Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Liu, W.; Tamai, Hidesada; Onuki, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Sato, Takashi; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2005/05
A major concern in the design of RMWR is that sufficient cooling capability be provided to keep fuel cladding temperature below specified values, even for a postulated abnormal transient process. In this research, centered the postulated transient cases that may be possibly met in the RMWR running, transient BT tests are performed in 7-rod and 37-rod double-humped tight lattice bundles, under the RMWR nominal operating condition (P = 7.2 MPa, Tin =556 K) for mass velocity G = 300 - 800 kg / (m s). Experiments are analyzed with TRAC code, in which JAERI critical power correlation is implemented for BT judgment. The traditional quasi-steady-state prediction of BT in transient process is confirmed being applicable for the postulated nominal transients in the RMWR cores.
s). Experiments are analyzed with TRAC code, in which JAERI critical power correlation is implemented for BT judgment. The traditional quasi-steady-state prediction of BT in transient process is confirmed being applicable for the postulated nominal transients in the RMWR cores.
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(1), p.40 - 49, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this research, critical power correlation for tight-lattice rod bundles is newly proposed using 7-rod axially uniform-heated data, 7-rod and 37-rod axially double-humped-heated data at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). For low mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region (
s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m
s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Akimoto, Hajime
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.299 - 305, 2004/05
Experimental research on critical power in tight lattice bundle that simulates the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) has been carried out in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The bundle consists one center rod and six peripheral rods. The 7 rods are arranged on a 14.3 mm equilateral triangular pitch. Each rod is 13 mm in outside diameter. An axial 12-step power distribution is employed to simulate the complicate heating condition in RMWR. Experiments are carried out under  = 100-1400 kg/m
= 100-1400 kg/m s,
s, 
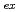 = 2-8.5 MPa. Effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure, radial peaking factor and axial peaking factor on critical power and critical quality are discussed. Compared with axial uniform heating condition, the axial non-uniform heating condition causes an obvious decrease in critical quality. Arai correlation, which is the only correlation that has been optimized for tight lattice condition, is verified with the present experimental data. The correlation is found to be able to give reasonable prediction only around RMWR nominal operating condition.
= 2-8.5 MPa. Effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure, radial peaking factor and axial peaking factor on critical power and critical quality are discussed. Compared with axial uniform heating condition, the axial non-uniform heating condition causes an obvious decrease in critical quality. Arai correlation, which is the only correlation that has been optimized for tight lattice condition, is verified with the present experimental data. The correlation is found to be able to give reasonable prediction only around RMWR nominal operating condition.