Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ide, Shunsuke; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 45(10), p.S48 - S62, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:82.57(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Ide, Shunsuke
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(10), p.773 - 778, 2005/10
In steady-state tokamak fusion reactors, an efficient external current drive and a large fraction of the bootstrap current are required for non-inductive operation at low circulating power. NBI is a powerful and reliable actuator for current drive and heating. A negative ion-based NBI (N-NBI) with a high beam energy more than 350 keV has been installed in the JT-60U tokamak in order to study the NBI current drive and heating in an ITER relevant regime. This paper presents recent progress of N-NBI experiments and its system in JT-60U towards steady-state operation for ITER and tokamak fusion reactors.
Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Naito, Osamu; Tsuda, Takashi; Kurita, Genichi; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 45(9), p.1101 - 1108, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:13.77(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Evolution of the current density profile associated with magnetic island formation in a neoclassical tearing mode plasma was measured for the first time in JT-60U by. As the island grew, the current density profile turned flat at the radial region of the island, followed by an appearance of a hollow structure. As the island shrank, the deformed region became narrower, and it finally diminished after the disappearance of the island. In an MHD-quiescent plasma, on the other hand, no deformation was observed. The observed deformation in the current density profile associated with the tearing mode is reproduced in a time dependent transport simulation assuming reduction of the bootstrap current in the radial region of the island. Comparison of the measurement with a calculated steady-state solution also explains the temporal behaviors of the current density and safety factor profiles with reduction and recovery of the bootstrap current. From the experimental observation and simulations, we reach conclusion that the bootstrap current decreases within the island O-point.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.933 - 941, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.62(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have investigated profile formation and sustainment of current hole (CH) plasma by 1.5D transport simulations with current limit model inside CH based on Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium. Sharp reduction of anomalous transport in RS region can reproduce JT-60U experiments. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in autonomous profile formation of ITB and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling. The scaling means that core plasma inside ITB is governed by MHD equilibrium limit, i.e., autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to penetration of inductive current. This shrink is prevented and CH size can be controlled by appropriate external CD. CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD. Application of CH plasma to reactor is discussed.
Kishimoto, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ninomiya, Hiromasa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.986 - 1023, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:27.12(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The Japanese large tokamak JT-60 has been focusing its research emphases to develop a high performance plasma, namely high confinement, high temperature and high density, and to sustain it non-inductively for a long time with possible minimization of external power input. The first demonstration of high bootstrap current discharges in a high-poloidal-beta mode (high- p) and the concept development of a steady-state tokamak reactor SSTR based on this experimental achievement initiated the so-called "advanced tokamak research". The first observation of internal transport barriers in the JT-60 high-
p) and the concept development of a steady-state tokamak reactor SSTR based on this experimental achievement initiated the so-called "advanced tokamak research". The first observation of internal transport barriers in the JT-60 high- p mode was followed by the world-wide explorations of reversed shear discharges associated with internal transport barriers. The advanced tokamak research is now the major trend of the current tokamak development. A new concept of compact ITER was developed and proposed in the context of this advanced tokamak approach pursued on JT-60.
p mode was followed by the world-wide explorations of reversed shear discharges associated with internal transport barriers. The advanced tokamak research is now the major trend of the current tokamak development. A new concept of compact ITER was developed and proposed in the context of this advanced tokamak approach pursued on JT-60.
Oikawa, Toshihiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Tsuda, Takashi; Kurita, Genichi
Physical Review Letters, 94(12), p.125003_1 - 125003_4, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:54.98(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Evolution of the current density profile associated with the magnetic island formation during a tearing mode was measured for the first time in the JT-60U tokamak. With the island growth, the current density profile turned flat at the radial region of the island, followed by appearance of a hollow structure. As the island shrank, the flat region became narrower, and it finally diminished after disappearance of the island. It was also observed that the local poloidal magnetic field fluctuated in correlation with the island rotation. This indicates that the observed deformation in the current density profile is localized in the O-point of the island. The result is the first experimental demonstration of theoretical predictions on the current density evolution in tearing modes.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
Profile formation and sustainment of tokamak plasmas with current hole (CH) have been investigated by using 1.5D transport simulations. A current limit model inside CH based on the Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium is introduced. We found that the sharp reduction of anomalous transport in the reversed-shear (RS) region can reproduce JT-60U experiment. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in the autonomous formation of internal transport barrier (ITB) and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling, which means autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with the full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to inductive current penetration. This shrink is prevented and the CH size can be controlled by appropriate external current drive (CD). The CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD.
Sengoku, Seio
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(11), p.940 - 943, 2004/11
Recent spherical tokamak (ST) experiments exhibit many advantageous results including plasma start-up without center solenoid, higher fraction of non-inductive current, formation of internal thermal-barrier as seen on conventional tokamak. In order to reflect these efforts on the design of so called "non-inductive steady-state (SS) operation scenario" and "current ramp-up scenario" of low-aspect reactor, fractions of bootstrap current and neutral-beam-driven current on VECTOR-OPT reactor are estimated. The operation with this SS scenario is shown to be feasible if the normalized beta,  n, is raised to grater than 5 typical in ST.
n, is raised to grater than 5 typical in ST.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Science and Technology, 45(4), p.521 - 528, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The 1.5D time-dependent transport analysis has been carried out to investigate steady state operation scenarios with a central current hole by off-axis current drive schemes consistent with a high bootstrap current fraction for a large superconducting tokamak JT-60SC. A steady state operation scenario with HH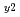 =1.4 and
=1.4 and 
 =3.7 has been obtained at I
=3.7 has been obtained at I =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B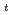 =2 T and q
=2 T and q =5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about
=5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about 
 =4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
=4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Kurita, Genichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Sakurai, Shinji; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(3), p.2281 - 2285, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High performance steady-state operation for JT-60SC are evaluated by the TOPICS analysis. 

 5 and bootstrap current fraction
5 and bootstrap current fraction  86% is kept steady at I
86% is kept steady at I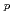 =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B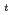 =2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at
=2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at 

 5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
 accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I
accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I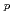 /aB
/aB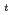 )q
)q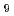
 and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from
and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from  4 to
4 to  6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.98(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Naito, Osamu; Matsuoka, Mamoru*; Kondoh, Takashi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.255 - 277, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:12.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on non-inductive current drive and development of an integrated steady-state high performance operation in JT-60 are reviewed. Experiments on lower hybrid current drive in JT-60 haven shown a large non-inductive current up to 3.5MA, high current drive efficiency of 3.6x1019m-2A/W. Basic studies on LH waves in JT-60 have contributed to understand current drive physics. Significant progress in neutral beam current drive has been made in JT-60 by testing the performance of negative ion based NBI (N-NBI). The CD efficiency of ~1.5x1019m-2A /W, and N-NB driven current of ~1MA have been demonstrated in N-NBCD. Strongly localized driven current by electron cyclotron current drive was identified with a fundamental O-mode scheme. Efficiency of 0.5x1019m-2A/W and EC driven current of 0.2MA were achieved and suppression of neo-classical tearing mode was demonstrated. Based on these developments, two integrated steady-state operation scenarios were developed in JT-60, which are reversed magnetic shear (R/S) plasmas and high bp ELMy H-mode. In these operation regimes, discharges have been sustained near the steady-state current profile under full non-inductive current drive. High performance plasmas with a high nDotETio and at high normalized density were also produced under fully non-inductive condition in high bp ELMy H-mode and R/S mode.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Proceedings of 29th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 4 Pages, 2002/00
This paper presents the feasibility and issues of steady state operation with a central current hole for JT-60SC, the superconducting tokamak to be modified from JT-60, from the view of reactor applicability of the current hole. An impact of the current hole on fusion engineering would stand in no necessity of central current drive leading to a remarkable reduction of neutral beam injection energy. The 1.5D time-dependent transport code analysis is made with using thermal and particle transport coefficients deduced from observations in JT-60U as a function of the magnetic shear. A steady state operation with HHy2~1.6 and beta_N~4 is obtained at Ip=1.5 MA, Bt=2 T and q95=4.5 by off-axis beams of 11.2 MW. The bootstrap fraction of ~75% of the plasma current and the current hole region of ~30% of the minor radius are sustained up to 70 s. The results suggest that a bootstrap current evolution near the current hole region and a relation between the location of ITB and the central current hole region are important to achieve a steady state plasma compatible with the current hole.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Isayama, Akihiko
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 77(5), p.409 - 419, 2001/05
Neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) which are induced by lack of the bootstrap current inside the magnetic island are reviewed based on the modified Rutherford equation. Theoretical bases and experimental observations of NTM are described. The beta value scaling of the growth of NTM and the mechanism of the growth are discussed. Influence of NTM on energy confinement is described, and the stabilization of NTM by electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) is introduced.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurita, Genichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 53(1-4), p.65 - 69, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ozeki, Takahisa; Azumi, Masafumi; Ishii, Yasutomo; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; G.Y.Fu*; Fujita, Takaaki; G.Rewoldt*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 39(5A), p.A371 - A380, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Kondoh, Takashi; JT-60 Team
Physics of Plasmas, 1(5), p.1489 - 1496, 1994/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:56.69(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nishitani, Takeo; Ishida, Shinichi; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Azumi, Masafumi; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Kawano, Yasunori; Koide, Yoshihiko; Hatae, Takaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 34(8), p.1069 - 1079, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:68.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Matsuoka, Mamoru; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tsuji, Shunji; Nishitani, Takeo; Koide, Yoshihiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Fujita, Takaaki; Nakamura, Hiroo; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research 1992, Vol.1, p.219 - 233, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Koide, Yoshihiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tsuji, Shunji; Shirai, Hiroshi; Naito, Osamu; Azumi, Masafumi
Physical Review Letters, 68(10), p.1531 - 1534, 1992/03
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:87.06(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English