Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
松下 太樹*; 小沢 耀弘*; 荒木 康史; 藤本 純治*; 佐藤 昌利*
Physical Review B, 111(24), p.245131_1 - 245131_11, 2025/06
被引用回数:0We investigate the intrinsic spin Nernst effect (SNE), a transverse spin current induced by temperature gradients, in topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs) and magnetic Weyl semimetals (MWSMs) with Ising spin-orbit coupling. The intrinsic SNE is described by the spin Berry curvature, which reflects the geometric nature of TDSMs and MWSMs. We clarified that the intrinsic SNE becomes significant when the Fermi energy is near, but slightly deviates from, the energy of the point nodes. In this situation, Bloch electrons with strong spin Berry curvature contribute to the SNE while avoiding carrier compensation between electrons and holes. We found that in TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces, the spin Nernst angle, which measures the efficiency of the SNE, is larger than that observed in heavy metals. This suggests that TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces can achieve efficient heat-to-spin current conversion. In MWSMs, variation in the magnitude of the exchange coupling with magnetic moments significantly changes the SNE, affecting both the direction and magnitude of the spin Nernst current. This implies that ferromagnetic transitions can be used to reverse the spin Nernst current. These results provide the fundamentals for future topological spin caloritronics.
Sud, A.*; 山本 慧; 飯浜 賢志*; 石橋 一晃*; 深見 俊輔*; 紅林 秀和*; 水上 成美*
Physical Review Letters, 134(24), p.246704_1 - 246704_7, 2025/06
被引用回数:1We investigate the nonlinear coupling between acoustic (ac) and optical (op) modes in the coupled magnetization dynamics of synthetic antiferromagnets (SyAFs), utilizing current-driven resonance spectroscopy. A clear spectral splitting is evident in the ac mode when strongly excited by the radio frequency (RF) current at the driving frequency half that of the op mode resonance. The Landau-Lifshitz phenomenology aligns with the experimental observations, affirming the coupling of the RF-excited ac and op modes through three-magnon mixing. The nonlinearity enables a Rabi-like splitting in in-plane magnetized SyAF without breaking its natural symmetries. This discovery holds potential for advancing our understanding of nonlinear antiferromagnetic dynamics.
目黒 智成*; 小沢 耀弘*; 小林 浩二*; 荒木 康史; 野村 健太郎*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022065_1 - L022065_8, 2025/06
We theoretically find a topological spin-orbit torque (SOT) in the compensated ferrimagnetic Weyl semimetal Ti MnAl. The topological SOT arises from all the occupied states, which is free from dissipation. However, it is negligible in metallic magnets and was not reported in Weyl semimetals. We show the enhancement of the topological SOT from the mixed Berry curvature around the Weyl points in Ti
MnAl. The topological SOT arises from all the occupied states, which is free from dissipation. However, it is negligible in metallic magnets and was not reported in Weyl semimetals. We show the enhancement of the topological SOT from the mixed Berry curvature around the Weyl points in Ti MnAl. This finding provides a guiding principle for designing highly efficient SOT devices using the topological nature of ferrimagnetic Weyl semimetals.
MnAl. This finding provides a guiding principle for designing highly efficient SOT devices using the topological nature of ferrimagnetic Weyl semimetals.
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; 江崎 蘭世; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
It remains an open question whether or not the scalar spin chirality itself can exhibit a Hall-type transport. In this work, we show that the answer is yes: The scalar spin chirality is Hall-transported in Kagome ferromagnets and antiferromagnets under an external bias, engendering a phenomenon which we dub the scalar spin chirality Nernst effect. Our findings call for the need to lift the conventional assumption that the scalar spin chirality is a static quantity in order to discover the active roles of the scalar spin chirality in transport properties.
 SRによるイオンダイナミクス解析の精密化に向けた動的久保-鳥谷部モデルの拡張
SRによるイオンダイナミクス解析の精密化に向けた動的久保-鳥谷部モデルの拡張伊藤 孝; 門野 良典*
固体物理, 60(4), p.197 - 206, 2025/04
 SRを用いた固体内イオンダイナミクス解析法が抱える深刻な矛盾を解消するために、その根幹をなす動的久保・鳥谷部モデルの拡張を試みた。我々の新しいモデルは、ミュオン静止描像の上での定量的な解析を可能にするだけでなく、この前提の妥当性を評価する手段を同時に提供する。
SRを用いた固体内イオンダイナミクス解析法が抱える深刻な矛盾を解消するために、その根幹をなす動的久保・鳥谷部モデルの拡張を試みた。我々の新しいモデルは、ミュオン静止描像の上での定量的な解析を可能にするだけでなく、この前提の妥当性を評価する手段を同時に提供する。
Sheng, L.*; 山本 慧; 他18名*
Nature Physics, 8 Pages, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:82.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Controlling the spin current lies at the heart of spintronics and its applications. In ferromagnets, the sign of spin currents is fixed once the current direction is determined. However, spin currents in antiferromagnets can possess opposite polarizations, but this requires enormous magnetic fields to lift the degeneracy between the two modes. Therefore, controlling spin currents with opposite polarization is still a challenge. Here we demonstrate the control of spin currents at room temperature by magnon interference in a canted antiferromagnet, namely, haematite that has recently been classified as an altermagnet. Magneto-optical characterization by Brillouin light scattering reveals that the spatial periodicity of the beating patterns is tunable via the microwave frequency. We further observe that the inverse spin Hall voltage changes sign as the frequency is tuned, evincing a frequency-controlled switching of polarization of pure spin currents. Our work highlights the use of antiferromagnetic magnon interference to control spin currents, which substantially extends the horizon for the emerging field of coherent antiferromagnetic spintronics.
Huang, Y.-C.*; 吉川 貴史; 他5名*
Applied Physics Letters, 126(9), p.092403_1 - 092403_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)The application of spin-current volume effect (SVE) with volume magnetostriction of iron gallium (FeGa) films is examined for micro-diaphragm actuation. A silicon diaphragm measuring 1.5 1.5 mm
1.5 mm is coated with Pt (100-nm-thick) and FeGa (100-nm-thick) thin films. An alternating charge current passed through the FeGa/Pt/Si diaphragm under a magnetic field perpendicular to the charge current generates an alternating spin current via the spin Hall effect in the Pt film, transferring angular momentum from the Pt film to the FeGa film. The injected spin current provides energy and changes the effective temperature, thereby varying the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments. In a magnetic material with volume magnetostriction, the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments affects its volume. When the spin fluctuations change, the volume magnetostriction induces a corresponding expansion or contraction of the material. Both electrodeposited and ion-beam sputter-deposited FeGa films are investigated, and it is observed that the FeGa film exhibits SVE. The force generated by the SVE is evaluated based on the vibration amplitude at the fundamental resonant mode. This study demonstrates that the force generated by the SVE is correlated with the volume magnetostriction and the deposition process.
is coated with Pt (100-nm-thick) and FeGa (100-nm-thick) thin films. An alternating charge current passed through the FeGa/Pt/Si diaphragm under a magnetic field perpendicular to the charge current generates an alternating spin current via the spin Hall effect in the Pt film, transferring angular momentum from the Pt film to the FeGa film. The injected spin current provides energy and changes the effective temperature, thereby varying the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments. In a magnetic material with volume magnetostriction, the thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moments affects its volume. When the spin fluctuations change, the volume magnetostriction induces a corresponding expansion or contraction of the material. Both electrodeposited and ion-beam sputter-deposited FeGa films are investigated, and it is observed that the FeGa film exhibits SVE. The force generated by the SVE is evaluated based on the vibration amplitude at the fundamental resonant mode. This study demonstrates that the force generated by the SVE is correlated with the volume magnetostriction and the deposition process.
杉本 聡志*; 荒木 康史; 高橋 有紀子*; 家田 淳一; 葛西 伸哉*
Communications Physics (Internet), 8, p.100_1 - 100_9, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Current-induced spin-orbit torque (SOT) at heavy metal/ferromagnet (HM/FM) interfaces plays a critical role in modern spintronics. The challenges in SOT research are to enhance the conversion efficiency and generate unconventional torque components. Here, we propose a simple protocol to meet such demands by engineering symmetrical structures, specifically by a wedge-shaped topological material interface in R-3m Bi Te
Te (001)/FM heterostructures. The symmetry of the topological interface is manipulated to lead to unconventional emergences of both out-of-plane and in-plane spin polarizations. Torque measurements show that these polarizations have conversion efficiencies up to 10 percent. This considerable improvement in the SOT efficiency is characterized both qualitatively and quantitatively based on the nonreciprocal ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) spectra and the SOT dependence on the magnetic field direction. The observed enhancement in the unconventional SOT is attributed to the wedge-oriented symmetry reduction of the spin-momentum locking structure of interfacial Dirac fermions. This advance opens new avenues for designing geometrically novel spintronics devices, demonstrating the potential of using multidirectional SOTs for forthcoming nanotechnological applications.
(001)/FM heterostructures. The symmetry of the topological interface is manipulated to lead to unconventional emergences of both out-of-plane and in-plane spin polarizations. Torque measurements show that these polarizations have conversion efficiencies up to 10 percent. This considerable improvement in the SOT efficiency is characterized both qualitatively and quantitatively based on the nonreciprocal ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) spectra and the SOT dependence on the magnetic field direction. The observed enhancement in the unconventional SOT is attributed to the wedge-oriented symmetry reduction of the spin-momentum locking structure of interfacial Dirac fermions. This advance opens new avenues for designing geometrically novel spintronics devices, demonstrating the potential of using multidirectional SOTs for forthcoming nanotechnological applications.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Ba, Y.*; 山本 慧; 他6名*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104401_1 - 104401_15, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ferrimagnet insulator yttrium iron garnet (Y Fe
Fe O
O , YIG) attracts much interest in magnonics and microwave applications due to its relatively low magnetic damping and long magnon relaxation time. The magnetoelastic interaction between YIG magnetization and surface acoustic waves (SAWs) has been the basis in the development of acoustic-surface-wave isolators. However, the investigation of SAW-driven magnetic resonance in YIG is limited by the low compatibility of YIG and SAW devices. In this work, we demonstrate nonreciprocal resonant SAW absorption in an on-chip YIG-SAW device integrated by the focused ion beam technique. We observed two distinct SAW absorption signals attributed to the perpendicular standing spin waves (PSSW). Furthermore, the large observed nonreciprocity is compared to theoretical predictions incorporating the influence of asymmetric surface conditions on PSSW mode profiles and nonreciprocal magnon-SAW coupling. The strongly nonreciprocal SAW attenuation in YIG offers a promising opportunity for highly efficient rf signal processing technologies.
, YIG) attracts much interest in magnonics and microwave applications due to its relatively low magnetic damping and long magnon relaxation time. The magnetoelastic interaction between YIG magnetization and surface acoustic waves (SAWs) has been the basis in the development of acoustic-surface-wave isolators. However, the investigation of SAW-driven magnetic resonance in YIG is limited by the low compatibility of YIG and SAW devices. In this work, we demonstrate nonreciprocal resonant SAW absorption in an on-chip YIG-SAW device integrated by the focused ion beam technique. We observed two distinct SAW absorption signals attributed to the perpendicular standing spin waves (PSSW). Furthermore, the large observed nonreciprocity is compared to theoretical predictions incorporating the influence of asymmetric surface conditions on PSSW mode profiles and nonreciprocal magnon-SAW coupling. The strongly nonreciprocal SAW attenuation in YIG offers a promising opportunity for highly efficient rf signal processing technologies.
 with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMR松村 拓輝*; 徳永 陽; 酒井 宏典; 神戸 振作; 他13名*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To investigate the intrinsic magnetic properties of UTe , we performed
, we performed  Te-NMR measurements on the ultra-clean single-crystalline UTe
Te-NMR measurements on the ultra-clean single-crystalline UTe with superconducting transition temperature
with superconducting transition temperature  = 2.1 K and compared the results with those of the
= 2.1 K and compared the results with those of the  = 1.6 K sample. The broadening of the linewidth of the NMR spectrum in the a-axis magnetic field and the low-temperature magnetic fluctuations observed in the 1.6 K sample are suppressed in the ultra-clean sample, indicating that such magnetic properties originate from a tiny amount of U deficiency. The present results suggest that the magnetic properties in UTe
= 1.6 K sample. The broadening of the linewidth of the NMR spectrum in the a-axis magnetic field and the low-temperature magnetic fluctuations observed in the 1.6 K sample are suppressed in the ultra-clean sample, indicating that such magnetic properties originate from a tiny amount of U deficiency. The present results suggest that the magnetic properties in UTe are sensitive to the U deficiency. We also observed a peculiar angular dependence of the NMR quantities due to large magnetic anisotropy with the a-axis as the magnetic easy axis.
are sensitive to the U deficiency. We also observed a peculiar angular dependence of the NMR quantities due to large magnetic anisotropy with the a-axis as the magnetic easy axis.
 GeTe
GeTe homojunctions
homojunctions小幡 玲二*; 齊藤 英治; 吉川 貴史; 他13名*
Advanced Materials, 37(8), p.2411459_1 - 2411459_11, 2025/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Twistronics, a novel engineering approach involving the alignment of van der Waals (vdW) integrated two-dimensional materials at specific angles, has recently attracted significant attention. Novel nontrivial phenomena have been demonstrated in twisted vdW junctions (the so-called magic angle), such as unconventional superconductivity, topological phases, and magnetism. However, there have been only few reports on integrated vdW layers with large twist angles 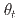 , such as twisted interfacial Josephson junctions using high-temperature superconductors. Herein, vdW homojunctions of the thin-magnetic flakes, Fe
, such as twisted interfacial Josephson junctions using high-temperature superconductors. Herein, vdW homojunctions of the thin-magnetic flakes, Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT), with large
(FGT), with large 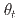 ranging from 0 to 90 deg, without inserting any tunnel barriers are assembled. Nevertheless, these vdW homojunctions exhibit tunnel-magnetoresistance (TMR) like behavior (pseudo-TMR (PTMR) effect) with the ratios highly sensitive to the
ranging from 0 to 90 deg, without inserting any tunnel barriers are assembled. Nevertheless, these vdW homojunctions exhibit tunnel-magnetoresistance (TMR) like behavior (pseudo-TMR (PTMR) effect) with the ratios highly sensitive to the 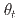 values, revealing that the vdW gap at the junction interface between the twisted FGT layers behaves like a tunnel barrier and the
values, revealing that the vdW gap at the junction interface between the twisted FGT layers behaves like a tunnel barrier and the 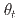 serves a control parameter for PTMR by drastically varying magnitudes of the lattice-mismatch and the subsequent appearance of antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin alignment. First-principles calculations considering vacuum gaps indicate strong dependence of TMR on the
serves a control parameter for PTMR by drastically varying magnitudes of the lattice-mismatch and the subsequent appearance of antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin alignment. First-principles calculations considering vacuum gaps indicate strong dependence of TMR on the 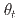 driven by the sixfold screw rotational symmetry of bulk FGT. The present homojunctions hold promise as a platform for novel AFM spin-dependent phenomena and spintronic applications.
driven by the sixfold screw rotational symmetry of bulk FGT. The present homojunctions hold promise as a platform for novel AFM spin-dependent phenomena and spintronic applications.
 のワイル電子を活用したスピン制御
のワイル電子を活用したスピン制御荒木 康史; 家田 淳一
まぐね, 20(1), p.12 - 17, 2025/02
スピントロニクスにおいて、スピンの電気的操作に際して発生する電力損失は大きな課題である。このジュール発熱を回避する過程として、我々は電子状態のトポロジカル構造を組み込んだ電場誘起スピントルクの理論を構築した。このトポロジカルな寄与は散逸の影響を受けず、従来のスピン移行トルクに比べて単位電流あたりのトルク効率を著しく向上させる。本原理によるスピントルクの発現は、トポロジカルな電子系の典型例である「ワイル電子」を持つ、強磁性酸化物SrRuO における磁化反転実験によって検証された。
における磁化反転実験によって検証された。
 Fe
Fe O
O
森 道康; Tomasello, B.*; Ziman, T.*
Physical Review B, 111(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_12, 2025/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The spin Seebeck effect (SSE) is a phenomenon of thermoelectric generation that occurs within a device consisting of a bilayer of a metal and a ferromagnet. When Tb Fe
Fe O
O (TbIG) is substituted for the ferromagnet, the effect goes to zero at low temperatures, yet it increases to positive values with the application of a magnetic field. This is opposite to the expectation that the SSE should be suppressed by a magnetic field due to the increase in
(TbIG) is substituted for the ferromagnet, the effect goes to zero at low temperatures, yet it increases to positive values with the application of a magnetic field. This is opposite to the expectation that the SSE should be suppressed by a magnetic field due to the increase in  magnon gap. In this paper, the crystal-field excitations (CFE) in TbIG are calculated within a mean field theory exploiting the parameters of Terbium Gallium Garnet Tb
magnon gap. In this paper, the crystal-field excitations (CFE) in TbIG are calculated within a mean field theory exploiting the parameters of Terbium Gallium Garnet Tb Fe
Fe O
O (TGG) from the neutron-scattering experimental literature. Like TGG, the primitive cell of TbIG hosts twelve Tb sites with six inequivalent magnetic sublattices, but due to the net
(TGG) from the neutron-scattering experimental literature. Like TGG, the primitive cell of TbIG hosts twelve Tb sites with six inequivalent magnetic sublattices, but due to the net ![$$[111]$$](/search/images/ERNTCMJRLUSA.gif) -molecular field from the tetrahedral and octahedral Fe ions, these can be classified into two distinct groups, the
-molecular field from the tetrahedral and octahedral Fe ions, these can be classified into two distinct groups, the 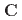 and the
and the 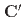 sites, which account for the "double umbrella" magnetic structure. We show that when an external magnetic field is applied along the [111] direction of the crystal, the lowest CFE of the
sites, which account for the "double umbrella" magnetic structure. We show that when an external magnetic field is applied along the [111] direction of the crystal, the lowest CFE of the 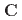 sublattices decreases. As a consequence of the magnetic field dependence of the lowest CFE, we find that at low temperatures the SSE in TbIG can result enhanced by an applied magnetic field.
sublattices decreases. As a consequence of the magnetic field dependence of the lowest CFE, we find that at low temperatures the SSE in TbIG can result enhanced by an applied magnetic field.
新居 陽一*; 山本 慧; 菅野 将誠*; 前川 禎通*; 小野瀬 佳文*
Physical Review Letters, 134(2), p.027001_1 - 027001_5, 2025/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:94.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)While the rectification phenomenon caused by the simultaneous breaking of time reversal and spatial inversion symmetries has been extended to a wide range of (quasi)particles and waves, the nonreciprocal diffraction, which is the imbalance of upward and downward deflections, was previously observed only for photons and remained to be extended to other (quasi)particles. Here, we present evidence of the nonreciprocal diffraction of surface acoustic wave (SAW) utilizing a magnetoelastic grating on a SAW device. Asymmetric diffraction intensities were observed when the ferromagnetic resonance was acoustically excited. Based on a theoretical model, we ascribe the microscopic origin of this phenomenon to the resonant scattering involving ferromagnetic resonance excitations. The novel property may pave an avenue to further development of SAW devices for various purposes including microwave communications and quantum engineering applications.

 H
H O
O藤原 理賀; 萩原 雅人; 幸田 章宏*; 中村 惇平*; 松尾 晶*; 金道 浩一*; 石角 元志*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014406_1 - 014406_9, 2025/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:82.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We reported the magnetic behavior of a rhombic lattice quantum antiferromagnet KCoPO
 H
H O. The rhombic lattice model is equivalent to a model of a square lattice with two different diagonal components, and competing exchange interactions potentially produce exotic quantum states. This compound is well characterized by the
O. The rhombic lattice model is equivalent to a model of a square lattice with two different diagonal components, and competing exchange interactions potentially produce exotic quantum states. This compound is well characterized by the 
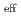 = 1/2 state. The magnetic structure of KCoPO
= 1/2 state. The magnetic structure of KCoPO
 H
H O is identified as an incommensurate helical structure, characterized by a magnetic modulation propagation vector
O is identified as an incommensurate helical structure, characterized by a magnetic modulation propagation vector 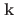 = (0.1747(1) 0 0) with an in-plane moment rotating along the
= (0.1747(1) 0 0) with an in-plane moment rotating along the  axis. Moreover, a magnetic field-induced phase transition is observed at approximately 1 T. The application of a magnetic field suppresses spin ordering and enhance spin fluctuations. Our experimental results suggest the presence of a quantum phase in the magnetic phase diagram of the spin-1/2 Heisenberg rhombic lattice antiferromagnet with easy-plane anisotropy.
axis. Moreover, a magnetic field-induced phase transition is observed at approximately 1 T. The application of a magnetic field suppresses spin ordering and enhance spin fluctuations. Our experimental results suggest the presence of a quantum phase in the magnetic phase diagram of the spin-1/2 Heisenberg rhombic lattice antiferromagnet with easy-plane anisotropy.
堀内 皓斗*; 荒木 康史; 若林 勇希*; 家田 淳一; 山ノ内 路彦*; 他7名*
Advanced Materials, p.2416091_1 - 2416091_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Spin Berry curvature characterizes the band topology as the spin counterpart of Berry curvature and is crucial in generating novel spintronics functionalities. By breaking the crystalline inversion symmetry, the spin Berry curvature is expected to be significantly enhanced; this enhancement will increase the intrinsic spin Hall effect in ferromagnetic materials and, thus, the spin-orbit torques (SOTs). However, this intriguing approach is not applied to devices; generally, the spin Hall effect in ferromagnet/heavy-metal bilayer is used for SOT magnetization switching. Here, SOT-induced partial magnetization switching is demonstrated in a single layer of a single-crystalline Weyl oxide SrRuO (SRO) with a small current density of
(SRO) with a small current density of 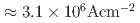 . Detailed analysis of the crystal structure in the seemingly perfect periodic lattice of the SRO film reveals barely discernible oxygen octahedral rotations with angles of
. Detailed analysis of the crystal structure in the seemingly perfect periodic lattice of the SRO film reveals barely discernible oxygen octahedral rotations with angles of 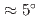 near the interface with a substrate. Tight-binding calculations indicate that a large spin Hall conductivity is induced around small gaps generated at band crossings by the synergy of inherent spin-orbit coupling and band inversion due to the rotations, causing magnetization reversal. The results indicate that a minute atomic displacement in single-crystal films can induce strong intrinsic SOTs that are useful for spin-orbitronics devices.
near the interface with a substrate. Tight-binding calculations indicate that a large spin Hall conductivity is induced around small gaps generated at band crossings by the synergy of inherent spin-orbit coupling and band inversion due to the rotations, causing magnetization reversal. The results indicate that a minute atomic displacement in single-crystal films can induce strong intrinsic SOTs that are useful for spin-orbitronics devices.
山根 結太*; 荒木 康史; 深見 俊輔*
Physical Review B, 111(14), p.144412_1 - 144412_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI) appearing at the interface of a nonmagnetic/noncollinear-antiferromagnetic bilayer. The DMI is an antisymmetric exchange interaction between neighboring magnetic spins, arising in the absence of an inversion center between the spins, the explicit expression of which is dictated by system symmetry. We formulate the interfacial DMI for different crystalline orientations of the noncollinear antiferromagnet with a stacked-kagome lattice structure. From this formulation, we show that, when the kagome planes are perpendicular to the sample film plane, the DMI serves as a uniaxial magnetic anisotropy for the antiferromagnetic order parameter. Our findings reveal an important physical manifestation of a DMI, shedding light on microscopic mechanisms of the magnetic anisotropy in noncollinear antiferromagnets.
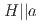 in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
北川 俊作*; 徳永 陽; 酒井 宏典; 神戸 振作; 他11名*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2024/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report the re-measurement of the  -axis spin susceptibility component in an early-stage sample of the spin-triplet superconductor UTe
-axis spin susceptibility component in an early-stage sample of the spin-triplet superconductor UTe with the transition temperature of
with the transition temperature of 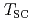 = 1.6 K. Using Knight-shift measurements along the
= 1.6 K. Using Knight-shift measurements along the  axis and at a 10-degree tilt from the
axis and at a 10-degree tilt from the  axis towards the
axis towards the  axis, we accurately determined the
axis, we accurately determined the  -axis component without directly measuring the
-axis component without directly measuring the  -axis Knight shift. The experiment reveals that the previously reported absence of the reduction in Knight shift is attributed to the missing of signal from the superconducting region and to the detection of residual signals from the non-superconducting region instead.
-axis Knight shift. The experiment reveals that the previously reported absence of the reduction in Knight shift is attributed to the missing of signal from the superconducting region and to the detection of residual signals from the non-superconducting region instead.
家田 淳一; 深田 幸正; 福田 竜生
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 66(10), p.521 - 524, 2024/10
, 66(10), p.521 - 524, 2024/10
放射性廃棄物に含まれる放射性同位体(RI)は、見方を変えれば長期間安定したエネルギー源と考えられる。主にアルファ線による熱エネルギーをスピントロニクス技術により電力変換する「スピン熱電発電」、そして主にガンマ線の光電変換を用いた「ガンマ線発電」のための素子開発を進めることで、RIのエネルギーを再資源化する事を目指している。
家田 淳一
日本磁気学会研究会資料, 250, p.1 - 5, 2024/10
近年スピントロニクスの効果を利用することで、らせん磁性金属薄膜がインダクタとして機能することが指摘された。従来のコイルインダクタの原理である電流誘起磁場による電磁誘導ではなく、磁化と電流の相互作用に基づくスピントルク(STT)とスピン起電力(SMF)の連続作用の結果として薄膜素子断面積に反比例する特徴的なインダクタンスがもたらされる。この仕組みは、提案者の永長により「創発インダクタ」(emergent inductor)と命名され、横内らによってらせん磁性体Gd Ru
Ru Al
Al を用いた実験で実証された。本稿では、簡略化したモデルでその基礎的な振る舞いを確認したのち、当該研究におけるスピン軌道相互作用が果たす役割を中心にこれまでの研究動向を概観する。
を用いた実験で実証された。本稿では、簡略化したモデルでその基礎的な振る舞いを確認したのち、当該研究におけるスピン軌道相互作用が果たす役割を中心にこれまでの研究動向を概観する。