Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
森 道康
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(11), p.114705_1 - 114705_7, 2020/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:9.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The nuclear magnetic relaxation time  in a ferrimagnetic insulators is calculated within the mean-field approximation for the magnetic exchange interactions and the Raman process involving the hyperfine interaction. We find that the value of 1/
in a ferrimagnetic insulators is calculated within the mean-field approximation for the magnetic exchange interactions and the Raman process involving the hyperfine interaction. We find that the value of 1/ on one type of site increases rapidly near the compensation temperature
on one type of site increases rapidly near the compensation temperature 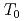 , whereas that on the other type of site does not increase up to Curie temperature
, whereas that on the other type of site does not increase up to Curie temperature  . This is due to the fact that the soft-magnon bandwidth becomes comparable to
. This is due to the fact that the soft-magnon bandwidth becomes comparable to 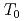 . An increase in 1/
. An increase in 1/ below
below  is found also in another type ferrimagnet, which shows a hump structure in the temperature dependence of magnetization instead of compensation. Also in that case, we find the rapid increase in 1/
is found also in another type ferrimagnet, which shows a hump structure in the temperature dependence of magnetization instead of compensation. Also in that case, we find the rapid increase in 1/ below
below  , even though the magnetization does not show compensation. The coexistence of soft and hard magnons leads to these remarkable properties of ferrimagnets.
, even though the magnetization does not show compensation. The coexistence of soft and hard magnons leads to these remarkable properties of ferrimagnets.
今井 正樹; 中堂 博之; 松尾 衛; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review B, 102(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_5, 2020/07
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:33.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The angular momentum compensation temperature 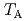 of ferrimagnets has attracted much attention because of high-speed magnetic dynamics near
of ferrimagnets has attracted much attention because of high-speed magnetic dynamics near 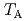 . We show that NMR can be used to investigate domain wall dynamics near
. We show that NMR can be used to investigate domain wall dynamics near 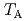 in ferrimagnets. We performed
in ferrimagnets. We performed  Fe-NMR measurements on the ferrimagnet Ho
Fe-NMR measurements on the ferrimagnet Ho Fe
Fe O
O with
with 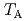 = 245 K. In a multi-domain state, the NMR signal is enhanced by domain wall motion. We found that the NMR signal enhancement shows a maximum at
= 245 K. In a multi-domain state, the NMR signal is enhanced by domain wall motion. We found that the NMR signal enhancement shows a maximum at 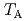 in the multi-domain state. The NMR signal enhancement occurs due to increasing domain-wall mobility toward
in the multi-domain state. The NMR signal enhancement occurs due to increasing domain-wall mobility toward 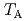 . We develop the NMR signal enhancement model involves domain-wall mobility. Our study shows that NMR in multi-domain state is a powerful tool to determine
. We develop the NMR signal enhancement model involves domain-wall mobility. Our study shows that NMR in multi-domain state is a powerful tool to determine 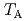 , even from a powder sample and it expands the possibility of searching for angular momentum-compensated materials.
, even from a powder sample and it expands the possibility of searching for angular momentum-compensated materials.
 Dy
Dy Fe
Fe O
O detected by the Barnett effect
detected by the Barnett effect今井 正樹; 中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛; 大沼 悠一*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 114(16), p.162402_1 - 162402_4, 2019/04
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:69.77(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate that the angular momentum compensation temperature 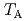 , at which the net angular momentum in the sample disappears, can be controlled in Ho
, at which the net angular momentum in the sample disappears, can be controlled in Ho Fe
Fe O
O by partially substituting Dy for Ho. The
by partially substituting Dy for Ho. The 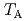 can be detected using the Barnett effect, by which mechanical rotation magnetizes an object due to spin-rotation coupling. We found that
can be detected using the Barnett effect, by which mechanical rotation magnetizes an object due to spin-rotation coupling. We found that 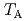 increases with the Dy content and clarified that the
increases with the Dy content and clarified that the 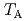 of Ho
of Ho Dy
Dy Fe
Fe O
O coincides with room temperature. The Barnett effect enables us to explore materials applicable to magnetic devices utilizing the angular momentum compensation only by rotating the powder sample at room temperature.
coincides with room temperature. The Barnett effect enables us to explore materials applicable to magnetic devices utilizing the angular momentum compensation only by rotating the powder sample at room temperature.
今井 正樹; 緒方 裕大*; 中堂 博之; 小野 正雄; 針井 一哉; 松尾 衛*; 大沼 悠一*; 前川 禎通; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Letters, 113(5), p.052402_1 - 052402_3, 2018/07
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:65.79(Physics, Applied)We report direct observation of gyromagnetic reversal, which is the sign change of gyromagnetic ratio in a ferrimagnet Ho Fe
Fe O
O , by using the Barnett effect measurement technique at low temperatures. The Barnett effect is a phenomenon in which magnetization is induced by mechanical rotation through the coupling between rotation and total angular momentum
, by using the Barnett effect measurement technique at low temperatures. The Barnett effect is a phenomenon in which magnetization is induced by mechanical rotation through the coupling between rotation and total angular momentum  of electrons. The magnetization of Ho
of electrons. The magnetization of Ho Fe
Fe O
O induced by mechanical rotation disappears at 135 K and 240 K. The temperatures correspond to the magnetization compensation temperature
induced by mechanical rotation disappears at 135 K and 240 K. The temperatures correspond to the magnetization compensation temperature 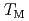 and the angular momentum compensation temperature
and the angular momentum compensation temperature 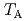 , respectively. Between
, respectively. Between 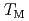 and
and 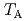 , the magnetization flips over to be parallel against the angular momentum due to the sign change of gyromagnetic ratio. This study provides an unprecedented technique to explore the gyromagnetic properties.
, the magnetization flips over to be parallel against the angular momentum due to the sign change of gyromagnetic ratio. This study provides an unprecedented technique to explore the gyromagnetic properties.
 =1/2 Heisenberg antiferromagnet in two dimensions
=1/2 Heisenberg antiferromagnet in two dimensions中野 博生*; 坂井 徹
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(3), p.030305_1 - 030305_4, 2015/03
フェライトの基本的な磁性機構であるフェリ磁性の不安定性を明らかにするため、フラストレートした二次元 =1/2ハイゼンベルグ反強磁性体の数値対角化による研究を行った。その結果、弱いフラストレーションで自発磁化を持つフェリ磁性の基底状態が現れることがわかった。
=1/2ハイゼンベルグ反強磁性体の数値対角化による研究を行った。その結果、弱いフラストレーションで自発磁化を持つフェリ磁性の基底状態が現れることがわかった。
中野 博生*; 坂井 徹
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(3), p.030305_1 - 030305_4, 2015/03
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:41.17(Physics, Applied)フェライトの磁性の基礎を与えるフェリ磁性の不安定性を明らかにするため、フラストレーションのあるS=1/2二次元ハイゼンベルグ反強磁性体について数値対角化により研究した。その結果、弱いフラストレーションにおいてフェリ磁性状態が自発磁化をもたらすことがわかった。
 O
O
吉井 賢資; 池田 直*; 中村 彰夫
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 378-380, p.585 - 586, 2006/05
被引用回数:39 パーセンタイル:79.70(Physics, Condensed Matter)電荷及び磁気フラストレーションを有する酸化物TmFe O
O の磁性と誘電性を調べた。磁化測定からは240K付近に鉄スピンのフェリ磁性が観測された。また、100K以下程度で、磁気構造が変化していることが示唆された。交流誘電率測定からは、3000程度の比誘電率、及び特徴的な誘電分散が見られた。これらの結果は、すでに報告されているRFe
の磁性と誘電性を調べた。磁化測定からは240K付近に鉄スピンのフェリ磁性が観測された。また、100K以下程度で、磁気構造が変化していることが示唆された。交流誘電率測定からは、3000程度の比誘電率、及び特徴的な誘電分散が見られた。これらの結果は、すでに報告されているRFe O
O (R:希土類)と同様の物性であることがわかった。
(R:希土類)と同様の物性であることがわかった。
安居院 あかね; 水牧 仁一朗*; 松下 智裕*; 河村 直己*; 中谷 健
Physica Scripta, T115, p.611 - 613, 2005/00
希土類ガーネットは典型的なFerri磁性体である。その一つである、Dy Fe
Fe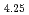 O
O 系の磁化方向の起源について明らかにするために、原研ビームラインBL23SUにて円磁気2色性測定実験を行った。Feの一部をInもしくはGaで置換した試料の測定を行い、FeのTdサイト,Onサイトそれぞれのスピンの状態が磁化方向に大きく寄与していることがわかったので報告する。
系の磁化方向の起源について明らかにするために、原研ビームラインBL23SUにて円磁気2色性測定実験を行った。Feの一部をInもしくはGaで置換した試料の測定を行い、FeのTdサイト,Onサイトそれぞれのスピンの状態が磁化方向に大きく寄与していることがわかったので報告する。
 X
X (X=Ge,Si)
(X=Ge,Si)S.Purwanto*; 大橋 正義*; 小野寺 秀也*; 森井 幸生; 舩橋 達; 山内 宏*; 山口 泰男*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.318 - 320, 1995/00
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.08(Physics, Condensed Matter)高分解能中性子粉末回折法により、TbMn Ge
Ge は4K
は4K T
T Tt=95.3Kでフェリ磁性をTt
Tt=95.3Kでフェリ磁性をTt T
T 414Kで反強磁性を示すことが判明した。またTbMn
414Kで反強磁性を示すことが判明した。またTbMn Si
Si では、54.3K
では、54.3K T
T 64.5Kではこれより低温の相、高温の相、長周期構造構の共存状態にあることが判明した。この二つの物質の磁気秩序温度が高いことを考慮すると、Tb-Tb間の交換相互作用が大きすぎて、DyMn
64.5Kではこれより低温の相、高温の相、長周期構造構の共存状態にあることが判明した。この二つの物質の磁気秩序温度が高いことを考慮すると、Tb-Tb間の交換相互作用が大きすぎて、DyMn Geで観測されたTbモーメントがフラストレーション状態にある交換相互作用競合状態を作り出すことができないでいると示唆される。Tbの一部をYで置換した系についての実験から磁気秩序温度はより低温へと減少しており、交換相互作用競合状態が実現している可能性がある。
Geで観測されたTbモーメントがフラストレーション状態にある交換相互作用競合状態を作り出すことができないでいると示唆される。Tbの一部をYで置換した系についての実験から磁気秩序温度はより低温へと減少しており、交換相互作用競合状態が実現している可能性がある。
 MUO
MUO (M=Fe,Co,Ni)
(M=Fe,Co,Ni)日夏 幸雄
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 215, p.161 - 167, 1994/00
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:59.43(Chemistry, Physical)秩序化ペロブスカイト構造を持つウラン-遷移金属複合酸化物Ba MUO
MUO (M=Fe,Co,Ni)を合成し、磁化率と常磁性共鳴(EPR)吸収スペクトルの測定を通して、結晶中のUとMの電子状態を検討した。Ba
(M=Fe,Co,Ni)を合成し、磁化率と常磁性共鳴(EPR)吸収スペクトルの測定を通して、結晶中のUとMの電子状態を検討した。Ba FeUO
FeUO は120Kでフェリ磁性転移することを見い出した。EPRスペクトルを室温で測定し、g値は2.00だった。化合物中での鉄は+3価の酸化状態にあり、ウランは+5価の酸化状態にあることを明らかにした。Ba
は120Kでフェリ磁性転移することを見い出した。EPRスペクトルを室温で測定し、g値は2.00だった。化合物中での鉄は+3価の酸化状態にあり、ウランは+5価の酸化状態にあることを明らかにした。Ba CoUO
CoUO とBa
とBa NiUO
NiUO は、9K,25Kで強磁性転移することを見い出した。Ba
は、9K,25Kで強磁性転移することを見い出した。Ba NiUO
NiUO では5Kで、10000G以上の磁場で、磁化の完全な飽和を見い出した。EPRスペクトルを室温で測定し、g値は2.17だった。これらの化合物中では、コバルトとニッケルは+2価、ウランは+6価の酸化状態にあることを明らかにした。
では5Kで、10000G以上の磁場で、磁化の完全な飽和を見い出した。EPRスペクトルを室温で測定し、g値は2.17だった。これらの化合物中では、コバルトとニッケルは+2価、ウランは+6価の酸化状態にあることを明らかにした。
 MUO
MUO (M=Sc, Y, Gd, Yb, Mn)
(M=Sc, Y, Gd, Yb, Mn)日夏 幸雄
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 105, p.100 - 106, 1993/00
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:47.22(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)秩序化したペロブスカイト構造を持つウラン複合酸化物Ba MUO
MUO (M=Sc,Y,Gd,Yb,Mn)を合成し、磁化率と常磁性共鳴吸収スペクトルを測定した。Ba
(M=Sc,Y,Gd,Yb,Mn)を合成し、磁化率と常磁性共鳴吸収スペクトルを測定した。Ba YUO
YUO ,Ba
,Ba ScUO
ScUO 中のU
中のU の有効磁気モーメントは異常に小さかった。Ba
の有効磁気モーメントは異常に小さかった。Ba GdUO
GdUO ,Ba
,Ba YbUO
YbUO のモーメントは7.74,4.69
のモーメントは7.74,4.69
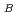 でGd
でGd ,Yb
,Yb の理論値に近かった。Ba
の理論値に近かった。Ba GdUO
GdUO の常磁性共鳴吸収スペクトルが測定でき、g値は1.92だった。Ba
の常磁性共鳴吸収スペクトルが測定でき、g値は1.92だった。Ba MnUO
MnUO では、約50K以下でフェリ磁性が見られた。有効磁気モーメントは5.52
では、約50K以下でフェリ磁性が見られた。有効磁気モーメントは5.52
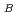 、g値は2.00で、化合物中のマンガンイオンは高スピン状態にある2価であることがわかった。
、g値は2.00で、化合物中のマンガンイオンは高スピン状態にある2価であることがわかった。
今井 正樹; 中堂 博之; 松尾 衛*; 前川 禎通*; 齊藤 英治
no journal, ,
Ferrimagnets contains multiple types of magnetic ions; their magnetic moments align in opposite direction. In some ferrimagnets, the net angular momentum becomes zero at the angular momentum compensation temperature 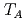 . We demonstrated the observation of
. We demonstrated the observation of 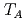 by using the Barnett effect and NMR.
by using the Barnett effect and NMR.