Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Iwahara, Daisuke*
Isotope News, (798), p.26 - 27, 2025/04
no abstracts in English
Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Yamada, Masako*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Bourgeois, D.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Langmuir, 40(46), p.24257 - 24271, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Microscopic structures in liquid-liquid extraction, such as structuration between extractants or extracted complexes in bulk organic phases and at interfaces, can influence macroscopic phenomena, such as the distribution behavior of solutes, including extraction efficiency, selectivity, and phase separation of the organic phase. In this study, we correlated the macroscopic behavior of the extraction of Zr(IV) ions from nitric acid solutions with microscopic structural information in order to understand at the molecular level the key factors contributing to the higher metal ion extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system comprising fluorous phosphate (TFP) in perfluorohexane as compared to the analogous organic extraction system comprising organic phosphate (THP) in n-hexane. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure, neutron reflectometry, and small-angle neutron scattering revealed the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion, the accumulation of extractant molecules at the interface, and the structuration of extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase, respectively. In the fluorous extraction system, extractant aggregates with were formed after contact with nitric acid. In contrast, in the organic extraction system, only extractant dimers were formed. We speculate that differences in the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion and the structuration of the extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase contribute to the high Zr(IV) extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system. In particular, the size of the aggregates hardly changed with increasing Zr(IV) concentration in the fluorous phase, which may be closely related to the absence of phase splitting in the fluorous extraction system.
Kumada, Takayuki
Shiki, 63, p.2 - 5, 2024/07
We introduce recent studies of spin-contrast-variation neutron scatterings, which utilizes the property that scattering power of neutron against proton remarkably depends on their relative spin directions, to reveal nanostructure of composite materials.
Kumada, Takayuki; Iwahara, Daisuke*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Daisuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Torikai, Naoya*; Amino, Naoya*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(21), p.8797 - 8802, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)We elucidated the entanglement of polybutadiene and silane coupling agent (SCA) molecules bound to Si substrates using spin-contrast-variation (SCV) neutron reflectivity (NR). In an annealed integral blend film of polybutadiene and SCA, a SCA layer generated on the Si substrate was composed of 70 vol. percent SCA molecules extended perpendicularly from the silicon substrate and entangled with 30 vol. percent polybutadiene molecules. By contrast, in an SCA-precoated polybutadiene film, the SCA-precoated layer is composed of densely packed SCA molecules forming crystal-like structure, and thus did not become entangled with the postcoated polybutadiene molecules. This poor entanglement resulted in poor binding between polybutadiene and Si substrate.
Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Bauduin, P.*; Girard, L.*; Diat, O.*
Langmuir, 39(31), p.10965 - 10977, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:71.78(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Liu, Y.*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Shundo, Atsuomi*; Kawaguchi, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Keiji*; Aoki, Hiroyuki
Langmuir, 39(29), p.10154 - 10162, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:74.82(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kumada, Takayuki; Miura, Daisuke*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oku, Takayuki; Torikai, Naoya*; Niizeki, Tomotake*
Hamon, 32(4), p.165 - 168, 2022/11
We demonstrated the advantage of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectometry on the structure analysis of buried interface between resin and porous silica layers. The interface structure was not reproduced by the normal Gaussian model, but by the asymmetric interface model where crosslinked polymer chains neither permeate the pore nor follow the surface roughness of the silica layer.
Kumada, Takayuki; Miura, Daisuke*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Oku, Takayuki; Torikai, Naoya*; Niizeki, Tomotake*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 55(5), p.1147 - 1153, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.55(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectivity obtains multiple reflectivity curves from a single sample and a single beam source. We used the strong point of the technique to reveal that, although methylated-perhydropolysilazane-derived silica layer has a higher porosity near the interface with acrylic urethane resin, the resin did not permeate the pore network.
Tamura, Kazuhisa; Akutsu-Suyama, Kazuhiro*; Cagnes, M.*; Darwish, T. A.*
ECS Advances (Internet), 1(2), p.020503_1 - 020503_5, 2022/06
The ionic liquid/Si electrode interface was investigated using neutron reflectivity. We precisely elucidated the structure of the electrical double layer formed at 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide ([BMIM]TFSA)/Si(100) electrode interface with the orientation of the [BMIM]TFSA molecule using a partially deuterated [BMIM]TFSA. The results revealed that [BMIM]TFSA molecules form a layered structure. Cation and anion molecules are alternatingly stacked and molecules in the first three layers are horizontally oriented to the electrode surface at E = -1.2 V, i.e., on the negatively charged electrode surface. It was also revealed that the imidazole ring in [BMIM] cation is parallel to the electrode surface.
Akutsu-Suyama, Kazuhiro*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Narita, Hirokazu*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 12(3), p.1215_1 - 1215_10, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.96(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Aoki, Hiroyuki; Liu, Y.*; Yamashita, Takashi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.22711_1 - 22711_9, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.13(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Takeda, Masayasu
Hamon, 31(1), p.18 - 19, 2021/02
no abstracts in English
Kumada, Takayuki; Miura, Daisuke*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
Hamon, 30(4), p.207 - 211, 2020/11
We developed a technique of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectivity (SCV-NR) for structural analyses of multilayer films. The SCV-NR curves of the polystyrene monolayer film were precisely reproduced using a common set of structural parameters and neutron scattering length density at each proton polarization. This result ensures that SCV-NR curves are not deformed by inhomogeneous PH due to the spin-diffusion mechanism. The number of structural parameters of the lamellar microphase-separated poly(styrene-block-isoprene) thin film is too large to determine with a single unpolarized reflectivity curve only. However, these parameters converged through the global analysis of the SCV-NR curves. In this manner, SCV-NR determines the structure of multilayer films while excluding the incorrect structural model that accidentally accounts for a single unpolarized reflectivity curve only.
Kumada, Takayuki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 96(4), p.176 - 180, 2020/04
We have developed time-resolved reflectivity measurement system using femtosecond laser pulses, which can measure structure of thin films generated by non-thermal effect.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 52(5), p.1054 - 1060, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We developed a technique of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectometry (SCV-NR). Polarized-neutron reflectivity curves of film samples vary as a function of their proton-polarization P. The P-dependent reflectivity curves of a polystyrene film was precisely reproduced using a common set of structure parameters and the P-dependent neutron scattering length. The reflectivity curve of poly (styrene-block-isoprene) (PSPI) presented a shoulder attributed to holes with the depth corresponding to one period of periodic lamellae on the free surface only at a specific P. In this way, structural information about specific surfaces or interfaces can be obtained by controlling the P.
Kumada, Takayuki; 7 of others*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 22, p.011015_1 - 011015_5, 2018/11
Amemiya, Kenta*; Sakamaki, Masako*; Mizusawa, Mari*; Takeda, Masayasu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034004_1 - 034004_6, 2015/09
Yamada, Norifumi*; Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai
Hamon, 24(4), p.288 - 295, 2014/11
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Hino, Masahiro*
Hamon, 24(3), p.200 - 205, 2014/08
no abstracts in English
Ishino, Masahiko; Yoda, Osamu*; Koike, Masato
JAERI-Research 2005-019, 13 Pages, 2005/09
We have developed soft X-ray multilayer mirrors for use around the wavelength region of 4 nm including the K-absorption edge of carbon (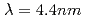 ). We have chosen Co
). We have chosen Co O
O and Cr as the final candidate materials for absorber layers, and SiO
and Cr as the final candidate materials for absorber layers, and SiO and Sc for the spacer materials as the result of theoretical invitation. Co
and Sc for the spacer materials as the result of theoretical invitation. Co O
O /SiO
/SiO , Co
, Co O
O /Sc and Cr/Sc multilayer mirrors have been fabricated by means of an ion beam sputtering (IBS) method. As the result of structure evaluations with X-ray diffraction measurement, we have found that the fabricated Co
/Sc and Cr/Sc multilayer mirrors have been fabricated by means of an ion beam sputtering (IBS) method. As the result of structure evaluations with X-ray diffraction measurement, we have found that the fabricated Co O
O /Sc and Cr/Sc multilayer mirrors have stable structures. Soft X-ray reflectivity measurements for fabricated multilayer mirrors are carried out in the wavelength region of 4 nm with a synchrotron radiation source. We have found that the Cr/Sc multilayer mirror has a high soft X-ray reflectivity. However, soft X-ray reflectivities below the absorption edge of carbon are reduced. The analyses obtained by EPMA and SIMS suggested that this phenomenon was attributed to contamination of carbon.
/Sc and Cr/Sc multilayer mirrors have stable structures. Soft X-ray reflectivity measurements for fabricated multilayer mirrors are carried out in the wavelength region of 4 nm with a synchrotron radiation source. We have found that the Cr/Sc multilayer mirror has a high soft X-ray reflectivity. However, soft X-ray reflectivities below the absorption edge of carbon are reduced. The analyses obtained by EPMA and SIMS suggested that this phenomenon was attributed to contamination of carbon.