Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion Science, 251, p.112897_1 - 112897_15, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Experimental and modeling studies of the oxygen ingression at the crevices of stainless steels were conducted in high-temperature water (288 C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression,
C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression, 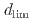 , was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite
, was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite  magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the
magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the 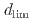 position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell.
position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell. 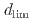 increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD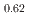 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 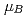 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD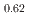 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized a crystalline graphane nanoribbon (GANR) via pressure-induced polymerization of 2,2'-bipyrazine (BPZ). By performing Rietveld refinement of in situ neutron diffraction data, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectra, and theoretical calculation, we found that BPZ experienced Diels-Alder polymerization between the 

 stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (
stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (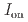 /
/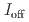 =18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
=18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 80(6), p.695 - 705, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)So far, the odd hydration number has been missing in the water-rich magnesium chloride hydrate series (MgCl

 H
H O). In this study, we have identified magnesium chloride heptahydrate, MgCl
O). In this study, we have identified magnesium chloride heptahydrate, MgCl
 7H
7H O (or MgCl
O (or MgCl
 7D
7D O) which forms at high pressures and high temperatures of above 2 GPa and above 300 K, respectively. Its structure has been determined by a combination of
O) which forms at high pressures and high temperatures of above 2 GPa and above 300 K, respectively. Its structure has been determined by a combination of  single crystal X-ray diffraction at 2.5 GPa and 298 K and powder neutron diffraction at 3.1 GPa and 300 K. The results showed an orientational disorder of water molecules, which was also examined by the density-functional-theory calculations. The disorder involves the reconnection of hydrogen bonds, which differs from those in water ice phases and known disordered salt hydrates. The shrinkage by compression occurs mainly in one direction. In the plane perpendicular to this most compressible direction, oxygen and chlorine atoms are in a hexagonal-like arrangement.
single crystal X-ray diffraction at 2.5 GPa and 298 K and powder neutron diffraction at 3.1 GPa and 300 K. The results showed an orientational disorder of water molecules, which was also examined by the density-functional-theory calculations. The disorder involves the reconnection of hydrogen bonds, which differs from those in water ice phases and known disordered salt hydrates. The shrinkage by compression occurs mainly in one direction. In the plane perpendicular to this most compressible direction, oxygen and chlorine atoms are in a hexagonal-like arrangement.
Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(12), p.618 - 622, 2024/12
, 66(12), p.618 - 622, 2024/12
The high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET is the first beamline dedicated to high-pressure neutron experiments in Japan. It was constructed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) located at Tokai-mura in Ibaraki Prefecture. Energy-dispersive data measurement using pulsed neutrons, state-of-the-art optical instruments, and a high-pressure device enable us to analyze the structure of crystals, liquids, and glasses over a wide range of pressure and temperature with unprecedented accuracy. In this paper, we will show how this has been achieved and introduce the recently published results on the symmetrization of hydrogen bonds in ice.
 S
S under pressure
under pressureKosaka, Yusuke*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 34(3), p.121 - 126, 2024/09
Transition-metal intercalated dichalcogenides have attracted attention due to the observation of chiral helimagnetism (CHM) and chiral soliton lattice in CrNb S
S . It forms a chiral monoaxial crystal structure with a space group P6
. It forms a chiral monoaxial crystal structure with a space group P6 22. To examine the pressure effect on the CHM period of CrNb
22. To examine the pressure effect on the CHM period of CrNb S
S , we performed small-angle neutron scattering experiments with a piston-cylinder pressure cell up to 1.2 GPa. We observed a decrease in the magnetic transition temperature with increasing pressure. Moreover, the CHM period decreased with increasing pressure. Compared to the decrease of the lattice constant, that of the CHM period is much larger. This indicates that applying pressure weakens the amplitude of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction.
, we performed small-angle neutron scattering experiments with a piston-cylinder pressure cell up to 1.2 GPa. We observed a decrease in the magnetic transition temperature with increasing pressure. Moreover, the CHM period decreased with increasing pressure. Compared to the decrease of the lattice constant, that of the CHM period is much larger. This indicates that applying pressure weakens the amplitude of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction.
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)High-pressure responses of the O-D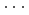 F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)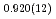 F
F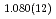 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.

Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (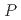
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 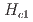 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 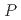 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
 O ice observed by neutron diffraction
O ice observed by neutron diffractionKomatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Klotz, S.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Yamashita, Keishiro*; Ito, Hayate*; Kobayashi, Hiroki*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5100_1 - 5100_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:67.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hydrogen bond symmetrisation is the phenomenon where a hydrogen atom is located at the centre of a hydrogen bond. Theoretical studies predict that hydrogen bonds in ice VII eventually undergo symmetrisation upon increasing pressure, involving nuclear quantum effect with significant isotope effect and drastic changes in the elastic properties through several intermediate states with varying hydrogen distribution. Despite numerous experimental studies conducted, the location of hydrogen and hence the transition pressures reported up to date remain inconsistent. Here we report the atomic distribution of deuterium in D O ice using neutron diffraction above 100 GPa and observe for the first time the transition from a bimodal to a unimodal distribution of deuterium at around 80 GPa. At the transition pressure, a significant narrowing of the peak widths of 110 was also observed, attributed to the structural relaxation by the change of elastic properties.
O ice using neutron diffraction above 100 GPa and observe for the first time the transition from a bimodal to a unimodal distribution of deuterium at around 80 GPa. At the transition pressure, a significant narrowing of the peak widths of 110 was also observed, attributed to the structural relaxation by the change of elastic properties.
Mori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Takano, Masahiro*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 634, p.118673_1 - 118673_8, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.61(Geochemistry & Geophysics)To investigate silicon effects on the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of iron, neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction experiments were conducted to examine hcp-Fe Si
Si under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe
under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe Si
Si at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe
at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe Si
Si , present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe
, present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe Si
Si is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,
is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,  , in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe
, in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe Si
Si Hx.
Hx.
Hattori, Takanori; Suzuki, Koji*; Miyo, Tatsuya*; Ito, Takayoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1059, p.168956_1 - 168956_9, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)Radial collimators (RC) with a 0.5 mm gauge size (GS) were specially designed for high-pressure neutron diffraction experiments and their performance and efficacy were investigated. The RCs with nominal GS of 0.75 mm, 1.5 mm, and 3.0 mm effectively exhibited GS of 0.50 mm, 1.07 mm, and 2.78 mm, respectively. The transmissions of all three RCs were almost equivalent. The assessment using a P-E press and a DAC revealed that the anvil scattering was considerably minimized and the sample-to-anvil signal ratio reached values of 0.5 and 2.0 for the PE press and DAC, respectively, when using the 0.5 mm-GS RCs. These results indicate that the 0.5mm-GS RCs have been fabricated as intended and exhibit efficacy for the high-pressure-neutron diffraction experiments, specifically those exceeding 30 GPa. Among those ever manufactured for neutron scattering experiments, the RCs display the smallest GS.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionKobayashi, Hiroki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ito, Hayate*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(47), p.10664 - 10669, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.29(Chemistry, Physical)Ice IV is a metastable high-pressure phase of ice in which the water molecules exhibit orientational disorder. Although orientational ordering is commonly observed for other ice phases, it has not been reported for ice IV. We conducted  powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D
powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Nakayama, Kazuya*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Munakata, Koji*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 79(5), p.414 - 426, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:41.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a recently-found hyperhydrated form of sodium chloride, NaCl 13H(D)
13H(D) O, has been determined by
O, has been determined by  single-crystal neutron diffraction at 1.7 GPa and 298 K. It has large hydrogen-bond networks and some water molecules have distorted bonding features such as bifurcated hydrogen bonds and five-coordinated water molecules. The hydrogen-bond network has similarities to ice VI in terms of network topology and disordered hydrogen bonds. Assuming the equivalence of network components connected by pseudo symmetries, the overall network structure of this hydrate can be expressed by breaking it down into smaller structural units which correspond to the ice VI network structure. This hydrogen-bond network contains orientational disorder of water molecules in contrast to the known salt hydrates. Here, we present an example for further insights into a hydrogen-bond network containing ionic species.
single-crystal neutron diffraction at 1.7 GPa and 298 K. It has large hydrogen-bond networks and some water molecules have distorted bonding features such as bifurcated hydrogen bonds and five-coordinated water molecules. The hydrogen-bond network has similarities to ice VI in terms of network topology and disordered hydrogen bonds. Assuming the equivalence of network components connected by pseudo symmetries, the overall network structure of this hydrate can be expressed by breaking it down into smaller structural units which correspond to the ice VI network structure. This hydrogen-bond network contains orientational disorder of water molecules in contrast to the known salt hydrates. Here, we present an example for further insights into a hydrogen-bond network containing ionic species.
Abeykoon, S.*; Howard, C.*; Dominijanni, S.*; Eberhard, L.*; Kurnosov, A.*; Frost, D. J.*; Boffa Ballaran, T.*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 128(9), p.e2023JB026710_1 - e2023JB026710_17, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.17(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Small amounts of iron sulphide minerals are found in most rocks from the Earth's mantle and as inclusions trapped in natural diamonds. Hydrogen may dissolve into iron sulphide minerals under high pressures and temperature, but is most likely lost once pressure and temperature are removed. In this study, we determined deuterium contents in iron sulphide, held under high pressure and temperature conditions, using neutron diffraction measurements with 6-ram multi-anvil press at PLANET, J-PARC. Deuterium contents in iron sulphide were measured at high-P, up to 11.4 GPa and high-T to 1300 K in in situ neutron diffraction experiments. The total deuterium content increases with both P and T. The results are used to estimate hydrogen contents of iron sulphide minerals in the deep continental lithospheric mantle, which are found to be in the range 1700-2700 ppm. This corresponds to approximately 2-3 ppm of hydrogen in the bulk mantle.
 Ni
Ni D
D at high
at high 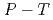 conditions
conditionsShito, Chikara*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Abe, Jun*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
American Mineralogist, 108(4), p.659 - 666, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:68.90(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The phase relation and crystal structure of Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D ) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under
) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under 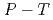 conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal (
conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal ( ) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe
) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe Ni
Ni D
D unlike fcc FeH
unlike fcc FeH (D
(D ). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium
). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium 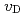 was determined as 2.45(4)
was determined as 2.45(4) 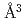 and 3.31(6)
and 3.31(6) 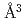 for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD
for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD . The
. The 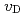 value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that
value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that 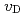 is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Yoshida, Koji*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 365, p.120181_1 - 120181_10, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.89(Chemistry, Physical)Neutron scattering measurements were performed on an aqueous 3 mol/kg NaCl solution in D O at temperature and pressure conditions of 0.1 MPa/298K, 1 GPa/298K, 1 GPa/523K, and 4 GPa/523K. The empirical potential structure refinement method was applied to the obtained data to extract the pair correlation function, coordination number distribution, angular distribution (orientation correlation), and spatial density function (3-D structure). From those results, pressure and temperature dependence of solvation and association of ions and solvent-water structure were discussed.
O at temperature and pressure conditions of 0.1 MPa/298K, 1 GPa/298K, 1 GPa/523K, and 4 GPa/523K. The empirical potential structure refinement method was applied to the obtained data to extract the pair correlation function, coordination number distribution, angular distribution (orientation correlation), and spatial density function (3-D structure). From those results, pressure and temperature dependence of solvation and association of ions and solvent-water structure were discussed.
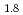 and TiH
and TiH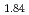 up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering
up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scatteringHattori, Takanori; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134309_1 - 134309_9, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen vibration excitations of fluorite-type ZrH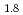 and TiH
and TiH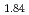 were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations
were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations 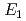 (meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2)
(meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2) (GPa) and
(GPa) and 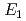 (meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8)
(meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8) (GPa) for ZrH
(GPa) for ZrH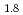 and TiH
and TiH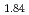 , respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (
, respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (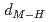 ) and
) and 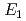 are found to be well described by the equations
are found to be well described by the equations 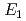 (meV) = 1.62(9)
(meV) = 1.62(9) 10
10
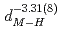 (
(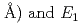 (meV) = 1.47(21)
(meV) = 1.47(21) 10
10
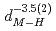 (AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
(AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
 Fe
Fe O
O solid solutions under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions
solid solutions under high-pressure and high-temperature conditionsYamanaka, Takamitsu*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Nakamoto, Yuki*; Mikouchi, Takashi*; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Mao, H.-K.*
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 49(10), p.41_1 - 41_14, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:7.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic and crystal structure of Mn Fe
Fe O
O solid solutions under high-PT conditions are investigated by neutron diffraction and synchrotron M
solid solutions under high-PT conditions are investigated by neutron diffraction and synchrotron M ssbauer spectroscopy. The ferrimagnetic-paramagnetic transition and tetragonal-cubic transition of Mn
ssbauer spectroscopy. The ferrimagnetic-paramagnetic transition and tetragonal-cubic transition of Mn FeO
FeO spinel occur at 100
spinel occur at 100 C and 180
C and 180 C, respectively, suggesting both the transitions are not coupled. The structure transition temperature decreases with pressure. M
C, respectively, suggesting both the transitions are not coupled. The structure transition temperature decreases with pressure. M ssbauer experiments and neutron diffraction revealed that the Fe
ssbauer experiments and neutron diffraction revealed that the Fe occupancy in tetrahedral site increases increase with pressure, suggesting Mn
occupancy in tetrahedral site increases increase with pressure, suggesting Mn FeO
FeO phase approaches inverse spinel. Magnetic structure refinement clarified paramagnetic and ferrimagnetic structure of MnFe
phase approaches inverse spinel. Magnetic structure refinement clarified paramagnetic and ferrimagnetic structure of MnFe O
O and Mn
and Mn FeO
FeO . These spinels transform into high-pressure orthorhombic phases at 18.4 and 14.0 GPa, respectively, indicating lower transition pressure with increasing Mn content.
. These spinels transform into high-pressure orthorhombic phases at 18.4 and 14.0 GPa, respectively, indicating lower transition pressure with increasing Mn content.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Klotz, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Fern ndez-D
ndez-D az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(40), p.e2208717119_1 - e2208717119_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here we present the first elucidation of the disordered structure of ice VII, the dominant high-pressure form of water, at 2.2 GPa and 298 K from both single-crystal and powder neutron diffraction techniques. We reveal the three-dimensional atomic distributions from the maximum entropy method and unexpectedly find a ring-like distribution of hydrogen in contrast to the commonly-accepted discrete sites. In addition, total scattering analysis at 274 K clarified the difference in the intermolecular structure from ice VIII, the ordered counterpart of ice VII, despite an identical molecular geometry. Our complementary structure analyses robustly demonstrate the unique disordered structure of ice VII. Furthermore, these noble findings are related to the proton dynamics which drastically vary with pressure, and will contribute to an understanding of the structural origin of anomalous physical properties of ice VII under pressures.
 Fe
Fe O
O spinel and postspinel with elevating pressure
spinel and postspinel with elevating pressureYamanaka, Takamitsu*; Rahman, S.*; Nakamoto, Yuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Jang, B. G.*; Kim, D. Y.*; Mao, H.-K.*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 167, p.110721_1 - 110721_10, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)High-pressure neutron diffraction proved that MnFe O
O and Mn
and Mn FeO
FeO spinels transform into CaMn
spinels transform into CaMn O
O -type structure above 18 GPa and 14 GPa, respectively. The transition pressure of Mn
-type structure above 18 GPa and 14 GPa, respectively. The transition pressure of Mn Fe
Fe O
O solutions decreases with increasing Mn content. Synchrotron X-ray M
solutions decreases with increasing Mn content. Synchrotron X-ray M ssbauer experiments revealed that Fe
ssbauer experiments revealed that Fe and Fe
and Fe distribution at the tetrahedral (A) and octahedral (B) sites in the spinel structure changes with pressure. MnFe
distribution at the tetrahedral (A) and octahedral (B) sites in the spinel structure changes with pressure. MnFe O
O and Mn
and Mn FeO
FeO spinels are ferrimagnetic and the CaMn
spinels are ferrimagnetic and the CaMn O
O -type phase is paramagnetic. The temperature dependence of resistivity indicates that both spinels are semiconductors wherein electrons hop between cations at the A and B sites. A pressure-induced shortening of B-B distance promoted conduction via greater electron mobility between adjacent B cations. The Fe
-type phase is paramagnetic. The temperature dependence of resistivity indicates that both spinels are semiconductors wherein electrons hop between cations at the A and B sites. A pressure-induced shortening of B-B distance promoted conduction via greater electron mobility between adjacent B cations. The Fe and Fe
and Fe occupancies at the B sites in MnFe
occupancies at the B sites in MnFe O
O are much larger than those in Mn
are much larger than those in Mn FeO
FeO . The CaMn
. The CaMn O
O -type phase is metallic. Theoretical calculation confirmed the metallic character and Fe d-orbitals strongly renormalized compared to Mn d-orbitals.
-type phase is metallic. Theoretical calculation confirmed the metallic character and Fe d-orbitals strongly renormalized compared to Mn d-orbitals.