Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7638 - 7643, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen glucose solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the glucose molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
Miyagawa, Reina*; Kamibayashi, Daisuke*; Nakamura, Hirotaka*; Hashida, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Somekawa, Toshihiro*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Ogura, Hiroyuki*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.20955_1 - 20955_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.69(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We evaluated Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structure (LIPSS) crystal structures using the stress imaging station at BL22XU of JAEA-BL on SPring-8. Crystallization of LIPPS was used different two types laser these are Ti:Sapphire laser (wavelength: 800 nm) and MIR-FEL (mid-infrared free electron laser, wavelength 11.4  m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20
m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20  m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Kato, Takenori*; Yokota, Rintaro*; Sasao, Eiji; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 192, p.104289_1 - 104289_16, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.44(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Quartz from a granitic pluton is found to have formed through sequential growth events under different mechanisms and crystallization temperatures, which can provide new insights into magmatic processes of granitic magmas that were eventually consolidified into plutons. The events were identified using (1) the description of crystal shape and occurrence, (2) the study of the internal structure with cathodoluminescence (CL), and (3) derivation of the crystallization temperatures based on TitaniQ thermometry. The magmatic quartz crystals from the Toki granite, central Japan, are characterized as having the following internal structures: oscillatory zonation, no-oscillatory zonation with luminescence graduation (gradational zonation), and heterogeneous CL. The quartz crystals with oscillatory zonation were formed in the temperature range of about 800  C to below 700
C to below 700  C, which is referred to as oscillatory zoning temperature (OZT) conditions. The CL zonation pattern was controlled by the temperature conditions and titanium diffusivity in the melt (magma). The crystallization process of quartz within the Toki granite reveals the cooling processes of the granitic pluton; the lithofacies with a high frequency of oscillatory-zoned quartz underwent slower cooling under the OZT conditions than those in other lithofacies.
C, which is referred to as oscillatory zoning temperature (OZT) conditions. The CL zonation pattern was controlled by the temperature conditions and titanium diffusivity in the melt (magma). The crystallization process of quartz within the Toki granite reveals the cooling processes of the granitic pluton; the lithofacies with a high frequency of oscillatory-zoned quartz underwent slower cooling under the OZT conditions than those in other lithofacies.
Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamazaki, Tatsuya*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Nihon Kessho Seicho Gakkai-Shi, 32(3), P. 160, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Asaoka, Hidehito; Cherepanov, V.*; Voigtl nder, B.*
nder, B.*
Surface Science, 588(1-3), p.19 - 25, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:68.25(Chemistry, Physical)We determined the average size of small Si and Ge clusters con ned to one half of a (7
ned to one half of a (7 7) or (5
7) or (5 5) unit cell of a Si or Ge(111) surface. The size of Si and Ge clusters con
5) unit cell of a Si or Ge(111) surface. The size of Si and Ge clusters con ned to a Si(111)-(7
ned to a Si(111)-(7 7) half unit cell was determined to be 8.3
7) half unit cell was determined to be 8.3 1 atoms and 7.5
1 atoms and 7.5 1 atoms, respectively for a growth temperature of 400 K. This is the same value within the error and shows, that the material of the clusters is less important for the cluster size. On the Ge surface it was found that the reconstruction unit cell is important for the cluster size. On the (5
1 atoms, respectively for a growth temperature of 400 K. This is the same value within the error and shows, that the material of the clusters is less important for the cluster size. On the Ge surface it was found that the reconstruction unit cell is important for the cluster size. On the (5 5) reconstructed Ge(111) surface the Si clusters have a smaller size of 4.7
5) reconstructed Ge(111) surface the Si clusters have a smaller size of 4.7 1 atoms compared to 8.2
1 atoms compared to 8.2 1 atoms for Si clusters on the Ge(111)-(7
1 atoms for Si clusters on the Ge(111)-(7 7) surface.
7) surface.
 Cu
Cu O
O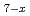 and its superconductive phase transition
and its superconductive phase transitionSuzuki, Takuya*; Takano, Hidekazu*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Kentaro*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Suzuki, Yoshio*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 36, p.249 - 257, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Huang, X.*; Mashimo, Tsutomu; Ono, Masao; Tomita, Takeshi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Mori, Nobuo*
Journal of Applied Physics, 96(3), p.1336 - 1340, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:46.55(Physics, Applied)Mega-gravity field experiments were performed on the Bi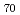 Sb
Sb (atomic percent) alloy and pure Bi below their melting points, to investigate the change in crystalline state. For the alloy centrifuged at 191-205
(atomic percent) alloy and pure Bi below their melting points, to investigate the change in crystalline state. For the alloy centrifuged at 191-205  C, no change in composition was observed, and the grain sizes of the crystals decreased from several mm to tens of
C, no change in composition was observed, and the grain sizes of the crystals decreased from several mm to tens of  m, while no distinct change in grain size was observed for the centrifuged pure Bi. The alloy centrifuged at 220-240
m, while no distinct change in grain size was observed for the centrifuged pure Bi. The alloy centrifuged at 220-240  C consisted of two regions with different morphologies-fine-grained crystals with grain sizes around tens of
C consisted of two regions with different morphologies-fine-grained crystals with grain sizes around tens of  m in the low gravity region, and large crystals with grain sizes several mm long and hundreds of
m in the low gravity region, and large crystals with grain sizes several mm long and hundreds of  m wide along the direction of gravity in the high gravity region, where sedimentation of atoms was confirmed. The large crystals with hexagonal structures were formed by preferential crystal growth roughly along the c axes, and a large strain that increased as the gravitational field increased existed inside these crystals. Formation of this anomalous crystal state might be correlated with the sedimentation of atoms.
m wide along the direction of gravity in the high gravity region, where sedimentation of atoms was confirmed. The large crystals with hexagonal structures were formed by preferential crystal growth roughly along the c axes, and a large strain that increased as the gravitational field increased existed inside these crystals. Formation of this anomalous crystal state might be correlated with the sedimentation of atoms.
Asaoka, Hidehito
KEK Proceedings 2004-5, p.52 - 53, 2004/08
no abstracts in English
Paul, N.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Voigtl nder, B.*
nder, B.*
Surface Science, 564(1-3), p.187 - 200, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.82(Chemistry, Physical)Using scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) the Ge epitaxy on a Bi terminated Si(111) surface is compared to the growth without surfactant. As soon as the 2 bilayer high wetting layer is completed with surfactant, Ge islands with a flat top and an underlying dislocation network occur. Elastic distortions due to the dislocation network result in periodic sub-Angstrom height undulations measured by the STM. In this case the Ge islands have the form of a mesa. With increasing Ge coverage, these mesas spread laterally. Beyond a Ge coverage of 10 bilayers, the Ge mesas have coalesced and further Ge deposition leads to a 2D layer-by-layer growth of Ge on Si(111). In epitaxy without the use of a surfactant as well, the formation of Ge islands with an underlying dislocation network is observed. However, in this case the Ge islands are much higher and show no tendency to coalesce. The partially relaxed islands coexist with another type of tall islands.
Paul, N.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Myslive ek, J.*; Voigtl
ek, J.*; Voigtl nder, B.*
nder, B.*
Physical Review B, 69(19), p.193402_1 - 193402_4, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:67.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We compare the initial stages of growth of Ge on Si(111) with Bi as a surfactant and without surfactant. At the beginning of growth, 3D islands with a strain relieving dislocation network at their base are formed in both growth systems. These islands can be regarded as seeds of a flat relaxed Ge layer on Si(111). However, such Ge layer forms at later stages of growth only in the growth with Bi surfactant, while the growing Ge layer without surfactant remains rough. What makes the dierence and the success of Bi surfactant mediated epitaxy is the lateral growth and coalescence of the seed islands that cover the entire surface within first 15 bilayers of Ge deposition. This happens due to a kinetic limitation of the incorporation of Ge into the growing layer in the presence of surfactant.
Wang, W. H.*; Okada, Taku; Wen, P.*; Wang, X. L.*; Pan, M. X.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; Utsumi, Wataru
Physical Review B, 68(18), p.184105_1 - 184105_6, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:79.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wang, Z. X.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; Pan, M. X.*; Wang, W. H.*; Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(35), p.5923 - 5932, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:73.85(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Arai, Shigeki; Chatake, Toshiyuki; Minezaki, Yoshiaki*; Niimura, Nobuo
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 58(Part 1), p.151 - 153, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:80.92(Biochemical Research Methods)no abstracts in English
Rong, L.*; Yamane, T.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of Crystal Growth, 217(1-2), p.161 - 169, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:84.02(Crystallography)no abstracts in English
Asaoka, Hidehito; Saiki, Koichiro*; Koma, Atsushi*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 284-288, p.2101 - 2102, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Saito, Tamotsu; Baba, Shinichi; Eto, Motokuni
JAERI-Research 99-070, p.21 - 0, 2000/01
no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo; Minezaki, Yoshiaki; ; Fujiwara, Satoru;
Journal of Crystal Growth, 200, p.265 - 270, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.98(Crystallography)no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo*
JAERI-Conf 96-001, 149 Pages, 1996/02
no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo*; Minezaki, Yoshiaki; ;
Journal of Crystal Growth, 154, p.136 - 144, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:97.51(Crystallography)no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo*; ; Minezaki, Yoshiaki;
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.745 - 747, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.55(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English