Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Noda, Yohei
no journal, ,
We have applied proton spin polarization to contrast variation method in small angle neutron scattering (SANS) study. Especially, we succeeded in applying this technique to silica-filled rubber, which is not easily fabricated in a deuterated form. At the last SANS experiment, degree of proton spin polarization (i.e., the population difference between up and down spins) was limited (26 % at maximum). It is essential to enhance proton spin polarization further in order to modify scattering contrast widely and separate partial scattering functions presicely. Toward this, as a result of inteisifying microwave irradiation, we finally enhanced proton spin polarization up to 50.8% for TEMPO-doped polystyrene. The achieved result will improve performance in SANS experiment at J-PARC.
Noda, Yohei; Kumada, Takayuki; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Shamoto, Shinichi
no journal, ,
We investigated the dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) performance of two-component type epoxy resin (Araldite(R) Standard and Araldite(R) Rapid) doped with TEMPO radical. The obtained TEMPO-doped epoxy resin sample was polarized up to 39% at 1.2 K and 3.35 Tesla. The achieved DNP performance was close to other conventionally used polymers.
Noda, Yohei; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Shamoto, Shinichi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Koizumi, Satoshi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Masui, Tomomi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed proton spin polarization technique for contrast variation in small angle neutron scattering (SANS), which utilizes that neutron scattering section can be controlled by polarizing proton spins. Consequently, we succeeded in the analysis of nano-structure in multi-component samples. We will report the detail of our recent activity for getting higher proton spin oplarization. The recent results of SANS measurement with proton spin polarization conducted for the first time at TAIKAN in J-PARC will also be reported.
Noda, Yohei; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Shamoto, Shinichi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Masui, Tomomi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron scattering length changes as aligning the spin direction of protons in a sample. By use of this phenomenon, we have developed spin contrast variation technique for studying nano-scale structure formed in multi-component systems. In this presentation, we report the results of our recent experiment at J-PARC TAIKAN.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei*; Ishikawa, Norito
no journal, ,
We compared dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) behavior of electron-beam irradiated and TEMPO-doped samples. Both of the growth and decay rates of the nuclear polarization of the irradiated samples linearly increased with the irradiation dose, whereas those of the doped sample were quadratically proportional to the TEMPO concentration. This result suggests that the irradiated samples are polarized due to pair of free radicals produced in a spur, whereas the doped sample is polarized by unspecified TEMPO radical pairs accidentally located nearby. We suggest that higher polarization is expected by optimizing irradiation temperature, on which the radical-radical distance in the pair depends.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei*; Ishikawa, Norito
no journal, ,
We compared dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) behavior of electron-beam irradiated and TEMPO-doped samples. Both of the growth and decay rates of the nuclear polarization of the irradiated samples linearly increased with the irradiation dose, whereas those of the doped sample were quadratically proportional to the TEMPO concentration. This result suggests that the irradiated samples are polarized due to pair of free radicals produced in a spur, whereas the doped sample is polarized by unspecified TEMPO radical pairs accidentally located nearby. We suggest that higher polarization is expected by optimizing irradiation temperature, on which the radical-radical distance in the pair depends.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
no journal, ,
Scattering power of neutrons against protons depends remarkably on relative directions of their spins. So, polarized neutron scattering profiles vary as a function of proton polarization of measuring specimen. We can extract fruitful structural information from these profiles. This technique named "spin-contrast variation" has been used to study meso-scale bulk structure using small-angle neutron scattering. Now, we plan to apply the spin-contrast variation technique to study surface structure using neutron reflectivity measurements. The spin-contrast neutron reflectivity measurement will determine surface structure of complex soft materials such as adhesives.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
no journal, ,
We developed a technique of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectometry (SCV-NR). Polarized-neutron reflectivity curves of a styrene homopolymer film vary as a function of their proton-polarization, P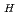 , coherently with what expected when the films are homogeneously polarized. This result ensures that the SCV-NR curves are not deformed by inhomogeneous P
, coherently with what expected when the films are homogeneously polarized. This result ensures that the SCV-NR curves are not deformed by inhomogeneous P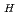 in the film, but determine the structures of surfaces and interfaces properly. Conventional unpolarized neutron reflectivity UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves of poly(styrene-block-isoprene) (PSPI) films are reproduced by the model that the film has a flat free surface, but positively-polarized SCV-NR curves are not. We found from the global fit that the holes with the depth corresponding to one period of periodic lamellae are produced on the free surface of the PSPI films, whose reflection is hidden by strong one from the PSPI-Si interface in the UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves.
in the film, but determine the structures of surfaces and interfaces properly. Conventional unpolarized neutron reflectivity UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves of poly(styrene-block-isoprene) (PSPI) films are reproduced by the model that the film has a flat free surface, but positively-polarized SCV-NR curves are not. We found from the global fit that the holes with the depth corresponding to one period of periodic lamellae are produced on the free surface of the PSPI films, whose reflection is hidden by strong one from the PSPI-Si interface in the UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves.
Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
We installed our DNP apparatus to neutron beamlines for structure analyses. This technique named spin contrast variation (SCV) relies on a property that the scattering power of neutron against proton depends heavily on their relative spin direction. SCV extracts detailed structure information from the polarized neutron scattering that greatly varies with proton polarization of the sample. Whereas only a small number of neutron facilities can handle SCV, we upgrade the SCV technique, and output good research examples to show how to use SCV.