Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizuta, Naoki; Aoki, Takeshi; Ueta, Shohei; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/05
Enhancement of safety and cooling performance of fuel elements are desired for a commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). Applying sleeveless fuel elements and dual side directly cooling structures with oxidation resistant SiC-matrix fuel compact has a possibility of improving safety and cooling performance at the pin-in-block type HTGR. The irradiated effective thermal conductivity of a fuel compact is an important physical property for core thermal design of the pin-in-block type HTGR. In order to discuss the irradiated effective thermal conductivity of the SiC-matrix fuel compact which could improve the cooling performance of the reactor, the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation of the pin-in-block type HTGR with dual side directly cooling structures are analytically evaluated. From these results, the desired irradiated thermal conductivity of SiC matrix are discussed. In addition, the suitable fabrication method of SiC-matrix fuel compact is examined from viewpoints of the sintering temperature, the purity and the mass productivity.
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Goto, Minoru; Takada, Shoji
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 103, p.114 - 121, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2005/05
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions were evaluated for a BWR Mk-II model plant. The evaluation was made for two scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area, or in the suppression pool. A probabilistic approach, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS), was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The fragility curves connecting the steam explosion loads and containment failure were developed based on simplified assumptions on the containment failure scenarios. The mean conditional probabilities of containment failure per occurrence of a steam explosion were 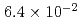 for suppression pool and
for suppression pool and 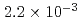 for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
;
Nuclear Technology, 81, p.7 - 12, 1988/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:39.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 84-172, 290 Pages, 1984/09
no abstracts in English
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Goto, Minoru; Takada, Shoji
no journal, ,
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Goto, Minoru; Takada, Shoji; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
no journal, ,
Coated fuel particles (CFPs) play an important role to the passive safety feature of the high temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR). However, random distribution of the CFPs also makes the simulation become more difficult and therefore affects the quality of the HTGR benchmark assessment. The highly accurate calculation enables the design of a commercial HTGR to operate with low cost and high performance. The purpose of this study was to develop MCNP model for the HTTR by using the explicit random model, namely Realized Random Packing (RRP), to improve the accuracy of the benchmark assessment. The RRP model was validated by comparing with the conventional uniform model as well as the experimental data. The neutronic and criticality calculations were performed by using MCNP6 code with ENDF/B-VII.1 nuclear data library.