Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Haga, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-022, 81 Pages, 2024/01
In the liquid mercury target system for the pulsed spallation neutron source of Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), pressure waves that is generated by the high-energy proton beam injection simultaneously with the spallation reaction, resulting severe cavitation erosion damage on the interior surface of the mercury target vessel. Because the bubble of pressure wave-induced cavitation collapsing near the interior surface of the mercury target vessel with applying the large amplitude of localized impact on the surface. Since the wall thickness of the beam entrance portion of the target vessel is designed to be 3 mm to reduce thermal stress due to the internal heating, the erosion damage has the possibility to cause the vessel fatigue failure and mercury leakage originated from erosion pits during operation. To reduce the erosion damage by cavitation, a technique of gas microbubble injection into the mercury for pressure wave mitigation, and double-walled structure of the beam window of the target vessel has been applied. A specimen was cut from the beam window of the used mercury target vessel in order to investigate the effect of the damage mitigation technologies on the vessel, and to reflect the consideration of operation condition for the next target. We have observed cavitation damage on interior surface of the used mercury target vessel by cutting out the disk shape specimens. Damage morphology and depth of damaged surface were evaluated and correlation between the damage depth and operational condition was examined. The result showed that the erosion damage by cavitation is extremely reduced by injecting gas microbubbles and the damage not formed inside narrow channel of the double-walled structure for relatively high-power operated target vessels.
Naoe, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Takada, Hiroshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 468, p.313 - 320, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:71.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mercury target vessel in the JSNS, which is made of 316L SS, is damaged owing to the pressure wave-induced cavitation resulting from the proton beam bombardment. The cavitation damage decreases the structural integrity of the target vessel and is currently a dominant factor to decide the service life in compared with the radiation damage. Injecting microbubbles into mercury is one of the prospective techniques to mitigate the pressure waves and cavitation damage. In the JSNS, a microbubble generator with a gas circulation system was installed and has been operated since October 2012. The effects of microbubble injection into mercury on pressure wave mitigation were studied using a laser Doppler vibrometer. The result showed that the vibrational velocity of the target vessel is clearly reduced according to the increase of void fraction. An average peak vibrational velocity under 340 kW operation with the void fraction of 0.1% was reduced to 1/4 of that without injecting microbubbles.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 618(1), p.012004_1 - 012004_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:83.99(Physics, Applied)Positronium (Ps; a bound state of positron and electron) has a negative work function in materials and forms a bubble state in liquids. On the way of stable bubble state, the bubble grows and probably oscillates. The usual fast bubble formation has not been observed with the time resolution of the positron annihilation methods that is usually 100-200 pico-seconds. There had been many anomalous phenomena observed in the room temperature ionic liquids (RTIL). Recently it was found that very slow bubble formation caused these anomalous phenomena. And hence the oscillation of the Ps bubble was successfully observed by the change of the annihilation rate of the triplet Ps that is affected by the size of the bubble. The oscillation and the decay of the bubble give the information of the viscoelastic properties at the sub-nano scale. The temperature dependence of the oscillation has been also successfully indicated.
Riemer, B. W.*; Wendel, M. W.*; Felde, D. K.*; Sangrey, R. L.*; Abdou, A.*; West, D. L.*; Shea, T. J.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 450(1-3), p.192 - 203, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:72.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Populations of small helium gas bubbles were introduced into a flowing mercury experiment test loop to evaluate mitigation of beam-pulse induced cavitation damage and pressure waves. The test loop was developed and thoroughly tested at the Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) prior to irradiations at the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center - Weapons Neutron Research Center (LANSCE-WNR) facility. Twelve candidate bubblers were evaluated over a range of mercury flow and gas injection rates by use of a novel optical measurement technique that accurately assessed the generated bubble size distributions. Final selection for irradiation testing included two variations of a swirl bubbler provided by Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) collaborators and one orifice bubbler developed at SNS. Bubble populations of interest consisted of sizes up to 150  m in radius with achieved gas void fractions in the 10
m in radius with achieved gas void fractions in the 10 to 10
to 10 range. The nominal WNR beam pulse used for the experiment created energy deposition in the mercury comparable to SNS pulses operating at 2.5 MW. Nineteen test conditions were completed each with 100 pulses, including variations on mercury flow, gas injection and protons per pulse. The principal measure of cavitation damage mitigation was surface damage assessment on test specimens that were manually replaced for each test condition. Damage assessment was done after radiation decay and decontamination by optical and laser profiling microscopy with damaged area fraction and maximum pit depth being the more valued results. Damage was reduced by flow alone; the best mitigation from bubble injection was between half and a quarter that of flow alone. Other data collected included surface motion tracking by three laser Doppler vibrometers (LDV), loop wall dynamic strain, beam diagnostics for charge and beam profile assessment, embedded hydrophones and pressure sensors, and sound measurement by a suite of conventional and contact microphones.
range. The nominal WNR beam pulse used for the experiment created energy deposition in the mercury comparable to SNS pulses operating at 2.5 MW. Nineteen test conditions were completed each with 100 pulses, including variations on mercury flow, gas injection and protons per pulse. The principal measure of cavitation damage mitigation was surface damage assessment on test specimens that were manually replaced for each test condition. Damage assessment was done after radiation decay and decontamination by optical and laser profiling microscopy with damaged area fraction and maximum pit depth being the more valued results. Damage was reduced by flow alone; the best mitigation from bubble injection was between half and a quarter that of flow alone. Other data collected included surface motion tracking by three laser Doppler vibrometers (LDV), loop wall dynamic strain, beam diagnostics for charge and beam profile assessment, embedded hydrophones and pressure sensors, and sound measurement by a suite of conventional and contact microphones.
Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Tokunaga, Kazutoshi*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; To, Kentaro*; Shikama, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.553 - 556, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Furuno, Shigemi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Hojo, Kiichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 241(1-4), p.559 - 562, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)Silicon carbide (SiC) specimens prepared for the TEM (transmission electron microscope) observation were amorphized with 30keV Ne or 4.5keV He ion irradiation at room temperature and successively annealed at 1273K in the TEM. Ne and He were selected as irradiation ion species to change the concentration of implanted rare gas atoms. The energy and flux of these ion species were selected in order to get similar dpa depth profiles and dpa rates based on TRIM calculation. In this condition, peak ion implantation of He was estimated to be about 5 times as large as that of Ne for the same peak dpa. Crystal nucleation occurred with annealing in the specimen irradiated with He up to 6.3dpa(peak), however, no crystal nucleation was observed in the specimen irradiated with Ne up to 15dpa(peak); Namely, crystal nucleation occurred with less dpa in the case of He irradiation than in the case of Ne irradiation. It was found that the concentration of implanted inert gas atom influences the crystal nucleation behavior.
Hojo, Tomohiro; Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Kiichi; Furuno, Shigemi*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Nitani, Noriko; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Minato, Kazuo; Sakuma, Takaaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 319, p.81 - 86, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Wakai, Eiichi; Igawa, Naoki; Nogami, Shuhei*; Snead, L. L.*; Hasegawa, Akira*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part2), p.1135 - 1140, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tamai, Hiroshi; Yoshino, Ryuji; Tokuda, Shinji; Kurita, Genichi; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Bakhtiari, M.; Khayratdinov, R. R.*; Lukash, V.*; Rosenbluth, M. N.*; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 42(3), p.290 - 294, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:70.47(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ono, K.*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Ohashi, Masahiro*; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi; Yoshida, Naoaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 283-287(Part.1), p.210 - 214, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -D
-D (HD) mixtures by high-resolution ESR spectroscopy
(HD) mixtures by high-resolution ESR spectroscopyKumada, Takayuki; ; Kumagai, Jun*; Aratono, Yasuyuki; Miyazaki, Tetsuro*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 103(45), p.8966 - 8968, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:38.89(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 O
O during H
during H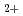 or He
or He ion irradiation
ion irradiationSasajima, Naohiko*; Matsui, Tsuneo*; Furuno, Shigemi*; Hojo, Kiichi;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 148(1-4), p.745 - 751, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:90.60(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Isamu
Radioisotopes, 46(9), p.657 - 663, 1997/09
no abstracts in English
Ono, K.*; Furuno, Shigemi; ; Hojo, Kiichi
Philos. Mag. Lett., 75(2), p.59 - 64, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:81.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ono, K.*; Furuno, Shigemi; Hojo, Kiichi;
Microstructures and Functions of Materials (ICMFM 96), 0, p.273 - 276, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
 O
O ) during helium- and xenon-ion irradiations
) during helium- and xenon-ion irradiationsSasajima, Naohiko*; Matsui, Tsuneo*; Furuno, Shigemi; Hojo, Kiichi; ; Muromura, Tadasumi;
Proc. of Int. Conf. on Microstructures and Functions of Materials (ICMFM 96), 0, p.265 - 268, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Hojo, Kiichi; ; Furuno, Shigemi; ;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 212-215, p.281 - 286, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:78.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
O.E.Mogensen*
J. Phys. IV, 3(C4), p.1 - 15, 1993/09
no abstracts in English
Bamba, Tsunetaka; ; Kozai, Naofumi; Inagaki, Yaohiro*
JAERI-M 93-116, 15 Pages, 1993/06
no abstracts in English
Hamada, Shozo; Hojo, Kiichi; Hishinuma, Akimichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 205, p.219 - 224, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English