Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takasaki, Koji
Hokeikyo Nyusu, (73), p.2 - 5, 2024/04
The development of radiation measurement and digital technology for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, which is being conducted by the Remote System and Sensing Technology Division of CLADS, will be presented.
Ochi, Kotaro; Barker, E.*; Nakama, Shigeo; Gleizes, M.*; Manach, E.*; Vincent, F.*; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Disaster Research, 19(2), p.429 - 445, 2024/04
There are no clear criteria for standardizing mapping techniques for ambient dose equivalent rate (air dose rate) distributions in different countries. Thus, in this study, manborne, carborne, and airborne radiation surveys were conducted jointly by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency and the French Institute for Radiological Protection and Nuclear Safety in the vicinity of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station to confirm the effectiveness of each organization's monitoring methods. For example, in the manborne survey, the discrepancy between the air dose rates measured by the two institutions was observed depending on whether or not the contribution from radionuclides with different gamma-ray energies was considered when converting the count rates obtained by the detectors to air dose rates. As in this study, comparing mapping techniques among various countries and providing feedback to each other should help to improve the accuracy of zoning scenarios after nuclear accidents.
Kim, M.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.*; Abe, Tomohisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Machida, Masahiko; Saito, Kimiaki
Kankyo Hoshano Josen Gakkai-Shi, 12(2), p.39 - 53, 2024/04
More than ten years have passed since the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. But with the progress of decontamination, the evacuation order has been lifted and the return of residents is still ongoing. Under these circumstances, in order to quantitatively evaluate the effect of decontamination activities and cultivation on air dose rate reduction, a detailed environmental model was constructed using 3D-ADRES for a real area located in the Okuma town, Fukushima prefecture. Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the model to calculate realistic distributions of radioactive Cs based on measurement results and air dose rates reflecting changes over time. As a result, the distribution of air dose rates at 100 cm above ground level in the target area according to decontamination and cultivation activities was calculated. The calculated air dose rates reproduced the measured values well, and were confirmed to be appropriate as a method for evaluating the effects of decontamination and cultivation activities. This method is expected to serve as a reference for further decontamination management measures to reduce the air dose rate in the difficult-to-return zone, where entry is still restricted.
Yamada, Ippei; Chimura, Motoki; Kamiya, Junichiro; Kinsho, Michikazu
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072018_1 - 072018_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
Yasumiishi, Misa*; Masoudi, P.*; Nishimura, Taku*; Ochi, Kotaro; Ye, X.*; Aldstadt, J.*; Komissarov, M.*
Radiation Measurements, 168, p.106978_1 - 106978_16, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we surveyed air dose rates using hand-held and backpack-type scintillators in a forest of deciduous and evergreen trees in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The effects of topographic features on air dose rates were examined using multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) against five selected topographic parameters. The air dose rates were distributed unevenly in the forest, and air dose rates varied by more than 1 Sv/h as a function of time, likely owing to ground wetness etc. The effect of different topographic parameters varied between survey dates. The MARS model predictions with all topographic parameters yielded an R
Sv/h as a function of time, likely owing to ground wetness etc. The effect of different topographic parameters varied between survey dates. The MARS model predictions with all topographic parameters yielded an R of 0.54 or higher. To discuss whether the effect of topography on air dose rates and soil contamination levels is consistent, air dose rates measured in the field were compared with those estimated from the depth profile of radiocesium in soil. Most air dose rates estimated from the soil samples were in the range of field measurements.
of 0.54 or higher. To discuss whether the effect of topography on air dose rates and soil contamination levels is consistent, air dose rates measured in the field were compared with those estimated from the depth profile of radiocesium in soil. Most air dose rates estimated from the soil samples were in the range of field measurements.
Yamada, Taichi; Abe, Hiroyuki*; Ogane, Katsuji*; Kawabata, Kuniaki
ROBOMECH Journal (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2023/06
Although Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) has significant industrial potential, it is not easy to discuss how well UAS performs in places and situations where the UAS is deployed. Therefore, we designed the approach for UAS evaluation and developed the evaluation methods that make it possible to compare the UAS performances in easy-to-understand for UAS users, people without technical knowledge focusing on GNSS-denied environments. The development proceeded with the demonstration and discussion with UAS manufacturers and users, and we repeatedly improved the evaluation methods with their opinions. Finally, we confirm that the evaluation methods can describe the difference between the UAS's performance by an experiment.
Takahashi, Shigeo*; Sakurai, Daisuke*; Nagao, Fumiya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Sanada, Yukihisa
Shimyureshon, 42(2), p.68 - 75, 2023/06
This paper introduces a case in which scientific knowledge on understanding the deposition process of radionuclides and evaluating the dose rate reduction due to decontamination work was obtained through visual analysis based on data on the spatio-temporal distribution of air dose rates accumulated through radiation monitoring after the accident. We will discuss the prospects for future efforts to effectively obtain important knowledge that will assist in the planning of policies for reconstruction from the nuclear power plant accident in the future.
Takahashi, Shigeo*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sakurai, Daisuke*
ERAN FY2022 Annual Report (Internet), 1 Pages, 2023/04
This study aims to establish a highly accurate evaluation technique for decontamination effects through multilateral and quantitative evaluation of decontamination effects. The applicability of the visual analysis technique was confirmed through a trial analysis.
Kusakabe, Kazuaki*; Watanabe, Masanori; Nishiuchi, Masashi*; Yamasaki, Takuhei*; Inoue, Hiromi*
Kankyo Hoshano Josen Gakkai-Shi, 11(1), p.15 - 23, 2023/03
The spread of radioactive materials caused by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident that occurred in March 2011 contaminated a wide area that includes Fukushima Prefecture. Although air dose rates in Fukushima Prefecture have been steadily decreasing because of decontamination and the physical decay of radioactive materials, it is important to confirm the sustainability of decontamination effects in living areas and to predict future trends in air dose rates to reassure residents who are concerned regarding radiation exposure. This report aims to confirm the sustainability of the decontamination effects in public facilities after decontamination on a continuous and detailed basis, and to verify whether the future transition in air dose rates can be predicted using existing model. The air dose rates in public facilities after decontamination were measured via fixed-point and walking surveys, and the changes in air dose rates were clarified quantitatively for each facility. The measured values were compared with values obtained using existing model, and prediction accuracy was considered. The results showed that there was no evident recontamination after decontamination at any of the surveyed facilities, indicating that the decontamination effects were sustained. It was also confirmed that future trends in air dose rates at the facilities after decontamination could be accurately predicted by existing model. Key words: air dose rate, decontamination, future prediction, public facilities.
Ina, Takuya; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Onodera, Naoyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on High Performance Computing in Asia-Pacific Region (HPC Asia 2023) (Internet), p.29 - 34, 2023/02
Mixed precision Krylov solvers with the Jacobi preconditioner often show significant convergence degradation when the Jacobi preconditioner is computed in low precision such as FP16 and BF16. It is found that this convergence degradation is attributed to loss of diagonal dominance due to roundoff errors in data conversion. To resolve this issue, we propose a new data conversion method, which is designed to keep diagonal dominance of the original matrix data. The proposed method is tested by computing the Poisson equation using the conjugate gradient method, the general minimum residual method, and the biconjugate gradient stabilized method with the FP16/BF16 Jacobi preconditioner on NVIDIA V100 GPUs. Here, the new data conversion is implemented by switching the round-nearest, round-up, round-down, and round-towards-zero intrinsics in CUDA, and is called once before the main iteration. Therefore, the cost of the new data conversion is negligible. When the coefficients of matrix is continuously changed by scaling the linear system, the conventional data conversion based on the round-nearest intrinsic shows periodic changes of the convergence property depending on the difference of the roundoff errors between diagonal and off-diagonal coefficients. Here, the period and magnitude of the convergence degradation depend on the bit length of significand. On the other hand, the proposed data conversion method is shown to fully avoid the convergence degradation, and robust mixed precision computing is enabled for the Jacobi preconditioner without extra overheads.
Iida, Kazuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chang, L.-J.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.20663_1 - 20663_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.67(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Spin excitation of an ilmenite FeTiO powder sample is measured by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamic magnetic pair-density function
powder sample is measured by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamic magnetic pair-density function 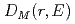 is obtained from the dynamic magnetic structure factor
is obtained from the dynamic magnetic structure factor 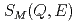 by the Fourier transformation.
by the Fourier transformation.
Suzuki, Gen*; Ishikawa, Tetsuo*; Oba, Takashi*; Hasegawa, Arifumi*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Miyatake, Hirokazu*; Yoshizawa, Nobuaki*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 63(6), p.796 - 804, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.92(Biology)To elucidate the association between radiation dose and thyroid cancer after the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident, it is essential to estimate individual thyroid equivalent doses (TEDs) to children. In a previous study, we reported a methodology for reconstructing TEDs from inhalation based on individual behavioural survey sheets combined with a spatiotemporal radionuclides database constructed by an atmospheric transport, diffusion, and deposition model (ATDM). In the present study, we further refined our methodology and estimated the combined TEDs from inhalation and ingestion among children in 16 municipalities around the nuclear power station utilizing 3,256 individual whereabouts questionnaire survey sheets. Distributions of estimated TEDs were similar to estimates based on direct thyroid measurements in 1080 children in Iwaki City, Kawamata Town, Iitate Village, and Minamisoma City. Mean TEDs in 1-year-old children ranged from 1.3 mSv in Date City to 14.9 mSv in Odaka Ward in Minamisoma City, and the 95th percentiles varied from 2.3 mSv in Date City to 28.8 mSv in Namie Town. In the future, this methodology can be useful for a case-control study of thyroid cancer after the FDNPS accident.
Chimura, Motoki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(6), p.063G01_1 - 063G01_26, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the low-energy region of a high-intensity ion linac, a strong space-charge field causes a rapid beam emittance growth over a short distance of only few meters. The beam emittance growth leads to a beam loss and the machine activation raising a serious issue for regular maintenance of the accelerator component and beam power ramp up. In this work, we studied the mechanism of beam emittance growth due to the space-charge field based on three-dimensional particle-tracking simulation and theoretical considerations. Numerical simulations done for the high-intensity linac at J-PARC shows that the nonlinear terms in the space-charge field directly cause a beam emittance growth and beam halo formation. Then, we also propose a method to mitigate the beam emittance growth by using an octupole magnetic field, which arises as one of the nonlinear terms in the space-charge field. By applying this method in the simulation, we have succeeded mitigating the beam emittance growth.
Ochi, Kotaro; Funaki, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sanada, Yukihisa
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 61(1), p.147 - 159, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.00(Biology)Ji, Y.-Y.*; Ochi, Kotaro; Hong, S. B.*; Nakama, Shigeo; Sanada, Yukihisa; Mikami, Satoshi
Health Physics, 121(6), p.613 - 620, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.00(Environmental Sciences)According to the implementing arrangement between JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) and KAERI (Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute) in the field of the radiation protection and environmental radiation monitoring, the joint measurement has been conducted to assess the radioactive cesium deposition in the ground around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (FDNPP). First, mobile gamma-ray spectrometry using backpack survey platform was conducted to assess the distribution of dose rate around specific three survey sites. The carborne survey using gamma-ray spectrometers, as loading inside a vehicle, was successfully conducted to compare measured dose rates in routes from site to site and verify evaluation methods including the attenuation correction.
Moriguchi, Yuichi*; Sato, Yosuke*; Morino, Yu*; Goto, Daisuke*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Terada, Hiroaki; Takigawa, Masayuki*; Tsuruta, Haruo*; Yamazawa, Hiromi*
KEK Proceedings 2021-2, p.21 - 27, 2021/12
no abstracts in English
Kim, M.; Malins, A.; Machida, Masahiko; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshida, Hiroko*; Yanagi, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*
RIST News, (67), p.3 - 15, 2021/09
no abstracts in English
Okabe, Kota; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Chimura, Motoki*; Hirano, Koichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011011_1 - 011011_6, 2021/03
To realize more stable operation of the J-PARC accelerators, we have a re-design plan of an MEBT1 (Medium Energy Beam Transport). At the J-PARC Linac, the MEBT1 has transverse and longitudinal beam matching section for the DTLs. However there are some locally activated spots in DTL area at the current beam power level. To reduce beam loss during a beam acceleration at the DTLs is a most important task for a stable user operation. The first thing we should do is investigation a connection between beam quality in the MEBT1 and parameters of the upstream hardware. In this presentation, we will report a high intensity beam study results at the MEBT1.
Saito, Kimiaki
Isotope News, (773), p.3 - 6, 2021/02
no abstracts in English
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.