Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.448 - 458, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steel
Cs in HCl solutions on the corrosion potential of Type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(11), p.284 - 288, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (114), p.33 - 38, 2022/10
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Suzuki, Shunichi*
Isotope News, (782), p.40 - 44, 2022/08
The stagnant water in the reactor building at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is exposed to the radiation from fuel debris and radioactive species. This water contains much amounts of impurities from the seawater which was injected in the emergency cooling. The impurities will affect the radiolysis and corrosive conditions in the water under irradiation. So, the water radiolysis data, corrosion data of steels under irradiations, and the evaluated potential impacts of corrosion in the decommissioning process of 1F are arranged as the database for corrosion under irradiation. This paper introduces the outline of this database.
Toigawa, Tomohiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsumura, Tatsuro
UTNL-R-0502 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/04
This report summarizes the results obtained in FY2020 at the Electron Linac Facility of the University of Tokyo. The radiolysis process of 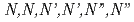 -hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA), which is expected to be used as an extractant in a separation process for minor actinides, diluted in dodecane was investigated by pulse radiolysis experiments. The radical cation and the triplet-excited state of HONTA were observed in the nanosecond time region. The transition from the radical cation to the triplet excited state was slowed down by adding electron scavengers, and further, the reactivity of the triplet excited state was also suppressed.
-hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA), which is expected to be used as an extractant in a separation process for minor actinides, diluted in dodecane was investigated by pulse radiolysis experiments. The radical cation and the triplet-excited state of HONTA were observed in the nanosecond time region. The transition from the radical cation to the triplet excited state was slowed down by adding electron scavengers, and further, the reactivity of the triplet excited state was also suppressed.
Hata, Kuniki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.468 - 473, 2021/12
In order to estimate corrosive environment in the contaminated water at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, effects of oxidants, such as H O
O , which were generated from water radiolysis, should be taken into account due to the irradiation field in the reactor building. The process of water radiolysis and the amounts of these oxidants can change depending on the conditions of water and types of radiation. After the accident, a variety of factors, which can affect water radiolysis, such as seawater constituents, surface of oxides, and
, which were generated from water radiolysis, should be taken into account due to the irradiation field in the reactor building. The process of water radiolysis and the amounts of these oxidants can change depending on the conditions of water and types of radiation. After the accident, a variety of factors, which can affect water radiolysis, such as seawater constituents, surface of oxides, and  -radionuclides, had been discussed. In this paper, these effects on radiolysis are reviewed for the better understanding of the corrosive environment in the contaminated water.
-radionuclides, had been discussed. In this paper, these effects on radiolysis are reviewed for the better understanding of the corrosive environment in the contaminated water.
Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.457 - 461, 2021/12
The Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F) have been exposed to a corrosive environment containing seawater components under irradiation condition. In such conditions, the hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H
) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H O
O concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N
concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O
gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O and H
and H O
O concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O
concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O and H
and H O
O as well as that of carbon steel in the O
as well as that of carbon steel in the O and H
and H O
O coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-001, 123 Pages, 2021/06
In the implement of the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), there are many problems to be solved. Specially, the mitigation of the aging degradation by the corrosion of the structural materials is important to implement the decommissioning safely and continuously. However, there are limited data for the environmental factors of corrosion in 1F, and the condition of 1F is continuously changing. So, the literature data for the water radiolysis and the corrosion under irradiation are listed as the database of corrosion under irradiation in this report. And the new obtained radiolysis and corrosion data, which have not been reported in the literature and will be required in the decommissioning of 1F, are reported.
Omori, Atsushi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; et al.
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(4), p.107 - 111, 2020/04
To evaluate the effect of oxidants, which are formed by radiolysis of water under gamma ray irradiation, on the corrosion of a carbon steel in humid environment, ozone was introduced as a model oxidant in to humidity-controlled air at 50 C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(1), p.2 - 8, 2019/01
It is important to control the cooling water of light water reactors (boiling water reactor and pressurized water reactor) to suitable quality in order to reduce corrosion of structural materials and generation of radioactive corrosion products. For that purpose, monitoring of water quality using electrochemical measurement method is necessary. In this article, the application of ECP measurement to BWR is mainly focused, I describe the water quality of light water reactors and the necessity of electrochemical measurement.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 20th Nuclear Plant Chemistry International Conference (NPC 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2016/10
ECP is the exclusive index to evaluate corrosion condition directly at the points of interest in the mixing of neutron and  -ray environment. ECP can be calculated through the combination of water radiolysis and ECP model. A water radiolysis model have been applied to experiments performed in in-pile loops in the experimental reactors and applicability was confirmed. An ECP model based on the Butler-Volmer equation was also prepared. ECP of stainless steel was measured under well controlled water chemistry condition in in-pile loop in the Halden reactor, and the model was applied to evaluate ECP measured in the Halden reactor. The measured data were well explained by the water radiolysis calculation and ECP model. Accumulation of in-pile ECP data are expected for further validation of the models.
-ray environment. ECP can be calculated through the combination of water radiolysis and ECP model. A water radiolysis model have been applied to experiments performed in in-pile loops in the experimental reactors and applicability was confirmed. An ECP model based on the Butler-Volmer equation was also prepared. ECP of stainless steel was measured under well controlled water chemistry condition in in-pile loop in the Halden reactor, and the model was applied to evaluate ECP measured in the Halden reactor. The measured data were well explained by the water radiolysis calculation and ECP model. Accumulation of in-pile ECP data are expected for further validation of the models.
 -ray irradiated condition
-ray irradiated conditionYamamoto, Masahiro; Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of European Corrosion Congress 2015 (EUROCORR 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2015/09
In Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, decommissioning procedures are continuing and it will take more than 30 years. As some structures are made of carbon steel, degradation by corrosion is large problem for structural reliability. To clarify an irradiation effect for corrosion of carbon steel, corrosion test was con-ducted in  Co
Co  -ray irradiated condition. Corrosion test results showed that corrosion rates of
-ray irradiated condition. Corrosion test results showed that corrosion rates of  -ray irradiated condition increased with
-ray irradiated condition increased with  -ray dose rates. The oxidant concentrations were also increased with
-ray dose rates. The oxidant concentrations were also increased with  -ray dose rate. From these results, a new estimation method for corrosion rate of carbon steel in water with
-ray dose rate. From these results, a new estimation method for corrosion rate of carbon steel in water with  -ray irradiated condition using radiolysis calculation is introduced and discussed.
-ray irradiated condition using radiolysis calculation is introduced and discussed.
Hata, Kuniki; Urushibara, Ayumi*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Lin, M.*; Muroya, Yusa*; Shikazono, Naoya; Yokoya, Akinari; Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Journal of Radiation Research, 56(1), p.59 - 66, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.68(Biology)Hirade, Tetsuya
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 76(2), p.84 - 89, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.81(Chemistry, Physical)There are many connections between radiation and positronium chemistry. The Spur Reaction model proposed by Mogensen needs much radiation chemistry knowledge. On the other hand, the Spur Reaction model could give new ideas to radiation chemists. Positronium formation reaction is very fast and hence there is a good relationship between reactions observed by a pulse radiolysis measurement and positronium formation, which was shown by Dupratre et al. Enhancement of positronium formation at low temperatures was successfully explained by the reaction of trapped electrons and positrons. The trapped electrons have been studied well by radiation chemists. That knowledge was needed to propose a new idea to explain the positronium formation at low temperatures. And now, probably it is becoming possible to use the positronum formation reaction to study the trapped electrons. Positron methods will be able to be used for the radiation chemistry research.
Yoshida, Yoichi*; Yang, J.*; Saeki, Akinori*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Namba, Hideki; Kojima, Takuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.143 - 144, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Iijima, Hokuto; Ueda, Toru*; Muroya, Yusa*; Sakumi, Akira*; Kumagai, Noritaka*; Tomizawa, Hiromitsu*
Proceedings of 1st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 29th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.628 - 630, 2004/08
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Yoichi*; Yang, J.*; Seki, Shuhei*; Saeki, Akinori*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji; Namba, Hideki
JAERI-Review 2003-033, TIARA Annual Report 2002, p.145 - 146, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Kozawa, Takahiro*; Tagawa, Seiichi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 106(39), p.9036 - 9041, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.49(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
; Namba, Hideki; Aoki, Yasushi; Watanabe, Ritsuko*; ; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Tech 96-046, 65 Pages, 1996/11
no abstracts in English
PNC TJ1602 96-002, 129 Pages, 1996/02
Since a chloride ion is assumed to be one of the predominant solutes dissolved in groundwater, a study of the radiolysis of chloride ion and oxychlorides in aqueous solutions has been carried out in order to obtain the reliable and predictable data for the understanding the radiation induced reactions taking place in groundwater, relevant to the geological radioactive waste repository. The rate constants of the reactions between water decomposition products and different oxychlorides were determined by means of pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis methods. By using the techniques of photometry and ion-chromatography, the products formed by irradiation were analyzed and the overall reactions were summarized. After the comparison between the simulation and the experimental results, the redox reactions of the oxychloride compounds in aqueous solution were summarized and future work to be done has been pointed out.