Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O
Mori, Michiyasu; Tomasello, B.*; Ziman, T.*
Physical Review B, 111(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_12, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zhu, M.*; Romerio, V.*; Steiger, N.*; Nabi, S. D.*; Murai, Naoki; Kawamura, Seiko; Povarov, K. Y.*; Skourski, Y.*; Sibille, R.*; Keller, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 133(18), p.186704_1 - 186704_6, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:91.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Akiba, Hiroshi*; Omasa, Yoshinori*; Kofu, Maiko*; Zhang, M.*; Sato, Shun*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091010_1 - 091010_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) S
S under pressure
under pressureKosaka, Yusuke*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 34(3), p.121 - 126, 2024/09
Transition-metal intercalated dichalcogenides have attracted attention due to the observation of chiral helimagnetism (CHM) and chiral soliton lattice in CrNb S
S . It forms a chiral monoaxial crystal structure with a space group P6
. It forms a chiral monoaxial crystal structure with a space group P6 22. To examine the pressure effect on the CHM period of CrNb
22. To examine the pressure effect on the CHM period of CrNb S
S , we performed small-angle neutron scattering experiments with a piston-cylinder pressure cell up to 1.2 GPa. We observed a decrease in the magnetic transition temperature with increasing pressure. Moreover, the CHM period decreased with increasing pressure. Compared to the decrease of the lattice constant, that of the CHM period is much larger. This indicates that applying pressure weakens the amplitude of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction.
, we performed small-angle neutron scattering experiments with a piston-cylinder pressure cell up to 1.2 GPa. We observed a decrease in the magnetic transition temperature with increasing pressure. Moreover, the CHM period decreased with increasing pressure. Compared to the decrease of the lattice constant, that of the CHM period is much larger. This indicates that applying pressure weakens the amplitude of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction.
Matsuura, Masato*; Zhang, J.*; Kamimura, Yasushi*; Kofu, Maiko; Edagawa, Keiichi*
Physical Review Letters, 133(13), p.136101_1 - 136101_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary) RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Iida, Kazuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kaneko, Koji; Chen, Y.-S.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Hsu, P.-T.*; Lee, M. K.*; Hall, A. E.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.033303_1 - 033303_7, 2024/09
The magnetic excitation extends at least from 0.3 to 140 meV. The integrated inelastic scattering intensity leads to a localized magnetic moment of about 5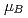 per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61
per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61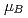 at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn
at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn RhSi.
RhSi.
Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:94.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Gu, Y. Q.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Liu, F.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Zhao, J.*
Physical Review Letters, 132(24), p.246702_1 - 246702_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary) BWO
BWO
Nagl, J.*; Flavi n, D.*; Hayashida, S.*; Povarov, K. Y.*; Yan, M.*; Murai, Naoki; Kawamura, Seiko; Simutis, F.*; Hicken, T. J.*; Luetkens, H.*; et al.
n, D.*; Hayashida, S.*; Povarov, K. Y.*; Yan, M.*; Murai, Naoki; Kawamura, Seiko; Simutis, F.*; Hicken, T. J.*; Luetkens, H.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023267_1 - 023267_18, 2024/06
Harada, Yoshinari*; Yamaguchi, Hibiki*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 130(1), p.758 - 762, 2024/06
The data assimilation was performed using deterministic sampling to selectively reduce uncertainties caused by the thermal neutron scattering in light water. The prompt neutron decay constant  of the water tank system was used for the data assimilation. The deterministic sampling method was applied to uncertainty quantification and data assimilation for light water thermal neutron scattering law data obtained by the CAB model. The uncertainty quantification results using the deterministic sampling method were comparable to those using the random sampling method.
of the water tank system was used for the data assimilation. The deterministic sampling method was applied to uncertainty quantification and data assimilation for light water thermal neutron scattering law data obtained by the CAB model. The uncertainty quantification results using the deterministic sampling method were comparable to those using the random sampling method.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 294, p.07001_1 - 07001_6, 2024/04
Graphite is a candidate of moderator in innovative nuclear reactors such as molten salt reactors. Scattering of thermal neutrons by the moderator material has a significant impact on the reactor core design. To contribute to the development of innovative nuclear reactors, an evaluation method of thermal neutron scattering law for reactor grade graphite was studied. The inelastic scattering component due to lattice vibration was evaluated based on the phonon density of states computed with first-principles lattice dynamics simulations. The simulations were performed for ideal crystalline graphite. The coherent elastic scattering component due to crystal structure was evaluated based on neutron transmission and scattering experiments recently performed in the J-PARC/MLF facility. In comparison with the neutron transmission experiments, it was found that the quantification of small-angle neutron scattering due to structures larger than crystal, such as pores in graphite, is important. Based on the above methods, thermal neutron scattering law data for reactor-grade graphite at room temperature were evaluated.
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.71(Physics, Applied)Shinohara, Yuya*; Iwashita, Takuya*; Nakanishi, Masahiro*; Osti, N. C.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nirei, Masami; Dmowski, W.*; Egami, Takeshi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 128(6), p.1544 - 1549, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:44.97(Chemistry, Physical)Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ishii, Rieko*; Hirai, Daigoro*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013006_1 - 013006_9, 2024/01
Inamura, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Testing 2023-002, 80 Pages, 2023/12
"Utsusemi" is a suite of software used to process data obtained from measurements of neutron scattering experiments at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF), J-PARC. To directly obtain the physical quantities which scientists want to get from the data produced by instruments at MLF, many processes are required, such as creating histogram format data, easily visualizing and converting units and correcting intensity adapting the instrument conditions. "Utsusemi" software consists of many software components, many functions for data processing, graphical interface software for executing Utsusemi functions, data visualization applications, and so on. "Utsusemi" has already played an important role in data processing and has been widely employed in MLF beamlines. This document describes how to install the "Utsusemi" software on each operating system to be of help of instrument staff and users who want to process data by themselves. Installation of "Utsusemi" on Windows and macOS requires only general knowledge of working with PC applications according to this document.
Tada, Kenichi
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The number of energy grids of the thermal neutron scattering law data has a large impact on the data size of a cross section file of continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation codes. The optimization of the number of energy grids is an effective way to reduce the data size. This study developed the linearization method of the thermal neutron scattering cross section to optimize the number of energy grids and the linearization function was implemented in the nuclear data processing code FRENDY. The linearization process which is used in the resonance reconstruction and the Doppler broadening was adopted. The criticality benchmarks which use ZrH as the moderator were calculated to estimate the impact of the difference of the energy grids on neutronics calculations. The calculation results indicate that the linearization of the thermal neutron scattering cross section improves the prediction accuracy of neutronics calculations.
Kawaguchi, Maho*; Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has been working on an experimental approach for evaluating the criticality of fuel debris produced by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNP) accident since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As part of the approach, JAEA has modified the STAtic experiment Critical facilitY (STACY) for critical experiments to evaluate characteriscs of pseudo-fuel debris. As the preliminary analyses, we verified critical characteristics with major nuclear data libraries for the proposed core configuration patterns. The three-dimensional continuous-energy Monte Carlo neutron and photon transport code, SERPENT-V2.2.0 was used with the latest JENDL, JENDL-5. As a result, larger multiplication factors of JENDL-5 across the modified STACY core configuration patterns were evaluated in comparison to the other libraries. And,  H scattering and
H scattering and  U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S(
U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S( ,
,  ) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
 RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Iida, Kazuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Hall, A. E.*; Chen, Y.-S.*; Lee, M. K.*; Balakrishnan, G.*; Chang, L.-J.*
Communications Physics (Internet), 6, p.248_1 - 248_6, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:38.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We show that the local spin correlation order has a spiral structure by neutron scattering measurement of a Mn RhSi single crystal. The possible origins of the magnetic cluster formation are discussed in terms of the Lifshitz invariant and the Griffiths phase, and compared with the room-temperature skyrmion phase of Co
RhSi single crystal. The possible origins of the magnetic cluster formation are discussed in terms of the Lifshitz invariant and the Griffiths phase, and compared with the room-temperature skyrmion phase of Co Zn
Zn Mn
Mn and non-Fermi liquid behavior of
and non-Fermi liquid behavior of  -Mn.
-Mn.
 solution in the gigapascal pressure range
solution in the gigapascal pressure rangeYamaguchi, Toshio*; Fukuyama, Nami*; Yoshida, Koji*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Liquids (Internet), 3(3), p.288 - 302, 2023/09
We report the structure of an aqueous 2 mol/kg MgCl solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg
solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl
forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl
due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl
solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)