Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Nagaoka, Mika; Nakano, Masanao; Ono, Yosuke; Suitsu, Yuichi
JAEA-Technology 2021-011, 39 Pages, 2021/08
In the Analyzed Liquid Treatment Facility of Japan Nuclear Fuel Co., Ltd. (JNFL) MOX Fuel Fabrication Plant (J-MOX), the interfere by salts with the analysis of gross alpha activity concentration analysis will be caused during the treatment process. Therefore, JNFL devised the desalting method using a solid-phase extraction chromatography. Japan Atomic Energy Agency carried out the experimental study to confirm the validity of this desalting method for the treatment liquid based on the contract with JNFL. This study consists of three experiments as follows: Step 1 - Selection of an optical solid-phase extraction agent, Step 2 - Evaluation of variation optical solid-phase extraction agent, and Step 3 - Application of the imitation liquid waste. The result of Step 1 determined the solid-phase extraction agent (InertSep ME-2) and the optimum condition (aspiration method by manifold (about 5-10 mL/min), 3M nitric acid as eluent, pH: 5, and no adjustment of ionic valence). Then, the result of Step 2 and 3 made sure the validation of this method by obtaining over 70% recovery for the imitation liquid waste sample of the Analyzed Liquid Treatment Facility of J-MOX.
Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Abe, Hironobu; Kitamura, Akihiro; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(29), p.19281 - 19290, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.51(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Online solid-phase extraction-inductively coupled plasma-quadrupole mass spectrometry with oxygen dynamic reaction cell (online SPE-ICP-MS-DRC) was shown to be a thorough automatic analytical system, circumventing the need for human handling. At three stepwise separations (SPE-DRC-Q mass filters), we showed that interference materials allowed the coexistence of abundance ratios of 1.5 10
10 for
for  Tc/Mo. Using this optimized system, a detection limit of
Tc/Mo. Using this optimized system, a detection limit of  Tc was 9.3 pg/L (5.9 mBq/L) for a 50 mL injection and sequential measurements were undertaken at a cycle of 24 min/sample.
Tc was 9.3 pg/L (5.9 mBq/L) for a 50 mL injection and sequential measurements were undertaken at a cycle of 24 min/sample.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Horigome, Kazushi; Kuno, Takehiko
Proceedings of IAEA Symposium on International Safeguards; Building Future Safeguards Capabilities (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/11
In this study, the single-column extraction chromatographic separation has been developed for analysis of U and Pu in highly active liquid waste by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS). The commercially available TEVA resin is selected as an extraction chromatography resin. The U is chromatographically separated from fission products (FP) elements by nitric acid while Pu(IV) is adsorbed on the resin. After that, Pu is eluted by reducing to Pu(III). The method has been successfully achieved the separation with yielding the enough recovery and sufficient decontamination factors for subsequent IDMS analysis. The column dose rate after the FP removal is decreased to the background. The analytical results obtained by the developed method are in a good agreement with those of the conventional method. It provides simple and rapid separation and expected that the method can be applied to join IAEA/Japan on-site analytical laboratory.
resin is selected as an extraction chromatography resin. The U is chromatographically separated from fission products (FP) elements by nitric acid while Pu(IV) is adsorbed on the resin. After that, Pu is eluted by reducing to Pu(III). The method has been successfully achieved the separation with yielding the enough recovery and sufficient decontamination factors for subsequent IDMS analysis. The column dose rate after the FP removal is decreased to the background. The analytical results obtained by the developed method are in a good agreement with those of the conventional method. It provides simple and rapid separation and expected that the method can be applied to join IAEA/Japan on-site analytical laboratory.
Asai, Shiho; Saito, Kyoichi*
Biomedical Research on Trace Elements, 28(1), p.1 - 10, 2017/04
Radionuclides are commonly determined with radiometry and mass spectrometry. For  -emitting nuclides, the activities can be measured without chemical separation due to the strong penetration ability. In contrast, the measurements of alpha and beta-emitting nuclides are generally associated with tedious and time-consuming chemical separation procedures to remove concomitants. Thus, an adsorbent that achieves rapid separation is desirable to reduce separation time and workload. Our research team has developed compact cartridge-type solid phase extraction materials which enable to facilitate separation procedures. In this review, basic separation performances of the developed cartridges were overviewed along with two application examples to radionuclide-containing samples.
-emitting nuclides, the activities can be measured without chemical separation due to the strong penetration ability. In contrast, the measurements of alpha and beta-emitting nuclides are generally associated with tedious and time-consuming chemical separation procedures to remove concomitants. Thus, an adsorbent that achieves rapid separation is desirable to reduce separation time and workload. Our research team has developed compact cartridge-type solid phase extraction materials which enable to facilitate separation procedures. In this review, basic separation performances of the developed cartridges were overviewed along with two application examples to radionuclide-containing samples.
松枝 誠; 寺島 元基; 飯島 和毅
高貝 慶隆*
【課題】煩雑な工程を必要とせずに、α線放出核種を同時に複数種定量分析することができる方法を提供する。 【解決手段】固相抽出用樹脂を備えたカラム2に試料溶液を導入し、カラム2の固相抽出用樹脂に試料溶液に含まれるα線放出核種を吸着させ、固相抽出用樹脂に吸着されたα線放出核種をグループごとに溶離液に溶出させ、当該溶離液を霧化してプラズマイオン源5に導入してイオン化し、当該イオン群に酸素又はアンモニアを導入して、それらガスとの反応により当該元素のイオンの質量を変換し、次いで、四重極マスフィルター9において特定の質量数を持つイオンを除去し、四重極マスフィルター9を通過したα線放出核種の特定信号を測定する。
 I and
I and  Cl for radioactive rubbles
Cl for radioactive rubblesOta, Yuki; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Motoki, Yoshiaki*; Do, V. K.; Furuse, Takahiro
no journal, ,
We have developed an analytical method of  I (half-life: 1.57x10
I (half-life: 1.57x10 years) and
years) and  Cl (half-life: 3.01x10
Cl (half-life: 3.01x10 years) in various radioactive rubbles generated by decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F). A sequential chemical separation procedure has been developed to isolate the nuclides from the sample matrix, followed by the quantification by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) and liquid scintillation counting (LSC), respectively.
years) in various radioactive rubbles generated by decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F). A sequential chemical separation procedure has been developed to isolate the nuclides from the sample matrix, followed by the quantification by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) and liquid scintillation counting (LSC), respectively.
Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo; Kawakami, Tomohiko*; Teruyama, Yuko*; Toyoda, Yamato*; Otsuki, Hibiki*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) can measure actinides simultaneously, but isobaric interferences between actinides inhibit quantification. We combined solid-phase extraction (SPE) using DGA resin (Eichrom Technologies) and ICP-MS with oxygen reaction in a collision and reaction cell (CRC) to simultaneously measure Th, U, Pu, Am and Cm isotopes. The method is automated as an on-line SPE-ICP-MS/MS consisting of flow injection with SPE column and ICP-MS/MS, but the quantification includes a risk of variability due to the sample matrix. In this study, various sample types were applied and the impact of the sample matrix on the analysis system was assessed.
Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Kuwata, Haruka*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Uezu, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Zr and
Zr and  Mo based on solid phase extraction combined with ICP-MS/MS, 1; Sequential chemical separation of Zr and Mo from Nb
Mo based on solid phase extraction combined with ICP-MS/MS, 1; Sequential chemical separation of Zr and Mo from NbFuruse, Takahiro; Do, V. K.; Aita, Rena; Ota, Yuki; Murakami, Erina; Tomitsuka, Tomohiro; Sano, Yuichi; Akimoto, Yuji*; Endo, Tsubasa*; Katayama, Atsushi; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to simplify the analysis of  Zr and
Zr and  Mo in radioactive waste from conventional radiation measurement, we have considered analysis method combining solid-phase extraction and ICP-MS/MS. In this presentation, we report the results of a study on sequential chemical separation of Zr and Mo from Nb and sample matrix using ZR resin as a solid-phase extraction resin.
Mo in radioactive waste from conventional radiation measurement, we have considered analysis method combining solid-phase extraction and ICP-MS/MS. In this presentation, we report the results of a study on sequential chemical separation of Zr and Mo from Nb and sample matrix using ZR resin as a solid-phase extraction resin.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Naito, Sho*; Hiruma, Yusuke*; Minowa, Kazuki*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
We attempted to downsize the pretreatment of separation process to reduce the risk of radiation exposure in radioactive waste analysis. The geometry (inner diameter and length) for separation was investigated to design a micro tube column packed with UTEVA resin as a selective solid-phase extractant for uranium. It was found that the uranium adsorption rate depended on the inner diameter and length, and the column volume could be downsized to 4  L.
L.
Hosokawa, Tomoaki*; Fujiwara, Hideki*; Kamoshida, Shuichi*; Anzai, Kiyoshi*; Nakano, Masanao; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Nagaoka, Mika
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Masanao; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Nagaoka, Mika; Hosokawa, Tomoaki*; Fujiwara, Hideki*; Kamoshida, Shuichi*; Anzai, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Pd in radioactive rubbles by ICP-MS/MS
Pd in radioactive rubbles by ICP-MS/MSIwahashi, Hiroyuki; Do, V. K.; Furuse, Takahiro; Ota, Yuki; Homma, Shunta; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Motoki, Yoshiaki*; Hirosawa, Takashi
no journal, ,
The radiometric determination of beta emitting  Pd (half-life of 6.5 million years) requires a multiple-step chemical separation and a time-consuming radioactive measurement. Inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) with recent technological advances in interference removal by two quadrupole mass filters and a collision/reaction cell could be an alternative for highly sensitive analysis of long-lived radionuclides. In this study, we have developed an analytical method for the determination of
Pd (half-life of 6.5 million years) requires a multiple-step chemical separation and a time-consuming radioactive measurement. Inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) with recent technological advances in interference removal by two quadrupole mass filters and a collision/reaction cell could be an alternative for highly sensitive analysis of long-lived radionuclides. In this study, we have developed an analytical method for the determination of  Pd in concrete rubble by ICP-MS/MS combined with single-column chromatographic separation. A simplified procedure for the separation of Pd from concrete matrices was developed. The measurement condition was optimized to completely suppress the interference including the isobar
Pd in concrete rubble by ICP-MS/MS combined with single-column chromatographic separation. A simplified procedure for the separation of Pd from concrete matrices was developed. The measurement condition was optimized to completely suppress the interference including the isobar  Ag and the sample matrices. The application of the developed method to radioactive concrete rubble is under consideration.
Ag and the sample matrices. The application of the developed method to radioactive concrete rubble is under consideration.
 Se in concrete by ICP-MS/MS
Se in concrete by ICP-MS/MSBanjarnahor, I. M.; Do, V. K.; Motoki, Yoshiaki*; Ota, Yuki; Iwahashi, Hiroyuki; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Furuse, Takahiro
no journal, ,
Pure beta-emitting  Se is one of the long-lived fission products that might release to the environment due to the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). A reliable and simple determination method of the radionuclide is important for proceeding the disposal of the wastes obtained from the decommissioning of FDNPP. We developed a new analytical procedure for the measurement of
Se is one of the long-lived fission products that might release to the environment due to the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). A reliable and simple determination method of the radionuclide is important for proceeding the disposal of the wastes obtained from the decommissioning of FDNPP. We developed a new analytical procedure for the measurement of  Se by inductively coupled plasma triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS). All interferences that potentially interfere in the measurement of
Se by inductively coupled plasma triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS). All interferences that potentially interfere in the measurement of  Se could be effectively removed by the chemical separation pretreatment and ICP-MS/MS. The method is tested with inactive concrete to verify the interference removal efficiency. Also, the analytical figures of merit such as detection capability etc. are reported.
Se could be effectively removed by the chemical separation pretreatment and ICP-MS/MS. The method is tested with inactive concrete to verify the interference removal efficiency. Also, the analytical figures of merit such as detection capability etc. are reported.
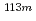 Cd using liquid scintillation counter
Cd using liquid scintillation counterIto, Chihiro; Tanaka, Yasuyuki; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Motoki, Yoshiaki*; Do, V. K.; Furuse, Takahiro
no journal, ,
In this presentation, an HCl-free analytical method for 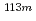 Cd in aqueous solution samples containing multiple radionuclides by liquid scintillation counting is reported. We aimed to develop a chemical separation procedure of
Cd in aqueous solution samples containing multiple radionuclides by liquid scintillation counting is reported. We aimed to develop a chemical separation procedure of 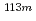 Cd from co-existing nuclides such as
Cd from co-existing nuclides such as  Co and/or
Co and/or  Fe, which interfere with the beta-counting. The use of hydrochloric acid (HCl) was avoided to prevent facilities from corrosion. Accordingly, after a sample-matrix separation with a chelating disk, Cd was adsorbed on a cation exchange resin and then selectively eluted by sodium thiosulfate (Na
Fe, which interfere with the beta-counting. The use of hydrochloric acid (HCl) was avoided to prevent facilities from corrosion. Accordingly, after a sample-matrix separation with a chelating disk, Cd was adsorbed on a cation exchange resin and then selectively eluted by sodium thiosulfate (Na S
S O
O ), which has a high affinity for Cd. This developed method allowed the separation and purification of Cd from the sample matrix without the use of halogen acids.
), which has a high affinity for Cd. This developed method allowed the separation and purification of Cd from the sample matrix without the use of halogen acids.
 Sr to environmental samples with online solid phase extraction/ICP-MS
Sr to environmental samples with online solid phase extraction/ICP-MSHagiwara, Hiroki; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Kuwata, Haruka*; Tanabe, Tsutomu; Uezu, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Oikawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Junichi*; Sudowe, R.*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terashima, Motoki; Endo, Takashi*; Kimuro, Shingo; Miyakawa, Kazuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English