Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otsuka, Naohiko*; Tada, Kenichi; Cabellos, O.*; Iwamoto, Osamu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 212, p.110977_1 - 110977_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The uranium-233 neutron capture cross section between 3 keV and 1 MeV was evaluated considering the recent new alpha-value measurement performed at the Los Alamos National Laboratory LANCE facility. The obtained capture cross section is systematically lower than the capture cross section in the JENDL-5 library and the reduction is close to 50% around 20 keV. The newly evaluated cross section was validated against 166 criticality experiments chosen from the ICSBEP handbook by performing Monte Carlo neutron transport calculation with the JENDL-5 library, and slight reduction of the chi-square value was achieved by adoption of the newly evaluated capture cross section.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.32 - 37, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2023, P. 46, 2024/07
The present work is an attempt to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for some nuclides which are of importance in decommissioning to evaluate produced radioactivity. This work selected some of objective nuclides for decommissioning, such as  Fe,
Fe,  Er and
Er and  Hf, and measured thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for these nuclides by a neutron activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The present results were obtained as follows:1.23
Hf, and measured thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for these nuclides by a neutron activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The present results were obtained as follows:1.23 0.03 barn for
0.03 barn for  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe reaction, 8.19
Fe reaction, 8.19 0.35 barn for
0.35 barn for  Er(n,
Er(n, )
)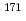 Er reaction and 13.57
Er reaction and 13.57 0.14 barn for
0.14 barn for  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reaction. As a by-product, the measurement of Hf sample also presented 0.427
Hf reaction. As a by-product, the measurement of Hf sample also presented 0.427 0.006 barn for
0.006 barn for 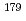 Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
)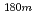 Hf reaction. It has been revealed that the data adopted in an evaluated data library differ from the present results by more than experimental uncertainties.
Hf reaction. It has been revealed that the data adopted in an evaluated data library differ from the present results by more than experimental uncertainties.
Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara; Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Chiba, Go*; Ono, Michitaka*; Tojo, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.830 - 839, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:89.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear data processing code is important to connect evaluated nuclear data libraries and radiation transport codes. The nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 1 was released in 2019 to generate ACE formatted cross section files with simple input data. After we released FRENDY version 1, many functions were developed, e.g., neutron multi-group cross section generation, explicit consideration of the resonance interference effect among different nuclides in a material, consideration of the resonance upscattering, ACE file perturbation, and modification of ENDF-6 formatted file. FRENDY version 2 was released including these new functions. It generates GENDF and MATXS formatted neutron multi-group cross section files from an ACE formatted cross section file or an evaluated nuclear data file. This paper explains the features of the new functions implemented in FRENDY version 2 and the verification of the neutron multigroup cross section generation function of this code.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugihara, Kenta*
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.45(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclide production cross sections are crucial in nuclear research, development, space exploration, and astrophysical investigations. Despite their importance, limited experimental data availability restricts the practicality of phenomenological approaches to comprehensive cross-section estimation. To address this, we propose a Gaussian process-based machine learning (ML) model capable of transferring knowledge from elements with abundant data to those with limited or no experimental data. Our ML model not only enables comprehensive cross-section estimations for various elements but also demonstrates predictive capabilities akin to physics models, even in regions with scarce training data.
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
 U and
U and  Th
ThFilipescu, D.*; Gheorghe, I.*; Goriely, S.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Suzaki, Fumi; Hirose, Kentaro; 10 of others*
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_23, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.45(Physics, Nuclear) Re in the keV energy region
Re in the keV energy regionKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Sato, Yaoki*; Takebe, Karin*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Umezawa, Seigo*; Fujioka, Ryo*; Saito, Tatsuhiro*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.224 - 229, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*;  elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (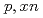 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Tada, Kenichi
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The number of energy grids of the thermal neutron scattering law data has a large impact on the data size of a cross section file of continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation codes. The optimization of the number of energy grids is an effective way to reduce the data size. This study developed the linearization method of the thermal neutron scattering cross section to optimize the number of energy grids and the linearization function was implemented in the nuclear data processing code FRENDY. The linearization process which is used in the resonance reconstruction and the Doppler broadening was adopted. The criticality benchmarks which use ZrH as the moderator were calculated to estimate the impact of the difference of the energy grids on neutronics calculations. The calculation results indicate that the linearization of the thermal neutron scattering cross section improves the prediction accuracy of neutronics calculations.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2022, P. 73, 2023/07
The present study is concerned with the neutron capture cross-sections that contribute to the evaluation of the amount of radionuclides possessing problems in decommissioning. In this study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag,
Ag,  In and
In and  W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then
W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then  rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors (
rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92
Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92 0.10)
0.10) 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of
/sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of  Sc and
Sc and  Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.05001_1 - 05001_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:70.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and the spallation neutron source, it is crucial to evaluate the damage of beam-interception materials and accelerator components, such as a magnet coil. The displacement per atom (dpa) is used as a damage index, which is derived by integrating the particle flux and the displacement cross section based on the NRT model. Although the dpa is employed as the standard, the experimental data of displacement cross section are scarce for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV. To obtain the data for superconducting materials for high-intensity accelerators and magnets, the displacement cross section of Nb for proton irradiation with a kinetic energy range between 0.4 and 3 GeV was measured. For sustaining damage in the sample, the Nb sample was cooled at a cryogenic temperature ( 8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01033_1 - 01033_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:70.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Chiba, Go*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(2), p.132 - 139, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new multi-group neutronics analysis sequence ACE-FRENDY-CBZ is proposed. This sequence is free from uses of any application libraries; with the ACE files as the starting point, multi-group cross section data of media comprising a target system are calculated with the FRENDY code, and multi-group neutron transport calculations are performed with modules of the CBZ code system. The ACE-FRENDY-CBZ sequence was tested against the eight fast neutron systems, and good agreement with the reference Monte Carlo results was obtained within 30 pcm differences in the bare systems and the thorium-reflected system, and approximately 100 pcm differences in the uranium-reflected systems. The use of the current-weighted total cross sections in the multi-group neutron transport calculations had non-negligible impacts over 100 pcm on k-eff, and the calculations with the current-weighted total cross sections systematically underestimated k-eff in the uranium-reflected systems.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 409, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Nakano, Keita*; Sugihara, Kenta*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.132 - 136, 2023/01
J-PARC accelerator facility is the only accelerator facility in Japan that can provide proton beams in the energy range of 400 MeV or higher. In the J-PARC accelerator facility, it is difficult to install users' experimental equipment inside the proton beam duct in order to maintain stable user operation. In addition, due to the characteristics of the synchrotron accelerator, it is not possible to supply a low-intensity beam enough to confirm the detector. In addition, it is important to improve the intranuclear cascade model (INCL) for high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS), etc. In order to improve the INCL, DDX of the forward-most emitted particles is important, but new data should be obtained since there are few experimental data available. In order to promote space utilization and to improve the accuracy of the INCL, energy spectra of scattered protons at the Al beam window placed at the inlet of the 3NBT dump were measured. In the experiment, plastic scintillators were used with 400 MeV proton beam. The results show that the spectra have sharp peaks due to elastic scattering. The calculation of the PHITS code using INCL reproduced the sharp peak due to elastic scattering well, although it overestimated the contribution of quasi-elastic scattering in the experimental data. In conclusion, it is clear that the present method can be used to utilize protons in several GeV regions for space exploration.
Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Chiba, Go*; Tada, Kenichi
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 196(11), p.1267 - 1279, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)The resonance upscattering effect (the thermal agitation effect) is incorporated in the generation capability of multi-group neutron cross sections of the FRENDY nuclear data processing system. The resonance upscattering effect is considered by (1) the variation of self-shielding factors (effective cross sections) due to the change in ultra-fine group spectrum and (2) the variation of group-to-group elastic scattering cross sections. In the verification calculations, impacts on the ultra-fine group spectrum, effective cross sections, and neutronics characteristics (the Doppler effect) are confirmed. The effect of energy group structure and the treatments of resonance upscattering on the Doppler effect through the variation of effective cross sections and the elastic scattering matrix are studied. The results indicate that the FRENDY can provide appropriate multi-group cross sections considering the resonance upscattering effect.
Ono, Michitaka*; Tojo, Masayuki*; Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors 2022 (PHYSOR 2022) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/05
In this paper, nuclear calculations were performed using the ACE files and the multigroup libraries created by both FRENDY and NJOY, and the impacts on the neutronics characteristics due to nuclear data processing were investigated using those libraries. MCNP was used to compare the ACE files by calculating many benchmark problems including ICSBEP and it was confirmed that the k-eff values are generally agreed with each other within the range of statistical errors. The multigroup cross sections are verified by the BWR design codes LANCR/AETNA through calculation of a commercial-grade BWR5 equilibrium core loaded with 9 9 fuels. These results indicate that fuel assembly and core characteristics are consistent with each other. From the above investigations, it was confirmed that FRENDY can provide comparable continuous/multi-group neutron cross sections with NJOY.
9 fuels. These results indicate that fuel assembly and core characteristics are consistent with each other. From the above investigations, it was confirmed that FRENDY can provide comparable continuous/multi-group neutron cross sections with NJOY.
Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Chiba, Go*; Ono, Michitaka*; Tojo, Masayuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors 2022 (PHYSOR 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/05
Nuclear data processing is an important interface between an evaluated nuclear data library and nuclear transport calculation codes. JAEA has developed a new nuclear data processing code FRENDY from 2013. FRENDY version 1 generates ACE files which are used for the continuous-energy Monte Carlo codes including PHITS, Serpent, and MCNP; it was released as an open-source software under the 2-clause BSD license in 2019. After FRENDY version 1 was released, many functions are developed: the multi-group neutron cross-section library generation, the statistical uncertainty quantification for the probability tables for unresolved resonance cross-section, the perturbation of the ACE file, and the modification of the ENDF-6 formatted nuclear data file, etc. We released FRENDY version 2 including these functions. This presentation explains the overview of FRENDY and features of the new functions implemented in FRENDY version 2.