Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 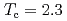 K for
K for 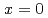 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 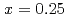 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 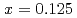 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 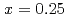 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 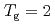 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 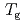 with a
with a 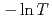 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
 Ge
Ge in the normal state
in the normal stateNakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Mori, Takeo*; Tsuruta, Atsushi*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Yasui, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(11), p.115160_1 - 115160_7, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) U M
U M ssbauer study on the magnetic properties of uranium-based heavy fermion superconductors
ssbauer study on the magnetic properties of uranium-based heavy fermion superconductorsTsutsui, Satoshi; Nakada, Masami; Nasu, Saburo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Homma, Tetsuo; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Okuni, Hitoshi*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Hyperfine Interactions, 126(1-4), p.335 - 340, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:37.56(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
 U M
U M ssbauer spectrosopic study of UPd
ssbauer spectrosopic study of UPd Al
Al and URu
and URu Si
Si
Tsutsui, Satoshi; Nakada, Masami; Nasu, Saburo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Homma, Tetsuo; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Okuni, Hitoshi*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 281-282, p.242 - 243, 2000/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:21.52(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Metoki, Naoto; Koike, Yoshihiro; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Homma, Tetsuo; Onuki, Yoshichika; Kimura, Noriaki*; Maezawa, Kunio*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 281-282, p.987 - 988, 2000/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.24(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Metoki, Naoto; Koike, Yoshihiro; Haga, Yoshinori; Homma, Tetsuo; Sato, Masugu; Onuki, Yoshichika
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 280(1-4), p.362 - 367, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:21.52(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 Si
Si studied by neutron scattering experiments
studied by neutron scattering experimentsHomma, Tetsuo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Metoki, Naoto; Koike, Yoshihiro*; Okuni, H.*; Suzuki, N.*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 68(2), p.338 - 341, 1999/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:86.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Metoki, Naoto; Koike, Yoshihiro*; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 259-261, p.660 - 661, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.94(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 Al
Al
Metoki, Naoto; Haga, Yoshinori; Koike, Yoshihiro*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Physical Review Letters, 80(24), p.5417 - 5420, 1998/06
Times Cited Count:98 Percentile:92.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Al
Al
Koike, Yoshihiro*; Metoki, Naoto; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika*; Morii, Yukio
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 241-243, p.823 - 825, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The Ni-substitutions of Co in the heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn are reported to suppress the superconductivity by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki Univ. To microscopically investigate the Ni doping effect, we have performed NMR study in the alloy system of Ce(Co, Ni)In
are reported to suppress the superconductivity by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki Univ. To microscopically investigate the Ni doping effect, we have performed NMR study in the alloy system of Ce(Co, Ni)In . We would like to discuss the spin fluctuations and the electronic state near the critical composition for the superconductivity in this system.
. We would like to discuss the spin fluctuations and the electronic state near the critical composition for the superconductivity in this system.
Sakai, Hironori
no journal, ,
Quantum criticalities tuned by pressure, external field, and chemical substitutions mark an important link in the heavy fermion superconductors. Systematic NMR investigations have suggested that 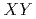 -type antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations are favorable for
-type antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations are favorable for  -wave superconductivity in 115 compounds. Recently, anisotropy of antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations is now being microscopically examined in several other tetragonal systems like CeRh
-wave superconductivity in 115 compounds. Recently, anisotropy of antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations is now being microscopically examined in several other tetragonal systems like CeRh Si
Si under pressures. Moreover, electrical inhomogeneity near quantum critical point is also detected in the chemically substituted CeCoIn
under pressures. Moreover, electrical inhomogeneity near quantum critical point is also detected in the chemically substituted CeCoIn .
.
 by example
by exampleSakai, Hironori
no journal, ,
In the heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn , dilute substitutions by Sn or Cd suppress the superconductivity or induce an antiferromagnetically ordered state. Such impurity effects have been microscopically investigated by nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) technique. While the Sn substituents weaken electronic correlations and suppress the superconductivity, the Cd substituents induce local moments closely around themselves but the bulk electronic state far from the substituents stays as in a pure CeCoIn
, dilute substitutions by Sn or Cd suppress the superconductivity or induce an antiferromagnetically ordered state. Such impurity effects have been microscopically investigated by nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) technique. While the Sn substituents weaken electronic correlations and suppress the superconductivity, the Cd substituents induce local moments closely around themselves but the bulk electronic state far from the substituents stays as in a pure CeCoIn . Such a heterogeneous electronic state in the Cd substituted system means a local breakage of Kondo hybridization by non-magnetic Cd substituents.
. Such a heterogeneous electronic state in the Cd substituted system means a local breakage of Kondo hybridization by non-magnetic Cd substituents.