Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(2), p.96 - 110, 2024/12
Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste requires not only selecting sites appropriate for the waste repository, where its isolation ability would not be damaged by natural phenomena for several tens of thousands of years, but also rationally constructing the disposal system depending on site-specific geological environments and their anticipated long-term variability. Recently, elemental/isotopic compositions of underground fluids (deep groundwaters, hot/cold spring waters, brines associated with oil and natural gas reservoirs, and so on) in Japan have been studied for evaluating the long-term stability of the geological environments of this country. Iodine and its radioactive isotope  I (half-life = 15.7 million years) are included in the subjects of the study. The current review paper provides overviews of (i) the iodine content and iodine-129/127 ratio (
I (half-life = 15.7 million years) are included in the subjects of the study. The current review paper provides overviews of (i) the iodine content and iodine-129/127 ratio ( I/
I/ I ratio) of various materials in Earth's surface layers, (ii) relevant sample pretreatments and measurements, and (iii)
I ratio) of various materials in Earth's surface layers, (ii) relevant sample pretreatments and measurements, and (iii)  I/
I/ I data of the underground fluids in Japan, then gives (iv) some interpretations of the fluid
I data of the underground fluids in Japan, then gives (iv) some interpretations of the fluid  I/
I/ I data, along with their problems and uncertainties, and (v) some implications towards evaluating the long-term stability of geological environments.
I data, along with their problems and uncertainties, and (v) some implications towards evaluating the long-term stability of geological environments.
Kamiya, Tomohiro; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of the Symposium on Shock Waves in Japan (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/03
We developed a ghost fluid method satisfying conservation laws to simulate steam explosions that can occur at the accident of a nuclear power plant. In the developed method, a first-order approximation is applied to interface effect regions, and a high-order approximation is applied to bulk regions. In other words, the algorithm of the developed method is not consistent. Therefore, we modify the way of getting ghost fluids and propose a comprehensive algorithm that applies a high-order approximation to interface effect regions. In the presentation, we will report the outlines and results of the numerical tests of it.
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Horiguchi, Naoki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Dai-29-Ki Sokai, Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/03
To reduce contaminated water at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and consider the fuel debris retrieval method, a numerical simulation method is required to evaluate the effects of water injection. Then, we are developing a multiphase CFD simulation method based on the three-dimensional two-fluid model to evaluate thermal-hydraulic behavior in the primary containment vessel. The numerical simulation method was developed by introducing the required functions into the ACE-3D. This paper presents an overview of the porous model introduced to the ACE-3D to evaluate thermal-hydraulic behavior in fuel debris. In addition, we performed the numerical simulation for the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant unit 2 under the condition in which water injection stopped. And we compared the analysis results by the modified ACE-3D with more detailed three-dimensional CFD results by JUPITER.
 /water nanofluid
/water nanofluidYoshida, Koji*; Sanada, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Matsuura, Masato*; Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 366, p.120218_1 - 120218_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.45(Chemistry, Physical)Uchibori, Akihiro; Shiina, Yoshimi*; Watanabe, Akira*; Takata, Takashi*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/03
An unstructured mesh-based analysis method has been integrated into the sodium-water reaction analysis code, SERAPHIM, in our recent studies. In this study, numerical analysis of an experiment on sodium-water reaction in a tube bundle domain was performed to investigate the effect of the unstructured mesh. The unrealistic behavior appeared in the coarse structured mesh was improved by the unstructured mesh. The numerical result in the case of the unstructured mesh reproduced the peak value of the temperature in the reacting flow.
Shimada, Koji; Goto, Akira; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimo, Michito*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 127(10), p.I - II, 2021/10
Continuous leaking point of high-temperature fluid (liquid/gas) from underground can be easily grasped by infrared images. We show images confirmed by a FLIR C5 camera that can simultaneously obtain an infrared image and a visible light image at the outcrops of Kawayu Onsen that naturally spring along the river. Outcrops and river surface temperature rise due to hot springs that leaking from riverbanks and riverbeds, rock temperature rise around cracks where gas containing high-concentration methane leaks with hot springs, abandoned fluid pathway due to construction of the bank and damming river for hot spring river bath in winter can be confirmed at a glance. Infrared images may be useful for quick identification of hot fluid leaking points from underground.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki; Yamada, Susumu; Yamashita, Susumu; Ina, Takuya*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Supa Kompyuteingu Nyusu, 22(5), p.18 - 29, 2020/09
A communication avoiding multigrid preconditioned conjugate gradient method (CAMGCG) is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in a multiphase CFD code JUPITER, and its computational performance and convergence property are compared against the conventional Krylov methods. The CAMGCG solver has robust convergence properties regardless of the problem size, and shows both communication reduction and convergence improvement, leading to higher performance gain than CA Krylov solvers, which achieve only the former. The CAMGCG solver is applied to extreme scale multiphase CFD simulations with 90 billion DOFs, and its performance is compared against the preconditioned CG solver. In this benchmark, the number of iterations is reduced to 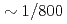 , and
, and 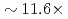 speedup is achieved with keeping excellent strong scaling up to 8,000 nodes on the Oakforest-PACS.
speedup is achieved with keeping excellent strong scaling up to 8,000 nodes on the Oakforest-PACS.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Koizumi, Yasuo; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Netsu Kogaku Konfuarensu 2018 Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
no abstracts in English
Uchibori, Akihiro; Watanabe, Akira*; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 84(859), p.17-00394_1 - 17-00394_6, 2018/03
For assessment of the wastage environment under tube failure accident in a steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactors, a mechanistic computer code called SERAPHIM calculating compressible multicomponent multiphase flow with sodium-water chemical reaction has been developed. The original SERAPHIM code is based on the finite difference method. In this study, unstructured mesh-based numerical method was developed and introduced into the SERAPHIM code to advance a numerical accuracy for the complex-shaped domain including multiple heat transfer tubes. Validity of the unstructured mesh-based SERAPHIM code was investigated through the analysis of an underexpanded jet experiment. The calculated pressure profile showed good agreement with the experimental data. Numerical analysis of water vapor discharging into liquid sodium was also performed. It was demonstrated that the proposed numerical method could be applicable to evaluation of the sodium-water reaction phenomenon.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Horiguchi, Naoki; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 84(859), p.17-00392_1 - 17-00392_10, 2018/03
no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.257 - 273, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.87(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)A preconditioned Chebyshev basis communication-avoiding conjugate gradient method (P-CBCG) is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in a multiphase thermal-hydraulic CFD code JUPITER, and its computational performance and convergence properties are compared against a preconditioned conjugate gradient (P-CG) method and a preconditioned communication-avoiding conjugate gradient (P-CACG) method on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8,208 KNLs. The P-CBCG method reduces the number of collective communications with keeping the robustness of convergence properties. Compared with the P-CACG method, an order of magnitude larger communication-avoiding steps are enabled by the improved robustness. It is shown that the P-CBCG method is 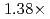 and
and 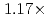 faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Koizumi, Yasuo; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Thermal Science and Engineering, 25(2), p.17 - 26, 2017/04
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Masaaki; Kobayashi, Jun; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*
Proceedings of OECD/NEA & IAEA Workshop on Application of CFD/CMFD Codes to Nuclear Reactor Safety and Design and their Experimental Validation (CFD4NRS-6) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2016/09
A numerical simulation code named MUGTHES which can deal with conjugate heat transfer problem between the fluid and the structure parts has been developed in order to predict the thermal response in the structure for estimation of the thermal fatigue issue. To perform fundamental validation of the MUGTHES, the benchmark simulation was considered using the experiment of planar triple parallel jets mixing sodium test (PLAJEST). Since it was known by literatures that three representative flow mixing patterns were shown in accordance with the velocity rate of the side jets to the center jet, three typical experimental conditions in the PLAJEST were employed as boundary conditions for the benchmark. Through the numerical simulations, applicability of the large eddy simulation (LES) approach with the standard Smagorinsky model to simulate thermal striping phenomena was confirmed.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Koizumi, Yasuo; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Dai-53-Kai Nihon Dennetsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2016/05
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9776, p.97762C_1 - 97762C_6, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.59(Optics)For the improvement of efficiency and output of the laser pumped plasma (LPP) extreme ultra-violet (EUV) light source, we present a hydrodynamics model of laser irradiated Sn targets. The model takes liquid/solid to gas transition and mixed phase condition of the flow into account for the calculation of the distribution of the particles produced by the pre-pulse laser irradiation and optimization of the EUV source. Firstly, we investigate the mechanisms of the fragmentation of the target and particle emission, including the effect of the equation of state of Sn, and secondly, an applicable model is proposed based on the analysis.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2015 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2015/11
A prototype coupling method consisting of the fluid-structure thermal interaction simulation code MUGTHES and the structural thermal stress analysis code FINAS with interface program MUFIN has been developed in order to estimate the thermal fatigue in the SFRs. As a fundamental validation of the coupled method, it was applied to the water experiment for thermal mixing phenomena in a T-junction piping system. In the experiment, thermal interaction between the fluid and the structure made of aluminum installed to the branch pipe side wall was considered. Through the numerical simulations, applicability of the coupled method was confirmed.
Togo, Satoshi*; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Nakamura, Makoto; Hoshino, Kazuo; Ogawa, Yuichi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.502 - 505, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A 1D SOL-divertor plasma simulation code introducing the anisotropic ion temperature with virtual divertor model has been developed. By introducing the anisotropic ion temperature directly, the second-derivative parallel ion viscosity term in the momentum transport equation can be excluded and the boundary condition at the divertor plate becomes unnecessary. In order to express the effects of the divertor plate and accompanying sheath implicitly, the virtual divertor model has been introduced which has an artificial sinks of particle, momentum and energy. The virtual divertor model makes the periodic boundary condition available. By using this model, SOL-divertor plasmas satisfying the Bohm condition has been successfully obtained. Also investigated are the dependence of the ion temperature anisotropy on the normalized mean free path of ion and the validity of the approximated parallel ion viscosity for the Braginskii expression and the limited one.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.6650 - 6663, 2015/08
For the fundamental validation of fluid-structure thermal interaction code (MUGTHES), numerical simulations for the planar triple parallel jets tests in WAJECO and PLAJEST have been conducted as the benchmark analysis. In comparison between the numerical results and the provided experimental results, thermal mixing process and large-scale eddy structures generated in the triple jets mixing and the relation between temperature fluctuation generation and large-eddy structures were revealed. And also, the attenuation process of temperature fluctuation from the fluid to the structure was indicated.
Sasaki, Akira; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Onishi, Naofumi*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 91(2), p.166 - 167, 2015/02
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Masaaki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Karakida, Yasuhisa*
Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Maintenance Science and Technology (ICMST-Kobe 2014), p.79 - 80, 2014/11
A coupled method of fluid-structure thermal interaction simulation and thermal stress analysis has been developed through the interface program to carry out direct numerical estimation of the thermal fatigue. The prototype method was applied to the thermal mixing phenomena in T-junction Piping System.