the driver region are varied parametrically with the 1st and the 2nd harmonics of the J-PARC RF frequency (2 or 4 MHz). The numerical results give an idea to the main physical processes between the oscillations of the plasma parameters and the extracted H
beam characteristics, the input electron and proton fluxes from the driver region are varied parametrically with the 1st and the 2nd harmonics of the J-PARC RF frequency (2 or 4 MHz). The numerical results give an idea to the main physical processes between the oscillations of the plasma parameters and the extracted H ion trajectories in the different RF phases. Countermeasures to reduce the oscillation mechanisms are also discussed in the presentation.
ion trajectories in the different RF phases. Countermeasures to reduce the oscillation mechanisms are also discussed in the presentation.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Okano, Yasushi; Uchibori, Akihiro; Yokoyama, Kenji; Seki, Akiyuki; Wakai, Takashi; Asayama, Tai
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00424_1 - 23-00424_13, 2024/04
The outline and development status of element functions and design optimization process in ARKADIA to transform advanced nuclear reactor design to meet expectations of a safe, economic, and sustainable carbon-free energy source are introduced. It is also briefly explained that ARKADIA will realize Artificial Intelligence (AI)-aided integrated numerical analysis to offer the best possible solutions for the design and operation of a nuclear plant including optimization of safety equipment, and merge state-of-the-art numerical simulation technologies and a knowledge base that stores data and insights from past nuclear reactor development projects and R&Ds with AI technologies.
Tada, Kenichi; Kondo, Ryoichi; Kamiya, Tomohiro; Nagatake, Taku; Ono, Ayako; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2024) (Internet), p.1488 - 1497, 2024/04
JAEA has developed a new high-fidelity multi-physics platform JAMPAN for connecting single-physics codes such as a neutronics code and a thermal-hydraulics code. It consists of the HDF5 formatted data container and input and output data handler modules to generate the input file and read the output file of the single-physics code. Users can easily add or exchange the code by implementing input and output data handler modules for this code. The first target of JAMPAN is the coupling of neutronics and thermal-hydraulics calculations to provide reference results of core analysis codes. The current version of JAMPAN couples the neutronics code MVP and the thermal-hydraulics codes JUPITER, ACE-3D, and NASCA. Users can select the thermal-hydraulics code depending on the scale of problems to be solved, computational performance, and so on. This presentation explains the overview of JAMPAN and shows the results of the neutronics and thermal-hydraulics coupling calculation.
Shimada, Kazumasa; Sakurahara, Tatsuya*; Farshadmanesh, P.*; Reihani, S.*; Mohagehgh, Z.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 197, p.110243_1 - 110243_12, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)This research improves the realism of Level 3 probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) for nuclear power plants (NPP) to avoid subjective expert judgment when setting evacuation behavior for residents. Therefore, the evacuation speed output by the traffic simulation code MATSim was input to the level 3 PRA code MACCS. Furthermore, to set the priority of the places where road closure is to be considered, a method to evaluate the road closure risk due to the earthquake using the natural disaster risk assessment code HAZUS was developed. Then, the relationship between the evacuation routes and the radiation dose was evaluated for the case study of the Sequoyah NPP adopted in the SOARCA study conducted by the US NRC. As a result, the present study found an evacuation route with low closure risk but causing high radiation dose of residents when it is closed. This showed effectiveness of the proposed Level 3 PRA methodology for supporting decision-makers to enhance evacuation routes.
Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:94.71(Engineering, Mechanical)Hydrogen(H) embrittlement in high-strength aluminum(Al) alloys is a crucial problem. H accumulation at the interface of precipitates in Al alloy is considered to cause embrittlement. However, there is no quantitative knowledge regarding the interaction between H distribution and stress field near cracks. In this study, using a multi-modal three-dimensional image-based simulation combining the crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis, we tried to capture the stress distribution near the crack, its influence on the H distribution, and the probability of crack initiation in the experimental condition. As a result, it was found that grain boundary cracks transition to quasi-cleavage cracks in the region where the cohesive energy of the semi-coherent interface of MgZn precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
Abe, Shinichiro
CROSS T&T, (76), p.39 - 43, 2024/02
Non-destructive faults (the so-called soft errors) in microelectronics caused by cosmic rays have been recognized as a serious reliability problem. To guarantee the reliability of microelectronic devices, it is necessary to evaluate the soft error rate. We have developed some technics for the soft error simulation using PHITS code. We have also developed the terrestrial SER estimation methodology based on simulation coupled with one-time neutron irradiation testing. These results will be reported as the explanatory article in the journal of CROSS T&T published by the Comprehensive Research Organization for Science and Society (CROSS).
 -Fe
-FeSuzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(7), p.075102_1 - 075102_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied)Fracture of body centred cubic (bcc) metals and alloys below the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is brittle. This is theoretically explained by the notion that the critical stress intensity factor of a given crack front for brittle fracture is smaller than that for plastic deformation; hence, brittle fracture is chosen over plastic deformation. Although this view is true from a macroscopic point of view, such brittle fracture is always accompanied by small-scale plastic deformation in the vicinity of the crack tip, i.e. crack tip plasticity. This short paper investigates the origin of this plasticity using atomistic modeling with a recently developed machine-learning interatomic potential of  -Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
-Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Ina, Takuya; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Fluid Dynamics Research, 55(6), p.065501_1 - 065501_25, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.16(Mechanics)We investigate the applicability of the data assimilation (DA) to large eddy simulations (LESs) based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). We carry out the observing system simulation experiment of a two-dimensional (2D) forced isotropic turbulence, and examine the DA accuracy of the nudging and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with spatially sparse and noisy observation data of flow fields. The advantage of the LETKF is that it does not require computing spatial interpolation and/or an inverse problem between the macroscopic variables (the density and the pressure) and the velocity distribution function of the LBM, while the nudging introduces additional models for them. The numerical experiments with 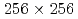 grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with
grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with 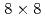 observation points (
observation points (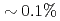 of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.