Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinotsuka, Hiroshi*; Nagata, Kenji*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Applied Surface Science, 685, p.162001_1 - 162001_11, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Silicon (Si) 2p photoelectron spectra of thermally oxidized Si(001) surfaces were analyzed using Bayesian estimation, a type of mathematical statistical processing, considering spin-orbit interactions. The accuracy of the estimation of fitting parameters and the model selection of the number of peaks were discussed. The spectral analysis was performed without any prior information on the positions of other Si peaks, except for the prominent bulk Si peak, and without using chemical-state assumptions. Our method completely verified previous findings on the surface species and the changes in peaks due to oxidation-induced strain as oxidation progressed.
Egashira, Naoya*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Seto, Yusuke*; Ito, Yusuke*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Sano, Tomokazu*; 4 of others*
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(10), p.105903_1 - 105903_8, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Kobata, Masaaki; Okane, Tetsuo; Satou, Yukihiko; Okochi, Takuo*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 23(1), p.16 - 21, 2025/02
Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Tominaga, Aki; Jeon, B. H.*; Bae, S.*
Construction and Building Materials, 459, p.139742_1 - 139742_17, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology) Cl on Cu oxide Surfaces; Cu
Cl on Cu oxide Surfaces; Cu O(111) and bulk Cu
O(111) and bulk Cu O precursor "29"; Structure on Cu(111)
O precursor "29"; Structure on Cu(111)Hayashida, Koki*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Yamada, Takashi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 669, p.160475_1 - 160475_6, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Kato, Hiroyuki S.*; Muroyama, Mizuho*; Kobayakawa, Nano*; Muneyasu, Riku*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Watanabe, Seiya*; Yamada, Takashi*; Kanematsu, Yusuke*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 15(43), p.10769 - 10776, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:42.16(Chemistry, Physical)Sato, Yuriko*; Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Sano, Tomokazu*; Ogino, Yosuke*
Communications Materials (Internet), 5, p.147_1 - 147_9, 2024/08
The flow dynamics of current-carrying molten metal jet breakup during arc discharge serves as mass and heat sources in wire-arc-based metal deposition processes, thereby optimizing the resultant product quality. However, the spatiotemporal flow interaction between the molten metal jet and the surrounding arc plasma remains unclear. Here, using in-situ synchrotron X-ray imaging, we simultaneously track surface deformation and internal flow in molten aluminum jets during argon arc discharge. We reveal that modulating the magnitude and path of the arc discharge current can accelerate the jet velocity by 200  300% beyond its initial injection speed, thereby facilitating significant jet elongation. Our results provide consistent evidence that the jet flow dynamics are predominantly governed by the interaction between the arc discharge current and its coaxial self-induced magnetic field. This study establishes a framework at the intersection of fluid dynamics and electromagnetism, contributing to optimized control and precision in wire-arc-based applications.
300% beyond its initial injection speed, thereby facilitating significant jet elongation. Our results provide consistent evidence that the jet flow dynamics are predominantly governed by the interaction between the arc discharge current and its coaxial self-induced magnetic field. This study establishes a framework at the intersection of fluid dynamics and electromagnetism, contributing to optimized control and precision in wire-arc-based applications.
 7
7Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Anai, Ryota*; Saiki, Taiju*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(31), p.13052 - 13063, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)0xidation at the interface and the surface of Si(111) substrate with thin Hf films were studied using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy in conjunction with supersonic oxygen molecular beams (SOMB). An Hf/Si(111) with a coverage of 0.5 monolayer (ML) included HfSi and HfSi . Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf
. Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi
valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi could be oxidized into the Hf
could be oxidized into the Hf . Following the thermal O
. Following the thermal O exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO
exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO
via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO was generated on the surface.
was generated on the surface.
 00) MOS structures by means of electrical measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
00) MOS structures by means of electrical measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyKobayashi, Takuma*; Suzuki, Asato*; Nakanuma, Takato*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 175, p.108251_1 - 108251_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:77.39(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Xu, P. G.; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 59(14), p.5831 - 5853, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
O -75MoO
-75MoO binary glasses composed of isolated MoO
binary glasses composed of isolated MoO

Masuno, Atsunobu*; Munakata, Sae*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaji, Toyonari*; Kosugi, Yoshihisa*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 63(12), p.5701 - 5708, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.79(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Transparent and brown La O
O -MoO
-MoO binary glasses were prepared in bulk form using a levitation technique. The glass-forming range was limited, with the primary composition being approximately 25 mol% La
binary glasses were prepared in bulk form using a levitation technique. The glass-forming range was limited, with the primary composition being approximately 25 mol% La O
O . This glass exhibited a clear crystallization at 546
. This glass exhibited a clear crystallization at 546  C, while determining its glass transition temperature was difficult. Notably, despite its amorphous nature, the glass possessed a density and packing density comparable to those of crystalline La
C, while determining its glass transition temperature was difficult. Notably, despite its amorphous nature, the glass possessed a density and packing density comparable to those of crystalline La Mo
Mo O
O . X-ray absorption fine structure and Raman scattering analyses revealed that the glass structure closely resembles La
. X-ray absorption fine structure and Raman scattering analyses revealed that the glass structure closely resembles La Mo
Mo O
O due to the presence of isolated MoO
due to the presence of isolated MoO
 units, whereas disordered atomic arrangement around La atoms was confirmed. The glass demonstrated transparency ranging from 378 to 5500 nm, and the refractive index at 1.0
units, whereas disordered atomic arrangement around La atoms was confirmed. The glass demonstrated transparency ranging from 378 to 5500 nm, and the refractive index at 1.0  m was estimated to be 2.0. The optical bandgap energy was 3.46 eV, which was slightly smaller than that of La
m was estimated to be 2.0. The optical bandgap energy was 3.46 eV, which was slightly smaller than that of La Mo
Mo O
O . Additionally, the glass displayed a transparent region ranging from 6.5 to 8.0
. Additionally, the glass displayed a transparent region ranging from 6.5 to 8.0  m. This occurrence results from the decreased diversity of MoO
m. This occurrence results from the decreased diversity of MoO units and connectivity of Mo-O-Mo, which resulted in the reduced overlap of multiphonon absorption. This glass formation, with its departure from conventional glass-forming rules, resulted in distinctive glasses with crystal-like atomic arrangements.
units and connectivity of Mo-O-Mo, which resulted in the reduced overlap of multiphonon absorption. This glass formation, with its departure from conventional glass-forming rules, resulted in distinctive glasses with crystal-like atomic arrangements.
Liss, K.-D.*; Xu, P. G.; Shiro, Ayumi*; Zhang, S. Y.*; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Akita, Koichi*
Advanced Engineering Materials, 26(4), p.202300470_1 - 202300470_9, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Cl dissociation, CH
Cl dissociation, CH abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH
abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)
Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)Makino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 642, p.158568_1 - 158568_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:39.87(Chemistry, Physical)Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Fujimori, Shinichi
Hoshako, 37(1), p.3 - 12, 2024/01
no abstracts in English
 investigated using synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
investigated using synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopySekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Photon Factory Activity Report 2023 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2024/00
For nuclear transmutation of cesium-135 ( Cs), which is long-lived fission product, we are developing selective absorbent which takes only Cs atom in, but does not CsI. In this study, absorbing property of Cs atom or CsI into fullerene (C
Cs), which is long-lived fission product, we are developing selective absorbent which takes only Cs atom in, but does not CsI. In this study, absorbing property of Cs atom or CsI into fullerene (C ) solid has been investigated using synchrotron-based angle-dependent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ARXPS). It was found that Cs penetrates into C
) solid has been investigated using synchrotron-based angle-dependent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ARXPS). It was found that Cs penetrates into C deep bulk. In contrast, CsI does not diffuse into bulk, although CsI over-layer was formed on the shallow surface. Furthermore, XPS spectra were measured as a function of Ar
deep bulk. In contrast, CsI does not diffuse into bulk, although CsI over-layer was formed on the shallow surface. Furthermore, XPS spectra were measured as a function of Ar -sputtering time in order to know Cs concentration profiles in further deep region. Results showed that Cs penetrates into deep region of several hundreds
-sputtering time in order to know Cs concentration profiles in further deep region. Results showed that Cs penetrates into deep region of several hundreds  .
.
 Na
Na TiO
TiO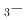 BaTiO
BaTiO solid solutions
solid solutionsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kobayashi, Toru; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Yuji; Noguchi, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 62(SM), p.SM1006_1 - SM1006_8, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:50.15(Physics, Applied)Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO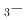 BaTiO
BaTiO (BNT
(BNT BT) solid solutions have been extensively studied because they exhibit good piezoelectric properties. In addition, a wide variety of phases are observed depending on the BT composition. Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and high-energy X-ray diffraction experiments of BNT
BT) solid solutions have been extensively studied because they exhibit good piezoelectric properties. In addition, a wide variety of phases are observed depending on the BT composition. Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and high-energy X-ray diffraction experiments of BNT BT solid solutions were performed using synchrotron radiation. From the electronic structure and local structure of BNT
BT solid solutions were performed using synchrotron radiation. From the electronic structure and local structure of BNT BT solid solution, the substitution effect of BT occurred mainly at the A site, which is the substitution site of Ba. The rhombohedral strain of the TiO
BT solid solution, the substitution effect of BT occurred mainly at the A site, which is the substitution site of Ba. The rhombohedral strain of the TiO octahedron did not change with the change in BT composition, suggesting that the change in the electronic structure at the O-
octahedron did not change with the change in BT composition, suggesting that the change in the electronic structure at the O- absorption edge is due to the change in the hybridization state.
absorption edge is due to the change in the hybridization state.
Shobu, Takahisa
Kensa Gijutsu, 28(11), p.64 - 70, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
 symmetry for anisotropic
symmetry for anisotropic 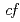 hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi
hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Higashiya, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165121_1 - 165121_10, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Takafumi*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Arakawa, Masakazu*; Maruyama, Akio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Sangyo Oyo Kogakukai Rombunshi, 11(2), p.109 - 114, 2023/09
Surface chemistry experimental end-station at BL23SU in SPring-8 is widely used to study various surfaces and interfaces of functional materials by means of soft X-rays synchrotron radiation. To analyze surface chemical reactions between gas and solid surfaces, an accurate control of flow-rates of gases is essential. This paper describes a computerized automatic gas flow control system to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of gas-surface reaction experiments in the pressure range of ultra-high vacuum (molecular flow) conditions. The system uses feedback control to operate the slow-leak valve to control the gas-pressure. As a result, the system achieved results equivalent to those of a skilled experimenter.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Takaki, Seiya; Takano, Masahide
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 663, p.414960_1 - 414960_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)We performed various synchrotron X-ray measurements to extract local and average structures of DyN-ZrN solid solutions. We performed the nanoscale structural analysis by combining X-ray absorption fine structure and high-energy X-ray diffraction. The DyN-ZrN solid solution has a rock-salt type cubic crystal structure, and there are instabilities such as the chemical order of the metal site and the distribution of the bond length of the nitrogen site.