Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.32 - 37, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
 Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*;  elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (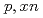 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Nakano, Keita*; Sugihara, Kenta*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.132 - 136, 2023/01
J-PARC accelerator facility is the only accelerator facility in Japan that can provide proton beams in the energy range of 400 MeV or higher. In the J-PARC accelerator facility, it is difficult to install users' experimental equipment inside the proton beam duct in order to maintain stable user operation. In addition, due to the characteristics of the synchrotron accelerator, it is not possible to supply a low-intensity beam enough to confirm the detector. In addition, it is important to improve the intranuclear cascade model (INCL) for high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS), etc. In order to improve the INCL, DDX of the forward-most emitted particles is important, but new data should be obtained since there are few experimental data available. In order to promote space utilization and to improve the accuracy of the INCL, energy spectra of scattered protons at the Al beam window placed at the inlet of the 3NBT dump were measured. In the experiment, plastic scintillators were used with 400 MeV proton beam. The results show that the spectra have sharp peaks due to elastic scattering. The calculation of the PHITS code using INCL reproduced the sharp peak due to elastic scattering well, although it overestimated the contribution of quasi-elastic scattering in the experimental data. In conclusion, it is clear that the present method can be used to utilize protons in several GeV regions for space exploration.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 409, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011046_1 - 011046_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinsuke
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (120), p.19 - 25, 2018/06
Toward development of accurate deuteron nuclear data, we have been developing a computational code dedicated for the deuteron-induced reaction, called DEURACS. The author presented the developmental status and the future outlook of DEURACS in the joint session of nuclear data subcommittee and sigma special advisory committee, and contributed the outline of the presentation to Nuclear Data News. From our preceding work, it has become possible to predict the  reactions on light nuclei and the
reactions on light nuclei and the 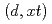 reactions. These reactions are important in relation to evaluation of neutron sources and tritium production, respectively. In the future, we plan to improve theoretical models implemented in DEURACS for accurate prediction of nuclide production cross-section on medium-heavy nuclei.
reactions. These reactions are important in relation to evaluation of neutron sources and tritium production, respectively. In the future, we plan to improve theoretical models implemented in DEURACS for accurate prediction of nuclide production cross-section on medium-heavy nuclei.
 reactions on
reactions on  Li at 25, 40, and 102 MeV
Li at 25, 40, and 102 MeVSadamatsu, Hiroki*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, p.135 - 140, 2018/01
In recent years, the demand for intense neutron sources has been increasing in various applications such as nuclear transmutation of high-level radioactive waste and medical radioisotopes production. Deuteron accelerator-based neutron sources are promised as one of the candidates. Therefore, we have developed a code system dedicated for the deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In the present work, we focus on deuteron-induced neutron production from  Li target. The calculated double differential cross sections for
Li target. The calculated double differential cross sections for  reactions at incident energies of 25, 40, and 102 MeV are compared with the measured ones, and the applicability of DEURACS is discussed.
reactions at incident energies of 25, 40, and 102 MeV are compared with the measured ones, and the applicability of DEURACS is discussed.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 122, p.04004_1 - 04004_9, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.63(Physics, Nuclear)In recent years, accelerator neutron sources using deuteron-induced reactions on  Li,
Li,  Be,
Be,  C, etc., are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires deuteron nuclear data in a broad incident energy range. We have developed a computational code system dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation in combination with some theoretical models. The code system has been applied to analyses of double-differential
C, etc., are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires deuteron nuclear data in a broad incident energy range. We have developed a computational code system dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation in combination with some theoretical models. The code system has been applied to analyses of double-differential 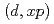 cross sections for
cross sections for  C,
C,  Al, and
Al, and  Ni at incident energies up to 100 MeV. On the other hand, there is few experimental double-differential
Ni at incident energies up to 100 MeV. On the other hand, there is few experimental double-differential  cross sections. Therefore, double-differential thick target neutron yields for light nuclei such as
cross sections. Therefore, double-differential thick target neutron yields for light nuclei such as  Be and
Be and  C are calculated and compared with experimental data. The presentation will show the validation result of the present modelling for nucleon emissions from deuteron-induced reactions through comparison with available experimental data.
C are calculated and compared with experimental data. The presentation will show the validation result of the present modelling for nucleon emissions from deuteron-induced reactions through comparison with available experimental data.
Kondo, Keitaro; Takagi, Satoshi*; Murata, Isao*; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Akito*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1527 - 1533, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:67.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fusion reactor development, double-differential charged-particle emission cross sections(DDXc) are necessary to estimate nuclear heating and material damages of candidate materials irradiated with neutrons. Especially in light nuclei such as Be, Li, and C, nuclear reactions are complicated and difficult to estimate energy spectra of emitted particles based only on theoretical calculations Therefore development of a new technique for precise measurements of DDXc is quite important. Recently we successfully developed a new spectrometer for measurement of DDXc using a pencil-beam DT neutron source of FNS in JAERI. In the present study we carried out measurements of DDXc of  Be,
Be,  C,
C,  F, and
F, and  Al using the spectrometer. The present technique was valid from the result of measurement for the
Al using the spectrometer. The present technique was valid from the result of measurement for the  Al(n,x
Al(n,x ) reactions. Slight differences appeared between measured data and evaluation or previous experimental values for
) reactions. Slight differences appeared between measured data and evaluation or previous experimental values for  Be(n,x
Be(n,x ) reactions at backward scattering angle and in lower energy region.
) reactions at backward scattering angle and in lower energy region.
Chiba, Satoshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Shibata, Keiichi; Yu, B.*; Kosako, Kazuaki*; Yamamuro, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(2), p.187 - 194, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Li at 10 to 20 MeV
Li at 10 to 20 MeVChiba, Satoshi; ; ; ; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Shibata, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Osamu; A.J.Koning*; G.M.Hale*; M.B.Chadwick*; et al.
Physical Review C, 58(4), p.2205 - 2216, 1998/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.47(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Akito*; Shibata, Keiichi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 71(11), p.1113 - 1122, 1995/11
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Chiba, Satoshi; Numajiri, M.*; Nakamura, Takashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(9), p.827 - 833, 1995/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:92.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yoshizawa, Nobuaki*; ; Takada, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(7), p.601 - 607, 1995/07
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:90.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takada, Hiroshi; ; Yoshizawa, Nobuaki*; Nakahara, Yasuaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 31(1), p.80 - 82, 1994/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takada, Hiroshi; Nakahara, Yasuaki; ; ; Yoshizawa, Nobuaki*
Proc. of NEA/NSC Specialists Meeting on Intermediate Energy Nuclear Data:Models and Codes, 0, p.121 - 136, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; ; ; ; ; ; ; et al.
JAERI-M 91-009, 56 Pages, 1991/02
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Akito*; Sasaki, Yasuhiro*; Maekawa, Fujio*; Sugimoto, Hisashi*
JAERI-M 89-214, 58 Pages, 1989/12
no abstracts in English
 U and
U and  Th
ThBaba, Mamoru*; ; ; ;
JAERI-M 89-143, 55 Pages, 1989/10
no abstracts in English
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Iwamoto, Hiroki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English