Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Applied Physics, 130(19), p.195701_1 - 195701_7, 2021/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:24.33(Physics, Applied)Hydrogen defects sometimes form shallow impurity levels in semiconductors, and it is an important topic for semiconductor research to investigate their details. One of the experimental methods to determine the state of hydrogen is the muon spin rotation ( SR) experiment. By observing formation of a pseudo-hydrogen atom, called muonium, it is possible to investigate the hydrogen defect levels. In a previous theoretical study, the pinning levels were calculated for various materials as a reference for hydrogen defect levels, and these levels were universally distributed near the hydrogen electrode potential. Based on the prediction,
SR) experiment. By observing formation of a pseudo-hydrogen atom, called muonium, it is possible to investigate the hydrogen defect levels. In a previous theoretical study, the pinning levels were calculated for various materials as a reference for hydrogen defect levels, and these levels were universally distributed near the hydrogen electrode potential. Based on the prediction,  SR experiments were performed for germanium sulfide (GeS) and germanium telluride (GeTe), where the hydrogen electrode potential is located in the bandgap for GeS, but not for GeTe. As a result, the
SR experiments were performed for germanium sulfide (GeS) and germanium telluride (GeTe), where the hydrogen electrode potential is located in the bandgap for GeS, but not for GeTe. As a result, the  SR spectra showed that the muonium forms in GeS, while it does not in GeTe. In GeS, 58
SR spectra showed that the muonium forms in GeS, while it does not in GeTe. In GeS, 58 of the muons formed muoniums. The activation energy was obtained as
of the muons formed muoniums. The activation energy was obtained as 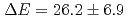 meV. The hyperfine coupling frequency was
meV. The hyperfine coupling frequency was 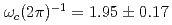 GHz, and the Bohr radius of muonium was 1.3 times larger than that in vacuum. These properties indicated that the identified muonium does not form a typical impurity level that affects the electrical properties.
GHz, and the Bohr radius of muonium was 1.3 times larger than that in vacuum. These properties indicated that the identified muonium does not form a typical impurity level that affects the electrical properties.
伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 下村 浩一郎*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(5), p.051007_1 - 051007_8, 2020/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:38.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Muonium (Mu) centers formed upon implantation of  in a solid have long been investigated as an experimentally accessible model of isolated hydrogen impurities. Recent discoveries of hydridic centers formed at oxygen vacancies have stimulated a renewed interest in H
in a solid have long been investigated as an experimentally accessible model of isolated hydrogen impurities. Recent discoveries of hydridic centers formed at oxygen vacancies have stimulated a renewed interest in H and corresponding Mu
and corresponding Mu centers in oxides. However, the two diamagnetic centers, Mu
centers in oxides. However, the two diamagnetic centers, Mu and Mu
and Mu , are difficult to separate spectroscopically. In this review article, we summarize established and developing methodologies for identifying Mu
, are difficult to separate spectroscopically. In this review article, we summarize established and developing methodologies for identifying Mu centers in solids, and review recent Mu studies on said centers supposedly formed in mayenite, oxygen-deficient SrTiO
centers in solids, and review recent Mu studies on said centers supposedly formed in mayenite, oxygen-deficient SrTiO , and BaTiO
, and BaTiO H
H oxyhydride.
oxyhydride.