Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 U and
U and  Th
ThFilipescu, D.*; Gheorghe, I.*; Goriely, S.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Suzaki, Fumi; Hirose, Kentaro; 10 of others*
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_23, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:79.28(Physics, Nuclear)Nakayama, Shinsuke; Furutachi, Naoya; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
NEA/NSC/R(2020)4 (Internet), p.345 - 349, 2022/10
Long-lived fission products (LLFPs) generated in nuclear reactors are strongly desired to be converted to stable or short-lived nuclides. Recently, it has been considered to transmute LLFPs by spallation reactions with high energy particles, and some experimental studies revealed that spallation reaction cross-sections induced by deuteron are larger than proton-induced ones. These results suggest the possibility that nuclear transmutation of LLFPs using deuteron beams is more efficient than one using proton beams. On the other hand, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. DEURACS has been originally developed to contribute to the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. In the present study, we apply DEURACS to calculation of deuteron-induced spallation reactions on LLFPs. Through comparison with measured data, the applicability of DEURACS will be discussed.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Few-Body Systems, 63(1), p.4_1 - 4_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.64(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for not only science and engineering fields but also medical applications. For the engineering design of such facilities, accurate and comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions are indispensable. However, it is difficult to meet the requirement by employing experimental data alone. Thus, theoretical model calculations play a key role in completing the necessary nuclear data by interpolation and extrapolation of experimental data. Under the above situations, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In the present work, calculations using DEURACS are compared with available experimental data and validation of the present modelling in DEURACS is discussed. Moreover, the importance of consideration of the breakup processes for accurate prediction of deuteron-induced reactions is also presented.
Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.30 - 41, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:66.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nuclide production cross sections for proton-induced reactions on Mn and Co at incident energies of 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV were measured by the activation method at the J-PARC. In total, 143 production cross sections of reaction products were obtained. Among them, the cross sections of  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) S and
S and  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011026_1 - 011026_6, 2021/03
The charge-exchange multi-turn injection by using a carbon stripper foil is adopted in high-intensity proton ring accelerators worldwide. It is a beneficial method to compress the pulsed proton beam with high intensity but there are serious issues for high intensity. First issue is a short lifetime of the foil by deformation or breaking itself. Another issue is high radiation dose corresponding to the scattered particles on the foil. Therefore, a non-destructive stripping injection method is required for higher intensity proton beam. We newly propose a non-destructive method of H stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
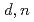 ) reaction at 12, 20, and 30 MeV
) reaction at 12, 20, and 30 MeVPatwary, M. K. A*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Aoki, Katsumi*; Yoshinami, Kosuke*; Yamaguchi, Masaya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(2), p.252 - 258, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)While designing deuteron accelerator neutron sources for radioisotopes production, nuclear data for light elements such as Li, Be, and C have been systematically measured in the deuteron energy range from a few MeV to around 50 MeV. Currently, the experimental data available on double-differential thick-target neutron yields (DDTTNYs) is insufficient, especially for deuteron energies between 18 and 33 MeV. In this study, we measured the DDTTNYs of (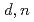 ) reactions on
) reactions on  C target for incident deuteron energies of 12, 20, and 30 MeV using the multiple-foils activation method to improve nuclear data insufficiency. We applied the GRAVEL code for the unfolding process to derive the DDTTNYs. The results were compared with the calculation by DEURACS. The present data were also used to confirm the systematics of the differential neutron yields at 0
C target for incident deuteron energies of 12, 20, and 30 MeV using the multiple-foils activation method to improve nuclear data insufficiency. We applied the GRAVEL code for the unfolding process to derive the DDTTNYs. The results were compared with the calculation by DEURACS. The present data were also used to confirm the systematics of the differential neutron yields at 0 and total neutron yield per incident deuteron in the wide range of deuteron energy.
and total neutron yield per incident deuteron in the wide range of deuteron energy.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.03014_1 - 03014_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for various applications such as irradiation test for fusion reactor materials and production of radioisotopes for medical use. In addition, transmutation system using deuteron-induced spallation reactions has been recently proposed for LLFPs. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data are indispensable in the design study of such facilities. Under the above situations, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEURACS. In the present work, calculations using DEURACS are compared with available experimental data up to 200 MeV such as DDXs for emission of neutron or light charged particles. We also analyze isotopic production cross sections of residual nuclei. Validation of the present modelling in DEURACS is discussed through comparison with the experimental data.
Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Abe, Shinichiro; Tampo, Motonobu*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 67(7), p.1566 - 1572, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.91(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Muon-induced single event upset (SEU) is predicted to increase with technology scaling. The angle of incidence of terrestrial muons is not always perpendicular to the chip surface. Consequently, the impact of the angle of incidence of muons on SEUs should be evaluated. This study conducts negative muon irradiation tests on bulk SRAM and FDSOI SRAM at two angles of incidence: 0 degree (vertical) and 45 degree (tilted). The tilted incidence drifts the muon energy peak to a higher energy. Moreover, the SEU characteristics (i.e., such as the voltage dependences of the SEU cross sections and multiple cells upset patterns) between the vertical and tilted incidences are similar.
Takei, Hayanori; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Yano, Yoshiharu*; Ogawa, Yujiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(9), p.996 - 1008, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experiences with existing high-power proton accelerators indicate that frequent beam trips are inevitable. One of the reasons for such frequent beam trips is the accidental interruption to protect accelerators against fatal failures. Generally, the failure frequency for the general machinery can be evaluated based on a reliability database for its components. On the other hand, the beam-trip frequency for the accidental interruption was not evaluated based on the reliability database because it has not yet been established. A principal reason for the lack of this reliability database is the inconsistency of data collection and analysis methods among laboratories. For example, there are at least three methods to estimate Mean Time Between accidental Interruptions (MTBI) for klystron systems. In the present study, the MTBI of the klystron systems of an electron/positron injector linac at the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) was evaluated based on the reliability engineering method, in order to build the reliability database using the unified data collection and analysis method. As the result, the mean values of the MTBI by the traditional three methods were evaluated as 30.9, 32.0, and 50.4 hours. On the other hand, that by the reliability engineering method was evaluated as 57.3 hours, i.e., more than 1.14 times of the traditional results. Although these results are obviously different from traditional results, it appears that the present estimation based on the reliability engineering method is suitable for the MTBI of accelerator components as typified by the klystron system.
Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1055 - 1059, 2018/08
The J-PARC Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) is designed as an 1-MW high power accelerator. It has been operated since 2007, and its injection energy and beam current are upgraded in 2014. Its operation is very smooth and provides the high intensity beam to the Material and Life science experimental facility (MLF) and the Main Ring (MR). The beam is injected with multi-turn mode. It is possible because the negative hydrogen ion beam from the Linac, H , and the circulating proton beam H
, and the circulating proton beam H are different state. The H
are different state. The H is converted to H
is converted to H at the injection point, where a charge stripper foil is set. A small fraction of the injected beam, which is not fully stripped, are transferred to the injection beam dump through H0 dump line to prevent un-necessary activation. Since the limit of beam dump is only 4 kW, which is about 3% of designed injection beam power 133 kW, the beam has to be stopped immediately in case of stripper foil break up incident.
at the injection point, where a charge stripper foil is set. A small fraction of the injected beam, which is not fully stripped, are transferred to the injection beam dump through H0 dump line to prevent un-necessary activation. Since the limit of beam dump is only 4 kW, which is about 3% of designed injection beam power 133 kW, the beam has to be stopped immediately in case of stripper foil break up incident.
Hotchi, Hideaki; J-PARC RCS Beam Commissioning Group
Proceedings of 61st ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams (HB 2018) (Internet), p.20 - 25, 2018/07
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, p.91 - 96, 2018/01
Toward evaluation of deuteron nuclear data, we have been developing a code system dedicated for the deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In the present work, we make an improvement in DEURACS and apply it to composite-particle emission from deuteron-induced reactions. The calculation using DEURACS reproduces the experimental double-differential cross sections of 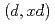 ,
, 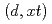 ,
, 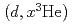 , and
, and 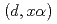 reactions on
reactions on  Al and
Al and  Ni at incident energy of 80 MeV quantitatively well. From the results of the analyses, it is shown that the treatment of inelastic scattering and pick-up reaction processes is important in the calculation of deuteron-induced composite-particle emission.
Ni at incident energy of 80 MeV quantitatively well. From the results of the analyses, it is shown that the treatment of inelastic scattering and pick-up reaction processes is important in the calculation of deuteron-induced composite-particle emission.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamane, Isao*; Saha, P. K.; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*; Kato, Shinichi
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.684 - 688, 2017/12
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC 3GeV RCS, we newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme. However, it is necessary that laser power is two order higher than latest laser one. To realize this big issue, we develop the laser storage ring, which can provide laser pulse of high repetition rate by recycling one. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe the concept of the laser storage ring with high repetition rate and report the current status.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.877 - 881, 2017/12
It is key issue to reduce the level of the radio-activation of the devices in high power proton accelerator, to achieve MW class high power beam operation. The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) adopted a beam collimation system which aims to localize the beam loss at the collimators and to reduce the level of residual doses at the other devices. However, relatively high residual doses are detected in not only the beam collimator area but also a vicinity of the stripper foil. The results of previous work, measurements of the detailed residual dose distribution and simulations of the radio-activation by the PHITS, indicate that the high level residual dose around the stripper foil is caused by secondary particles due to nuclear reaction at the foil. In order to suppress the secondary particles from foil, we try hard to reduce the number of foil hitting particles during the beam injection period. As a result, the level of the radio-activation around the foil can be decreased. At the same time, new beam loss monitor to detect the secondary particles from the foil is developed. In this presentation, we report the secondary particles detections and estimations of number of the foil hitting particles. In addition, we discuss the reduction of the radio-activation.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takeda, Osamu*; Miki, Nobuharu*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.374 - 378, 2017/12
The 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) aims to deliver 1-MW proton beam to the neutron target and Main Ring synchrotron. Present beam power of the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500-kW and the higher radiation doses were concentrated in the injection area. These activations were caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce the worker dose near the injection point, we have studied a new design of the injection scheme to secure enough space for radiation shielding and bellows. In the new system, two of four injection pulse bump magnets are replaced and we are able to ensure the additional space around the injection foil chamber. So far, new injection system seems not impossible. However, preliminary study result indicated that temperature of the duct and shielding metals would be slightly higher. The eddy current due to the shift bump magnet field generates heat. Thus we have to study details of above effect.
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Araki, Shohei*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03006_1 - 03006_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)The design of  neutron sources requires comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions. Therefore, we have launched a research project on deuteron nuclear data, which is composed of measurements, theoretical model code development, cross section evaluation, and application to production of radioisotopes for medical use. Our goal is to develop a state-of-art deuteron nuclear data library up to 200 MeV necessary for the design of accelerator neutron sources with deuteron beam. The present status is reported in the presentation.
neutron sources requires comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions. Therefore, we have launched a research project on deuteron nuclear data, which is composed of measurements, theoretical model code development, cross section evaluation, and application to production of radioisotopes for medical use. Our goal is to develop a state-of-art deuteron nuclear data library up to 200 MeV necessary for the design of accelerator neutron sources with deuteron beam. The present status is reported in the presentation.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12025_1 - 12025_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:91.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerator have been proposed for various applications. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data library over wide ranges of target mass number and incident energy are indispensable for the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. Thus, we have developed an integrated code system dedicated for analysis and prediction of deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS). In the present work, the analysis of  reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to
reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to 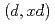 reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the
reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the  and
and 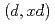 reactions well.
reactions well.
Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Miura, Akihiko
Proceedings of 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '17) (Internet), p.277 - 280, 2017/06
Multi-turn painting injection scheme is important for high intensity proton accelerators. At the J-PARC RCS, a transverse painting scheme was adapted by adding vertical painting magnets to the beam transport line before the injection point, with horizontal painting being performed by a set of dedicated pulse magnets in the ring. To establish a transverse painting condition, it is usual to base on the pulse magnet current pattern. However, it is more desirable to directly measure the beam orbit time variation for evaluation. A linac beam was chopped to match the ring RF bucket. We thought that it would be difficult to measure the position for each pulse; however, the average position could be extracted by introducing a particular device. For the beam injected into the ring, because the linac RF frequency component was diminished due to debunching quickly, one could determine its position in the beginning of the injection period. However, due to rebunching effect the position determination becomes difficult. This problem needs to be resolved.
 reactions on
reactions on  Be and
Be and  C
CNakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
RCNP Annual Report 2016 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2017/05
We are conducting a theoretical research on deuteron-induced reaction together with Kyushu University and Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. The research outcomes achieved in fiscal year 2016 are summarized as a part of the annual report of RCNP. In recent years, accelerator neutron sources using  reactions on light nuclei (Li, Be, C, etc.) are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires accurate prediction of
reactions on light nuclei (Li, Be, C, etc.) are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires accurate prediction of  reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. Therefore, we have developed a physics-based computational code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In fiscal year 2016, we calculated double-differential neutron yields from deuteron bombardment on thick
reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. Therefore, we have developed a physics-based computational code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In fiscal year 2016, we calculated double-differential neutron yields from deuteron bombardment on thick  Be and
Be and  C targets, and the calculation reproduced the experimental data quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. From the results, it has been found that DEURACS can accurately predict
C targets, and the calculation reproduced the experimental data quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. From the results, it has been found that DEURACS can accurately predict  reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. In addition, component-by-component analysis has revealed that the nonelastic breakup reactions make the most dominant contribution to neutron production.
reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. In addition, component-by-component analysis has revealed that the nonelastic breakup reactions make the most dominant contribution to neutron production.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yamane, Isao*; Kato, Shinichi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.983 - 986, 2016/11
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC 3GeV RCS, we newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme However, it is necessary that laser power is two order higher than latest laser one. To realize this big issue, we develop the laser storage ring, which can provide laser pulse of high repetition rate by recycling one. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe the concept of the laser storage ring with high repetition rate.