Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 00) MOS structures by means of electrical measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
00) MOS structures by means of electrical measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyKobayashi, Takuma*; Suzuki, Asato*; Nakanuma, Takato*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 175, p.108251_1 - 108251_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.58(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) /GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000
/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates
) substratesMizobata, Hidetoshi*; Tomigahara, Kazuki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Letters, 121(6), p.062104_1 - 062104_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Physics, Applied)The interface properties and energy band alignment of SiO /GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000
/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates were investigated by electrical measurements and synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. They were then compared with those of SiO
) substrates were investigated by electrical measurements and synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. They were then compared with those of SiO /GaN MOS structures on Ga-polar GaN(0001). Although the SiO
/GaN MOS structures on Ga-polar GaN(0001). Although the SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) structure was found to be more thermally unstable than that on the GaN(0001) substrate, excellent electrical properties were obtained for the SiO
) structure was found to be more thermally unstable than that on the GaN(0001) substrate, excellent electrical properties were obtained for the SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) structure by optimizing conditions for post-deposition annealing. However, the conduction band offset for SiO
) structure by optimizing conditions for post-deposition annealing. However, the conduction band offset for SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) was smaller than that for SiO
) was smaller than that for SiO /GaN(0001), leading to increased gate leakage current. Therefore, caution is needed when using N-polar GaN(000
/GaN(0001), leading to increased gate leakage current. Therefore, caution is needed when using N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates for MOS device fabrication.
) substrates for MOS device fabrication.
 ambient on threshold voltage stability in 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors
ambient on threshold voltage stability in 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistorsHosoi, Takuji*; Osako, Momoe*; Moges, K.*; Ito, Koji*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 15(6), p.061003_1 - 061003_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.60(Physics, Applied)The combination of NO annealing and subsequent post-nitridation annealing (PNA) in CO ambient for SiO
ambient for SiO /SiC structures has been demonstrated to be effective in obtaining both high channel mobility and superior threshold voltage stability in SiC-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). N atoms on the SiO
/SiC structures has been demonstrated to be effective in obtaining both high channel mobility and superior threshold voltage stability in SiC-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). N atoms on the SiO side of the SiO
side of the SiO /SiC interface incorporated by NO annealing, which are plausible cause of charge trapping sites, could be selectively removed by CO
/SiC interface incorporated by NO annealing, which are plausible cause of charge trapping sites, could be selectively removed by CO -PNA at 1300
-PNA at 1300 C without oxidizing the SiC. CO
C without oxidizing the SiC. CO -PNA was also effective in compensating oxygen vacancies in SiO
-PNA was also effective in compensating oxygen vacancies in SiO , resulting high immunity against both positive and negative bias-temperature stresses.
, resulting high immunity against both positive and negative bias-temperature stresses.
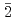 0) MOS devices
0) MOS devicesNakanuma, Takato*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 15(4), p.041002_1 - 041002_4, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:62.63(Physics, Applied)The leakage current and flat-band voltage (VFB) instability of NO-nitrided SiC (11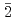 0) (a-face) MOS devices were systematically investigated. Although NO nitridation is effective in improving the interface properties, we found that it reduces the onset field of Fowler-Nordheim (F-N) current by about 1 MVcm
0) (a-face) MOS devices were systematically investigated. Although NO nitridation is effective in improving the interface properties, we found that it reduces the onset field of Fowler-Nordheim (F-N) current by about 1 MVcm , leading to pronounced leakage current. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the nitridation reduces the conduction band offset at the SiO
, leading to pronounced leakage current. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the nitridation reduces the conduction band offset at the SiO /SiC interface, corroborating the above finding. Furthermore, systematical positive and negative bias stress tests clearly indicated the VFB instability of nitrided a-face MOS devices against electron and hole injection.
/SiC interface, corroborating the above finding. Furthermore, systematical positive and negative bias stress tests clearly indicated the VFB instability of nitrided a-face MOS devices against electron and hole injection.
 O vapor on GaN surfaces
O vapor on GaN surfacesSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Sang, L.*; Harada, Yoshitomo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.189 - 198, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)GaN is an attracting material for power-electronic devices. Understanding the oxidation at GaN surface is important for improving metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices. In this study, the oxidation at GaN surfaces depending on the GaN crystal planes (+c, -c, and m-plane) was investigated by real time XPS and DFT-MD simulation. We found that H O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H
O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al
O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al Ga
Ga N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al
N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al O
O layer deposited by ALD using H
layer deposited by ALD using H O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H
O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H O and O
O and O should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al
should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al Ga
Ga N atomi layer deposition.
N atomi layer deposition.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Shih, H.-A.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA07_1 - 06KA07_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:25.92(Physics, Applied)Thermal oxidation of AlGaN surface and its impact on the electrical properties of AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were investigated by means of synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-PES), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and C-V measurements. SR-PES analysis revealed that the AlGaN surface is oxidized even at low temperature of 400 C, in contrast to no oxide formation on GaN surface. However, since no noticeable change in the surface morphology was observed at temperatures up to 800
C, in contrast to no oxide formation on GaN surface. However, since no noticeable change in the surface morphology was observed at temperatures up to 800 C, it can be concluded that an ultrathin oxide overlayer is formed on the AlGaN surface. On the other hand, for the oxidation treatments above 850
C, it can be concluded that an ultrathin oxide overlayer is formed on the AlGaN surface. On the other hand, for the oxidation treatments above 850 C, the formation of small oxide grains was observed over the entire area of the AlGaN surface, and the growth of oxide grains significantly degraded the surface morphology. Therefore, the AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were fabricated on the AlGaN surface oxidized at moderate temperatures up to 800
C, the formation of small oxide grains was observed over the entire area of the AlGaN surface, and the growth of oxide grains significantly degraded the surface morphology. Therefore, the AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were fabricated on the AlGaN surface oxidized at moderate temperatures up to 800 C. While we have confirmed that relatively good interface properties are obtained for direct AlON deposition without oxidation treatment, it was found that the oxidation treatment at 400
C. While we have confirmed that relatively good interface properties are obtained for direct AlON deposition without oxidation treatment, it was found that the oxidation treatment at 400 C leads to further improvement of interface properties and reduction of C-V hysteresis.
C leads to further improvement of interface properties and reduction of C-V hysteresis.
 /AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistors
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistorsWatanabe, Kenta*; Terashima, Daiki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA03_1 - 06KA03_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:46.31(Physics, Applied)The advantage of SiO /AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO , AlON and Al
, AlON and Al O
O single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
Nozaki, Mikito*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Shih, H.-A.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA02_1 - 06KA02_7, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:67.71(Physics, Applied)We fabricated AlON dielectric films by repeating thin AlN deposition and in situ O oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
 /GaN stacks for high-quality GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices with improved gate dielectric reliability
/GaN stacks for high-quality GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices with improved gate dielectric reliabilityYamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Hisashi*; Takahashi, Tokio*; Shimizu, Mitsuaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 11(1), p.015701_1 - 015701_4, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:85.02(Physics, Applied)A simple and feasible method for fabricating high-quality and highly reliable GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices was developed on the basis of systematic physical and electrical characterizations. Chemical vapor deposition of SiO films directly onto GaN substrates forming Ga-oxide interlayers was used to fabricate SiO
films directly onto GaN substrates forming Ga-oxide interlayers was used to fabricate SiO /GaO
/GaO /GaN stacked structures. Although well-behaved hysteresis-free GaN-MOS capacitors with extremely low interface state density below 10
/GaN stacked structures. Although well-behaved hysteresis-free GaN-MOS capacitors with extremely low interface state density below 10 cm
cm eV
eV were obtained by post-deposition annealing, Ga diffusion into overlying SiO
were obtained by post-deposition annealing, Ga diffusion into overlying SiO layers severely degraded the insulating property and dielectric breakdown characteristics of the MOS devices. However, this problem was found to be solved by employing rapid thermal processing, leading to superior performance of the GaN-MOS devices in terms of interface quality, insulating property and gate dielectric reliability.
layers severely degraded the insulating property and dielectric breakdown characteristics of the MOS devices. However, this problem was found to be solved by employing rapid thermal processing, leading to superior performance of the GaN-MOS devices in terms of interface quality, insulating property and gate dielectric reliability.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 111(4), p.042102_1 - 042102_5, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:57.82(Physics, Applied)AlGaN/GaN HFET (hetero-junction field-effect transitor) has gained much attention as next-generation high frequency and high power devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al O
O and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 121(3), p.035303_1 - 035303_9, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:92.64(Physics, Applied)Initial oxidation of GaN(0001) epilayers and subsequent growth of thermal oxides in dry oxygen ambient were investigated by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, spectroscopic ellipsometry, atomic force microscopy and X-ray diffraction measurements. It was found that, whereas initial oxide formation tends to saturate at temperatures below 800 C, selective growth of small oxide grains proceeds at dislocations in the epilayers, followed by noticeable grain growth leading to rough surface morphology at higher oxidation temperatures. This indicates that oxide growth and its morphology are crucially dependent on the defect density in the GaN epilayers. Structural characterizations also revealed that polycrystalline
C, selective growth of small oxide grains proceeds at dislocations in the epilayers, followed by noticeable grain growth leading to rough surface morphology at higher oxidation temperatures. This indicates that oxide growth and its morphology are crucially dependent on the defect density in the GaN epilayers. Structural characterizations also revealed that polycrystalline  - and
- and  -phase Ga
-phase Ga O
O grains in an epitaxial relation with the GaN substrate are formed from the initial stage of the oxide growth. On the basis of these experimental findings, we also developed a comprehensive model for GaN oxidation mediated by nitrogen removal and mass transport.
grains in an epitaxial relation with the GaN substrate are formed from the initial stage of the oxide growth. On the basis of these experimental findings, we also developed a comprehensive model for GaN oxidation mediated by nitrogen removal and mass transport.
Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sumiya, Masatomo*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sumita, Masato*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was employed to clarify the oxidized states on the polar and m-plane GaN surfaces under exposure of various oxidation gases of H O, O
O, O , N
, N O, and NO. It was found that H
O, and NO. It was found that H O vapor has the higher reactivity. The oxygen was hardly adsorbed on the surface by irradiating N
O vapor has the higher reactivity. The oxygen was hardly adsorbed on the surface by irradiating N O and NO gases. Apparently, two oxidation states for O
O and NO gases. Apparently, two oxidation states for O and H
and H O irradiation were detected on +c GaN surface. Physisorption of O
O irradiation were detected on +c GaN surface. Physisorption of O molecule was dominate. The dissociation and adsorption of H
molecule was dominate. The dissociation and adsorption of H O molecules co-existed on the +c surface. The chemisorption on the m-plane of GaN was dominant, and a stable Ga-O bond was formed on the surface. These chemical oxygen states were simulated by density functional molecular dynamics calculation using a theoretical model including both electronic spins on the surfaces and the polarity of GaN.
O molecules co-existed on the +c surface. The chemisorption on the m-plane of GaN was dominant, and a stable Ga-O bond was formed on the surface. These chemical oxygen states were simulated by density functional molecular dynamics calculation using a theoretical model including both electronic spins on the surfaces and the polarity of GaN.
Nozaki, Mikito*; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Interface reactions between Ti-based multilayer electrodes on n-type GaN epilayers were investigated by means of synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS). High-resolution SR-XPS analysis revealed formation of metallic Ga and TiN mixed interlayers at Ti/GaN interface even at room temperature by depositing Al capping layer. By comparing XPS spectra from the stacked Al/Ti electrode and single Ti electrode, an essential role of Al overlayers serving as oxygen diffusion barrier and oxygen scavenging element to produce reactive pure Ti underlayers on GaN was demonstrated. Moreover, growth of metallic interlayers consisting of Ga and Ti atoms during vacuum annealing was clearly identified from in situ SR-XPS analysis.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Initial oxide growth on GaN epitaxial films by thermal oxidation in dry O ambient was investigated by means of synchrotron radiation X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM). High-resolution SR-PES analysis showed that the intensity ratio of O 1s/N 1s core-level peaks for the sample oxidized at 700 degrees is slightly higher than that for the sample after HCl wet-cleaning, indicating that GaN surface is oxidized. However, the O 1s/N 1s intensity ratio was nearly identical with increasing temperature up to 800 degrees and AFM observation revealed the preferential formation of small grains at the dark pits. On the other hand, the O 1s/N 1s intensity ratio drastically increased with further increasing temperature higher than 800 degrees, indicating significantly enhanced oxide formation on GaN surface.
ambient was investigated by means of synchrotron radiation X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM). High-resolution SR-PES analysis showed that the intensity ratio of O 1s/N 1s core-level peaks for the sample oxidized at 700 degrees is slightly higher than that for the sample after HCl wet-cleaning, indicating that GaN surface is oxidized. However, the O 1s/N 1s intensity ratio was nearly identical with increasing temperature up to 800 degrees and AFM observation revealed the preferential formation of small grains at the dark pits. On the other hand, the O 1s/N 1s intensity ratio drastically increased with further increasing temperature higher than 800 degrees, indicating significantly enhanced oxide formation on GaN surface.
Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
Structural changes at Ti/GaN or Al/Ti/GaN interfaces were studied by using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that the Al capping layer plays an important role for oxygen diffusion barriers. The Al layer also stimulates interfacial reactions via introducing oxygen into Ti layers. We found that this reaction dramatically changes Ti/GaN interface structures.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To achieve high performance of GaN MOS devices, high quality interfaces between insulator and GaN are essentially needed. The precise control of native surface oxide and/or interfacial oxide layer is important. In this study, oxide formation process in thermally oxidized GaN surface is analyzed by using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy.
 /AlGaN interface property deposited by PECVD
/AlGaN interface property deposited by PECVDTerashima, Daiki*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Shih, H.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
Impact of input power and substrate temperature of SiO deposition by plasma-enhanced CVD on SiO
deposition by plasma-enhanced CVD on SiO /AlGaN interface was investigated by means of electrical characterization of MOS capacitors. Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy revealed that Ga oxide component on AlGaN surface increases with increasing input power of PECVD. MOS capacitors with SiO
/AlGaN interface was investigated by means of electrical characterization of MOS capacitors. Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy revealed that Ga oxide component on AlGaN surface increases with increasing input power of PECVD. MOS capacitors with SiO gate insulator deposited at low input power shows relatively better SiO
gate insulator deposited at low input power shows relatively better SiO /AlGaN interface quality, despite degraded interface quality for the sample with SiO
/AlGaN interface quality, despite degraded interface quality for the sample with SiO deposited at high input power. These results suggest that AlGaN surface oxidation during oxide deposition should be controlled to obtain good interface property.
deposited at high input power. These results suggest that AlGaN surface oxidation during oxide deposition should be controlled to obtain good interface property.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Shih, H.*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Initial oxidation process of AlGaN surface during thermal oxidation was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. Thermal oxidation of AlGaN/GaN/Si(111) substrates was carried out for 30 min in the temperature range from 200 to 1000 degrees in O ambient. The obtained Ga 2p spectra exhibited peak shift toward the higher binding energy with increasing oxidation temperature, suggesting the growth of Ga oxides on AlGaN surface. The peak deconvolution of Ga 2p spectra into Ga-O and Ga-N components revealed that the formation of Ga oxides was formed on AlGaN surface at above 400 degrees while GaN surface was stable below 600 degrees. These results indicate that AlGaN surface is easy to be oxidized compared to GaN surface.
ambient. The obtained Ga 2p spectra exhibited peak shift toward the higher binding energy with increasing oxidation temperature, suggesting the growth of Ga oxides on AlGaN surface. The peak deconvolution of Ga 2p spectra into Ga-O and Ga-N components revealed that the formation of Ga oxides was formed on AlGaN surface at above 400 degrees while GaN surface was stable below 600 degrees. These results indicate that AlGaN surface is easy to be oxidized compared to GaN surface.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
AlGaN/GaN HFET has gained much attention as next-generation high frequency and high power devices. Among various insulating materials, Al O
O is one of the potential candidates. However, large amount of electrical defects at MOS interfaces severely degrade both drive current and threshold voltage stability. Positive Vth shift due to electron trapping in Al
is one of the potential candidates. However, large amount of electrical defects at MOS interfaces severely degrade both drive current and threshold voltage stability. Positive Vth shift due to electron trapping in Al O
O layer by applying positive gate bias is often observed for Al
layer by applying positive gate bias is often observed for Al O
O /AlGaN/GaN MOS structures. We have recently reported that N incorporation into Al
/AlGaN/GaN MOS structures. We have recently reported that N incorporation into Al O
O significantly reduces electron traps in Al
significantly reduces electron traps in Al O
O layer for Si and SiC MOS devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al
layer for Si and SiC MOS devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al O
O and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.