Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Kei*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Takai, Kenichi*
Key Engineering Materials, 967, p.11 - 16, 2023/07
Hydrogen-enhanced strain-induced vacancy, one of the defects associated with promising hydrogen embrittlement mechanisms, was validated for tempered martensitic steel showing quasi-cleavage fracture with a tensile strength of 1500 MPa level by slow strain rate tensile test in-situ electrochemical hydrogen charging. The effect of newly formed vacancy-type defects on mechanical properties of tempered martensitic steel was also studied. Combined use of low-temperature thermal desorption spectroscopy (L-TDS) and the tensile test revealed the following three things: (i) hydrogen enhanced the accumulation of vacancy-type defects with plastic straining, (ii) accumulated vacancy-type defects deteriorated the ductility of the tempered martensitic steel after hydrogen release, and (iii) aging in the range from 50 C to 150
C to 150 C after applying given plastic strain with hydrogen charging decreased the amount of newly formed vacancy-type defects, and then resulted in the recovery of the ductility.
C after applying given plastic strain with hydrogen charging decreased the amount of newly formed vacancy-type defects, and then resulted in the recovery of the ductility.
 (001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Inami, Eiichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abe, Masayuki*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 65(11), p.526 - 530, 2022/11
The oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O
(001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
 based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation result
based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation resultWatanabe, Masashi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Suzuki, Kiichi; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 105(3), p.2248 - 2257, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.41(Materials Science, Ceramics)Properties of CeO were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
Wang, J.*; Hatano, Yuji*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Hinoki, Tatsuya*; Alimov, V. Kh.*; Schwarz-Selinger, T.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 559, p.153449_1 - 153449_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To study the effect of the content of chromium (Cr) in the tungsten (W) matrix on the vacancy formation and retention of hydrogen isotopes, the samples of the W-0.3Cr alloy were irradiated with 6.4 MeV Fe ions in the temperature range of 523-1273 K. These displacement-damaged samples were exposed to D gas at a temperature of 673 K. The addition of 0.3% Cr into the W matrix resulted in a significant decrease in the retention of deuterium compared to pure W after irradiation especially at high temperature. Positron lifetime for W-0.3Cr alloy irradiated at 1073 K was almost similar to that for non-irradiated one. These facts indicate the suppression of the formation of vacancy-type defects by 0.3% Cr addition.
gas at a temperature of 673 K. The addition of 0.3% Cr into the W matrix resulted in a significant decrease in the retention of deuterium compared to pure W after irradiation especially at high temperature. Positron lifetime for W-0.3Cr alloy irradiated at 1073 K was almost similar to that for non-irradiated one. These facts indicate the suppression of the formation of vacancy-type defects by 0.3% Cr addition.
 with Pu = 0.45 and 0.68 and related defect formation energy
with Pu = 0.45 and 0.68 and related defect formation energyHirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hino, Tetsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 558, p.153375_1 - 153375_8, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:49.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Jumpei*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Suemasu, Takashi*
Journal of Applied Physics, 130(19), p.195701_1 - 195701_7, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.33(Physics, Applied)Ebihara, Kenichi; Sugiyama, Yuri*; Matsumoto, Ryosuke*; Takai, Kenichi*; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 52(1), p.257 - 269, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We simulated the thermal desorption spectra of a small-size iron specimen to which was applied during charging with hydrogen atoms using a model incorporating the behavior of vacancies and vacancy clusters. The model considered up to vacancy clusters 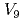 , which is composed of nine vacancies and employed the parameters based on atomistic calculations, including the H trapping energy of vacancies and vacancy clusters that we estimated using the molecular static calculation. As a result, we revealed that the model could, on the whole, reproduced the experimental spectra except two characteristic differences, and also the dependence of the spectra on the aging temperature. By examining the cause of the differences, the possibilities that the diffusion of clusters of
, which is composed of nine vacancies and employed the parameters based on atomistic calculations, including the H trapping energy of vacancies and vacancy clusters that we estimated using the molecular static calculation. As a result, we revealed that the model could, on the whole, reproduced the experimental spectra except two characteristic differences, and also the dependence of the spectra on the aging temperature. By examining the cause of the differences, the possibilities that the diffusion of clusters of 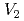 and
and 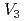 is slower than the model and that vacancy clusters are generated by applying strain and H charging concurrently were indicated.
is slower than the model and that vacancy clusters are generated by applying strain and H charging concurrently were indicated.
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(5), p.051007_1 - 051007_8, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Woo, W.*; Naeem, M.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Lee, C.-M.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; He, H.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 781, p.139224_1 - 139224_7, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:94.70(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) without stacking disorder by evacuating hydrogen from hydrogen hydrate
without stacking disorder by evacuating hydrogen from hydrogen hydrateKomatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Noritake, Fumiya*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Yamane, Ryo*; Yamashita, Keishiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.464_1 - 464_5, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:87.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Water freezes below 0 C at ambient pressure ordinarily to ice I
C at ambient pressure ordinarily to ice I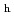 , with hexagonal stacking sequence. Under certain conditions, ice with a cubic stacking sequence can also be formed, but ideal ice I
, with hexagonal stacking sequence. Under certain conditions, ice with a cubic stacking sequence can also be formed, but ideal ice I without stacking-disorder has never been formed until recently. Here we demonstrate a route to obtain ice I
without stacking-disorder has never been formed until recently. Here we demonstrate a route to obtain ice I without stacking-disorder by degassing hydrogen from the high-pressure form of hydrogen hydrate, C
without stacking-disorder by degassing hydrogen from the high-pressure form of hydrogen hydrate, C , which has a host framework isostructural with ice I
, which has a host framework isostructural with ice I . The stacking-disorder free ice I
. The stacking-disorder free ice I is formed from C
is formed from C via an intermediate amorphous or nano-crystalline form under decompression, unlike the direct transformations occurring in ice XVI from neon hydrate, or ice XVII from hydrogen hydrate. The obtained ice I
via an intermediate amorphous or nano-crystalline form under decompression, unlike the direct transformations occurring in ice XVI from neon hydrate, or ice XVII from hydrogen hydrate. The obtained ice I shows remarkable thermal stability, until the phase transition to ice I
shows remarkable thermal stability, until the phase transition to ice I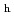 at 250 K, originating from the lack of dislocations. This discovery of ideal ice I
at 250 K, originating from the lack of dislocations. This discovery of ideal ice I will promote understanding of the role of stacking-disorder on the physical properties of ice as a counter end-member of ice I
will promote understanding of the role of stacking-disorder on the physical properties of ice as a counter end-member of ice I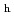 .
.
Woo, W.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Kim, D.-K.*; Lee, C. M.*; Choi, S.-H.*; Suh, J.-Y.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.1350_1 - 1350_15, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:95.72(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Naoe, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Shintaku, Yohei*; Li, T.*; Kanomata, Kenichi*
Choompa Techno, 30(5), p.16 - 20, 2018/10
A mercury target vessel has been used for the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. It has a complicated multi-layered structure composed of a mercury target and a surrounding double-walled water shroud, which is assembled with thin plates (minimum thickness of 3 mm) by welding. Thus, welding inspection during the manufacturing process is important. We investigated the applicability of new ultrasonic inspections using specimens (thickness of 3 mm) with defects to improve the accuracy of welding inspection for the mercury target vessel. Immersion ultrasonic testing using a probe (frequency of 50 MHz) could detect a spherical defect with a diameter of 0.2 mm. The size was smaller than target value of 0.4 mm. The length of unwelded region estimated using the phased array ultrasonic testing corresponded with the actual length (0.8 - 1.5 mm).
Hasegawa, Kunio; Li, Y.; Mare , V.*; Lacroix, V.*
, V.*; Lacroix, V.*
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 5 Pages, 2018/07
Appendix C-5320 of ASME Code Section XI provides a formula of bending stress at the plastic collapse, where the formula is applicable for both inner and outer surface flaws. Authors considered the separated pipe mean radii at the flawed ligament and at the un-flawed ligament and formulas of plastic collapse stresses for each inner and outer flawed pipe were obtained. It is found that the collapse stress for inner flawed pipe is slightly higher than that calculated by Appendix C-5320 formula, and the collapse stress for outer flawed pipe is slightly lower than that by Appendix C-5320 formula. The collapse stresses derived from the three formulas are almost the same in most instances. For less common case where the flaw angle and depth are very large for thick wall pipes, the differences among the three collapse stresses become large.
Takano, Kazuya; Maruyama, Shuhei; Hazama, Taira; Usami, Shin
Proceedings of Reactor Physics Paving the Way Towards More Efficient Systems (PHYSOR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), p.1725 - 1735, 2018/04
Irradiation dependence of the core excess reactivity was investigated for the Monju system startup tests at zero-power carried out in 2010. The excess reactivity basically decreases with the  decay of
decay of  Pu in zero-power operation. However, the excess reactivity little changed in the two month period of the startup tests, which suggests a positive reactivity insertion during the period. The investigated irradiation dependence shows that the positive reactivity increases with reactor operation and mostly saturates by the fission-dose attained during the Monju zero-power operation in a month (
Pu in zero-power operation. However, the excess reactivity little changed in the two month period of the startup tests, which suggests a positive reactivity insertion during the period. The investigated irradiation dependence shows that the positive reactivity increases with reactor operation and mostly saturates by the fission-dose attained during the Monju zero-power operation in a month ( 10
10 fissions/cm
fissions/cm ). The saturated positive reactivity is equivalent to approximately 47% of the initially accumulated self-irradiation damage recovery assuming the defects were recovered by the fission-fragment irradiation in the reactor operation.
). The saturated positive reactivity is equivalent to approximately 47% of the initially accumulated self-irradiation damage recovery assuming the defects were recovered by the fission-fragment irradiation in the reactor operation.
Hasegawa, Kunio; Li, Y.; Katsumata, Genshichiro*; Dulieu, P.*; Lacroix, V.*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/07
Net-section stress at the ligament between component free surface and subsurface flaw increases when the ligament distance is short. It can be easily expected that stress intensity factors increase when the subsurface flaw locates near the free surface. To avoid catastrophic failures caused by ligament failure, fitness-for-service (FFS) codes provide flaw-to-surface proximity rules. The proximity rules are used to determine whether the flaws should be treated as subsurface flaws as-is, or transformed to surface flaws. The stress intensity factor for the transformed surface flaw increases furthermore. The increment of the stress intensity factor before and after transformation depends on the location of the subsurface flaw. Although the concept of the proximity rules are the same, the specific criteria for the rules on transforming subsurface flaws to surface flaws differ amongst FFS codes. Particularly, the criteria are different amongst the same organizations of ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers). The proximity criteria of the FFS codes in the world were introduced in this paper. In addition, the stress intensity factors based on the different criteria used in the ASME Codes are compared.
 in GdBCO-coated conductors with crossed columnar defects around
in GdBCO-coated conductors with crossed columnar defects around 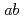 plane
planeSueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Iwanaga, Yasuya*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Takai, Yosuke*; Mukaida, Masashi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 27(4), p.8001305_1 - 8001305_5, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:39.40(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We investigated in detail the flux pinning properties around B 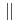
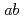 for GdBCO coated conductors with crossed columnar defects produced by heavy-ion irradiation, where the crossing angle was systematically controlled in the range from 5 to 15 relative to the ab-plane. A single peak of critical current density
for GdBCO coated conductors with crossed columnar defects produced by heavy-ion irradiation, where the crossing angle was systematically controlled in the range from 5 to 15 relative to the ab-plane. A single peak of critical current density  centered at B
centered at B 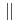
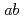 occurs for the crossing angle of 5, where an upward shift in
occurs for the crossing angle of 5, where an upward shift in  can be observed compared to an unirradiated sample. As the crossing angle is larger, the
can be observed compared to an unirradiated sample. As the crossing angle is larger, the  peak becomes smaller and broader while maintaining the peak at B
peak becomes smaller and broader while maintaining the peak at B 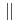
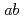 . Three
. Three  peaks emerges at B
peaks emerges at B 
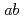 and at the two irradiation angles, independently from the others.
and at the two irradiation angles, independently from the others.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Nishimura, Takahiro*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Mitsugi, Fumiaki*; Ikegami, Tomoaki*; Ishikawa, Norito
Superconductor Science and Technology, 29(10), p.105006_1 - 105006_7, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.45(Physics, Applied)A systematic investigation of flux pinning by widely direction-dispersed columnar defects (CDs) in YBa Cu
Cu Oy thin films was carried out by using heavy-ion irradiation: a parallel configuration of CDs aligned along the
Oy thin films was carried out by using heavy-ion irradiation: a parallel configuration of CDs aligned along the  -axis, and two trimodal splay configurations composed of crossing CDs; relative to the
-axis, and two trimodal splay configurations composed of crossing CDs; relative to the  -axis, where the splay plane defined by the three irradiation angles is perpendicular (trimodal-A) or parallel (trimodal-B) to the transport current direction. The trimodal configurations show high pinning efficiency over a wide range of magnetic field orientations compared to the parallel one at low magnetic field. In particular, trimodal-B shows the higher critical current density of the two trimodal configurations.
-axis, where the splay plane defined by the three irradiation angles is perpendicular (trimodal-A) or parallel (trimodal-B) to the transport current direction. The trimodal configurations show high pinning efficiency over a wide range of magnetic field orientations compared to the parallel one at low magnetic field. In particular, trimodal-B shows the higher critical current density of the two trimodal configurations.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
"Suiso Zeika No Kihon Yoin To Tokusei Hyoka Kenkyukai Chukan Hokokukai" Shimposium Yokoshu (USB Flash Drive), p.30 - 35, 2016/09
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Noboru
Kagaku, 71(3), p.72 - 73, 2016/02
In Japan, the deterioration of the infrastructure built in the high economic growth period (1954-1979) becomes big social problem. We have developed the inspection method of the defect in the concrete by using the laser technologies. We have succeeded to demonstrate the high-speed inspection of a mock-defect in concrete by using the high repetition rate impact laser and laser vibrograph. The repetition rate of inspection was improved to be 25 Hz. We commented about this measurement technique.
Hasegawa, Kunio*; Li, Y.; Serizawa, Ryosuke*; Kikuchi, Masanori*; Lacroix, V.*
Procedia Materials Science, 12, p.36 - 41, 2016/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.04(Engineering, Mechanical)If subsurface flaws are detected that are close to component free surfaces, flaw-to-surface proximity rule is used to determine whether the flaws should be treated as subsurface flaws as is, or transformed to surface flaws. However, specific factors for the proximity rules on transforming subsurface to surface flaws differ among fitness-for-service codes. The objective of the paper is to reveal the proximity factor from the stress intensity factor interaction between the subsurface flaw and the free surface.