Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kasahara, Shigeki; Hata, Kuniki; Iwata, Keiko; Chimi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Review 2025-024, 243 Pages, 2025/11
It has been reported that intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) has occurred near weld fusion lines of low-carbon, namely unsensitized austenitic stainless steel for pipings and reactor internals used under the primary coolant environment of boiling water reactors in Japan since the early 2000s. It becomes one of the critical technical issues clarification of the mechanism and development of countermeasure techniques for IGSCC of low-carbon-containing stainless steel. From previous research, the hardness of stainless steel is increased due to the accumulation of local strain, after expansion and contraction during welding heat input, and the increment of hardness in such heat-affected zone is recognized one of the possible material factors caused by IGSCC. In particular, for boiling water reactor internal structures, it is essential to evaluate IGSCC taking into account neutron irradiation as well as strain accumulation for hardness increase, and it is desirable to accumulate multifaceted and systematic data that can be dedicated to evaluating the irradiation effect of weld heat-affected and hardened zones. In this study, we investigated and collected irradiation data on the crack growth rates and other material properties evaluated under simulated primary water conditions of boiling water reactor environments for neutron-irradiated low-carbon stainless steel weld heat-affected zones. Those were obtained through the ENI project of the Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization, including data that had not been made public until now.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion Science, 251, p.112897_1 - 112897_15, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Experimental and modeling studies of the oxygen ingression at the crevices of stainless steels were conducted in high-temperature water (288 C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression,
C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression, 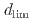 , was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite
, was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite  magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the
magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the 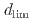 position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell.
position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell. 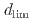 increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-71-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.253 - 256, 2024/11
In our previous study, we reported that Cl ions penetrating stainless steel crevices do not dissipate by diffusion, even in high-purity water (i.e., conductivity remains stable), likely due to electrochemical reactions inside and outside the crevice. This study further analyzes ion behavior by experimentally and computationally investigating ion concentration drivers in high-purity water. Results show that, at 50 C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100
C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100  S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm
S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm .
.
Irisawa, Eriko
Taikabutsu, 76(8), p.326 - 332, 2024/08
Liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) alloys have been considered as coolants for nuclear reactors, and research and development for LBE reactors has been conducted for many years. One of the most serious problems in using LBE as a coolant is the corrosion degradation of metallic structural materials due to exposure to high operating temperatures and flowing LBE. In the case of austenitic steels containing metal components such as Ni that are easily dissolved in LBE, it is known that it is necessary to monitor and control the concentration of dissolved oxygen in LBE in order to evaluate the amount of corrosion. This paper focuses on the relationship between the dissolved oxygen concentration, which is an important factor in the corrosion degradation mechanism, and the corrosion evaluation of stainless steel in LBE. The relationship between dissolved oxygen concentration in LBE, corrosion behavior and corrosion rate will be introduced using the example of corrosion evaluation of austenitic stainless steels in LBE in this paper.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 73(4), p.102 - 109, 2024/04
To evaluate the effects of dissolved oxygen concentration to water quality within SCC crack and the distribution of water quality in the depth direction under irradiation, immersion tests of stainless steel specimens given a gap and water radiolysis calculations for the water quality in the crevice gap were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that Fe O
O was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
was formed in the entire area within the crevice regardless of the dissolved oxygen concentration. It was also estimated that under irradiation, the oxidant species produced directly by radiolysis in the crack are consumed by the oxide growth, and anion enrichment occurs in the crack even in the irradiation conditions.
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steel
Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(11), p.284 - 288, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Soma, Yasutaka; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-70-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.199 - 202, 2023/10
Since an acidic corrosive environment (crevice environment) is formed inside the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel in high temperature water, it is important to understand the corrosion behavior in the crevice environment for the better understanding of crack growth behavior. In the previous study, the authors measured the electrical conductivity inside the crevice and obtained values of 380  S/cm and 1600
S/cm and 1600  S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH
S/cm for the crevice with and without intergranular corrosion, respectively. In this study, we defined the crevice environment I (pH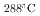 =4.41) and II (pH
=4.41) and II (pH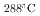 =3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
=3.13) corresponding the above conductivity values, and the corrosion behavior of Fe-xCr-20Ni (x=16.9, 19.8, 22.9, 24.3, 25.9) in each crevice environment was investigated. In the simulated crevice environment-I, the all alloys showed passive behavior, while in the environment-II, severe corrosion with intergranular cracking was observed for x = 16.9 and 19.8, and a thick oxide film was formed. On the other hand, above x=22.9, oxide film growth was suppressed and a clear passive region appeared on the polarization curve.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Pellegrini, M.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2023-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/09
A research project has been conducting thermophysical property measurement of a eutectic melt, eutectic melting reaction and relocation experiments, eutectic reaction mechanism investigation, and physical model development on the eutectic melting reaction for reactor application analysis in order to simulate the eutectic melting reaction and relocation behavior of boron carbide as a control rod material and stainless steel during a core disruptive accident in an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor designed in Japan. This paper describes the project overview and progress until JFY2022.
Fukai, Hirofumi*; Furuya, Masahiro*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(3), p.902 - 907, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:83.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper addresses reaction products and their distribution of the eutectic melting/solidifying reaction of boron carbide (B C) and stainless-steel (SS). The influence of the existence of carbon on the B
C) and stainless-steel (SS). The influence of the existence of carbon on the B C-SS eutectic reaction was investigated by comparing the iron boride (FeB)-SS reaction by Raman spectroscopy with Multivariate Curve Resolution (MCR) analysis. The scanning electron microscopy with dispersive X-ray spectrometer was also used to investigate the elemental information of the pure metals such as Cr, Ni, and Fe. In the B
C-SS eutectic reaction was investigated by comparing the iron boride (FeB)-SS reaction by Raman spectroscopy with Multivariate Curve Resolution (MCR) analysis. The scanning electron microscopy with dispersive X-ray spectrometer was also used to investigate the elemental information of the pure metals such as Cr, Ni, and Fe. In the B C-SS samples, a new layer was formed between B
C-SS samples, a new layer was formed between B C/SS interface, and the layer was confirmed that the formed layer corresponded to amorphous carbon (graphite) or FeB or Fe
C/SS interface, and the layer was confirmed that the formed layer corresponded to amorphous carbon (graphite) or FeB or Fe B. In contrast, a new layer was not clearly formed between FeB and SS interface in the FeB-SS samples.
B. In contrast, a new layer was not clearly formed between FeB and SS interface in the FeB-SS samples.
Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Yamano, Hidemasa
Dai-26-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Hasegawa, Kunio; Li, Y.; Lacroix, V.*
Proceedings of ASME 2022 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/07
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Corrosion, 78(6), p.503 - 515, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of electrochemical potential (ECP) on water chemistry within a crevice are of critical importance for understanding stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys in high temperature water. In this study, the effects of ECP on the electrical conductivity of a solution within a Type-316L stainless steel crevice (
 ) have been studied in 288
) have been studied in 288 C and 8 MPa water containing 10 ppb Cl
C and 8 MPa water containing 10 ppb Cl as major anionic species. In situ measurements of
as major anionic species. In situ measurements of 
 in a rectangular crevice with a gap of 15
in a rectangular crevice with a gap of 15  m and a depth of 23 mm have been conducted using small sensors installed at different crevice depths. An increase in ECP from -0.49 V (vs. standard hydrogen electrode) to -0.12 V resulted in an increase in
m and a depth of 23 mm have been conducted using small sensors installed at different crevice depths. An increase in ECP from -0.49 V (vs. standard hydrogen electrode) to -0.12 V resulted in an increase in 
 from 12
from 12  Scm
Scm to 160
to 160  Scm
Scm at a distance of 21 mm from the crevice mouth. The increase in
at a distance of 21 mm from the crevice mouth. The increase in 
 reached a maximum at about 0.15 V (about 300
reached a maximum at about 0.15 V (about 300  Scm
Scm ) and then tended to decrease with increasing potential. Finite element model analysis taking into account the electrochemical reaction quantitatively reproduced this behavior. It is considered that Cl
) and then tended to decrease with increasing potential. Finite element model analysis taking into account the electrochemical reaction quantitatively reproduced this behavior. It is considered that Cl is the major anionic species transported into the crevice at relatively low potentials, and that
is the major anionic species transported into the crevice at relatively low potentials, and that 
 increases monotonically with increasing ECP. On the other hand, when ECP exceeds around 0 V, a sufficient amount of HCrO
increases monotonically with increasing ECP. On the other hand, when ECP exceeds around 0 V, a sufficient amount of HCrO
 generated by transpassive dissolution also transported into the gap. Since this chemical species is highly oxidizing, unlike Cl, it is assumed that it reacts with metal cations to oxidize and precipitate them, thereby lowering conductivity.
generated by transpassive dissolution also transported into the gap. Since this chemical species is highly oxidizing, unlike Cl, it is assumed that it reacts with metal cations to oxidize and precipitate them, thereby lowering conductivity.
Sato, Rika*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
International Journal of Thermophysics, 43(6), p.85_1 - 85_15, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.07(Thermodynamics)In this study, we developed a simple viscosity measurement method based on the principle of least squares to derive the period and logarithmic decrement of oscillation. To confirm the reproducibility of the proposed method, the viscosity of molten nickel was measured and found to be in good agreement with those reported in the literature. The measurement error was less than  3%. Further, the experimental data showed good reproducibility, and the measurements were obtained with high accuracies using the proposed method.
3%. Further, the experimental data showed good reproducibility, and the measurements were obtained with high accuracies using the proposed method.
Takatsuka, Yuriko*; Matsumoto, Saori*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Hori, Ayumi*; Hayashi, Kiichiro*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Jikken Rikigaku, 22(2), p.117 - 119, 2022/06
This study clarified the effect of the viscosities of molten casting steels for high temperature by measuring them using the oscillating crucible method. The casting steels for high temperature samples used for viscosity measurements contained 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 mass% Ni. Viscosities were evaluated using Roscoe's equation and measured in the temperature range of 1693-1803 K.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(6), p.768 - 780, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo 2022 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.219 - 220, 2022/05
It is important to understand the electrochemical properties of stainless steel in environment created within crevice of stainless steel in high temperature water (crevice environment). This is because acidification and concentration of impurity ions occur in the crevice environment and this is common inside the stress corrosion crack. In this study, we reproduced the crevice environment in bulk scale and investigated mainly the effect of Cr concentration on the electrochemical properties of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys. Polarization curves of Fe-20Ni-xCr (x=16.4, 23, 26) were measured in water with a temperature of 288 C, a Cl concentration of 2
C, a Cl concentration of 2 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm , a pH value of about 4.5, and a dissolved hydrogen concentration of 10 ppb. The peak currents of active dissolution (at -400 mV) and passive current density (at -50 mV) for specimens with Cr concentrations x = 16.4, 23, and 26% were approximately 13.8, 15.9, 10.0
, a pH value of about 4.5, and a dissolved hydrogen concentration of 10 ppb. The peak currents of active dissolution (at -400 mV) and passive current density (at -50 mV) for specimens with Cr concentrations x = 16.4, 23, and 26% were approximately 13.8, 15.9, 10.0  Acm
Acm , and 18.4, 8.5, 8.5
, and 18.4, 8.5, 8.5  Acm
Acm , respectively. Although the current values of x=26 were slightly lower in both cases, it was concluded that there was no clear dependence of the polarization curve on Cr concentration in this environment.
, respectively. Although the current values of x=26 were slightly lower in both cases, it was concluded that there was no clear dependence of the polarization curve on Cr concentration in this environment.
 Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steel
Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.110 - 115, 2022/04
no abstracts in English
Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki
Dai-68-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.205 - 206, 2021/10
This study investigates the effect of temperature on dissipation behavior of Cl ion within the crevice of stainless steel. Concentration of Cl ion was evaluated by conductivity measured by using sensors installed at crevice specimen. At 50 and 80  C, Cl ions within the crevice of PEEK and Pt dissipated in accordance with concentration diffusion. On the contrary, dissipation speed of Cl ions inside the Type-304L stainless steel were much lower than those anticipated by simple concentration diffusion. This behavior attribute to the anodic dissolution of stainless steel inside the crevice, therefore, to quantitatively understand the effect of temperature on the dissipation behavior, it is necessary to know the anodic dissolution rate and occurrence of localized corrosion. Numerical analysis taking the effect of concentration diffusion and migration into account is also needed.
C, Cl ions within the crevice of PEEK and Pt dissipated in accordance with concentration diffusion. On the contrary, dissipation speed of Cl ions inside the Type-304L stainless steel were much lower than those anticipated by simple concentration diffusion. This behavior attribute to the anodic dissolution of stainless steel inside the crevice, therefore, to quantitatively understand the effect of temperature on the dissipation behavior, it is necessary to know the anodic dissolution rate and occurrence of localized corrosion. Numerical analysis taking the effect of concentration diffusion and migration into account is also needed.
 C-stainless steel alloys
C-stainless steel alloysNishi, Tsuyoshi*; Sato, Rika*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Kokubo, Hiroki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 552, p.153002_1 - 153002_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Determining high precision viscosities of molten B C-stainless steel (B
C-stainless steel (B C-SS) alloys is essential for the core disruptive accident analyses of sodium-cooled fast reactors and for analysis of severe accidents in boiling water reactors (BWR) as appeared in Fukushima Daiichi. However, there are no data on the high precision viscosities of molten B
C-SS) alloys is essential for the core disruptive accident analyses of sodium-cooled fast reactors and for analysis of severe accidents in boiling water reactors (BWR) as appeared in Fukushima Daiichi. However, there are no data on the high precision viscosities of molten B C-SS alloys due to experimental difficulties. In this study, the viscosities of molten SS (Type 316L), 2.5mass%B
C-SS alloys due to experimental difficulties. In this study, the viscosities of molten SS (Type 316L), 2.5mass%B C-SS, 5.0mass%B
C-SS, 5.0mass%B C-SS, and 7.0mass%B
C-SS, and 7.0mass%B C-SS alloys were measured using the oscillating crucible method in temperature ranges of 1693-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, and 1713-1793 K, respectively. The viscosity was observed to increase as the B
C-SS alloys were measured using the oscillating crucible method in temperature ranges of 1693-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, and 1713-1793 K, respectively. The viscosity was observed to increase as the B C concentration increased from 0 to 7.0 mass%. Using the experimental data of the molten 2.5mass%B
C concentration increased from 0 to 7.0 mass%. Using the experimental data of the molten 2.5mass%B C-SS and 5.0mass%B
C-SS and 5.0mass%B C-SS and 7.0mass%B
C-SS and 7.0mass%B C-SS in the temperature range of 1713-1793 K, the equation for the viscosity of molten B
C-SS in the temperature range of 1713-1793 K, the equation for the viscosity of molten B C-SS alloys was determined, and the measurement error of the viscosity of molten B
C-SS alloys was determined, and the measurement error of the viscosity of molten B C-SS alloys is less than
C-SS alloys is less than  8%.
8%.
 in NaCl
in NaClAoyama, Takahito; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Metals, 11(3), p.511_1 - 511_13, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effect of Cu in bulk solution on pitting corrosion resistance of extra high purity type 316 stainless steel was investigated. Pitting occurred in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
in bulk solution on pitting corrosion resistance of extra high purity type 316 stainless steel was investigated. Pitting occurred in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl whereas pitting was not initiated in 0.1 M NaCl. Although deposition of Cu
whereas pitting was not initiated in 0.1 M NaCl. Although deposition of Cu on the surface occurred regardless of potential region in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
on the surface occurred regardless of potential region in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl , Cu
, Cu in bulk solution had no influence on the passive film formation. The decrease in pitting corrosion resistance in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
in bulk solution had no influence on the passive film formation. The decrease in pitting corrosion resistance in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl resulted from the deposited Cu or Cu compound and continuous supply of Cu
resulted from the deposited Cu or Cu compound and continuous supply of Cu on the surface.
on the surface.