Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Fukushima University*
JAEA-Review 2025-002, 108 Pages, 2025/07
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of methodology combining chemical analysis technology with informatics technology to understand perspectives property of debris and tie-up style human resource development" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. The present study aims to Goal of this study is to implement a research plan relate to a development of combinational technology of new chemical analysis with informatics, and the aim is to develop new system for whole image estimation system using small quantities of information. Conducting the collaboration study with JAEA researchers (tie-up style) make connect to the development of human resource from master's course student to post-doctoral researchers who are progress in the local-based and/or many academics fields research. We are in progress to grow international-minded human resources.
Mochizuki, Akihito; Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Shibata, Masahito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 22, p.e04648_1 - e04648_20, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)The properties of low-pH cement used in the geological disposal of radioactive waste may change through atmospheric carbonation and degradation caused by groundwater during the long-term operation of a repository. In this study, we investigated the effects of atmospheric carbonation and groundwater contact on the chemical, microstructural, and transport properties of shotcrete made from low-pH, high-fly-ash silica-fume cement (HFSC) over a period of 16 years in an underground research laboratory. In both carbonated and degraded zones of the HFSC shotcrete, capillary porosity increased for pores of  300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEA has been creating input data for pressurized water reactor (PWR) analysis with RELAP5/MOD3.3 code, mainly based on design information for the four-loop PWR's Tsuruga Power Station Unit-2 as the reference reactor of the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF). The cold leg large-break loss-of-coolant accident (LBLOCA) calculation in the flamework of the BEMUSE program is cited as a representative OECD/NEA activity related to the PWR analysis. The new regulatory requirements for PWRs in Japan include the event of loss of recirculation functions from emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in the cold leg LBLOCA. This event should be evaluated the effectiveness of measures against severe core damage. The input data for this study were made preparations to analyze the PWR LBLOCA, which is one of the design basis accidents that should be postulated in the safety design. This report describes the main features of the input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis. The PWR model comprised a reactor vessel, pressurizer (PZR), hot legs, steam generators (SGs), SG secondary-side system, crossover legs, cold legs, and ECCS. A four-loop PWR was simulated by two loops in the LBLOCA calculation. Specifically, loop-A attached with the PZR corresponded to three loops, and loop-B mounted with the break was equal to one loop. The nodalization schemes of the PWR components were referred to those of the LSTF components. Moreover, interpretations were added to the main input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis, and further information such as the basis for determining the input data was provided. In addition, transient analysis was performed employing the prepared input data for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event. The present transient analysis was confirmed to be appropriate generally by comparing with the calculation in the previous study using the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses were executed exploiting the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code to clarify the effects of a discharge coefficient through the break and water injection flow rate of the alternative recirculation on the fuel rod cladding surface temperature. This report explains the results of the sensitivity analyses within the defined ranges, which complement some of the content of the previous study's calculation for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event.
Iwasawa, Yuzuru; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Moriyama, Kiyofumi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-001, 199 Pages, 2025/06
A steam explosion is defined as a phenomenon that occurs when a hot liquid comes into contact with a low-temperature cold liquid with volatile properties. The rapid transfer of heat from the hot liquid to the cold liquid results in a chain reaction of the explosive vaporization of the cold liquid and fine fragmentation of the hot liquid. The explosive vaporization of the cold liquid initiates the propagation of shock waves in the cold liquid. The expansion of the hot and cold liquid mixture exerts mechanical forces on the surrounding structures. In severe accidents of light water reactors, the molten core (melt) is displaced into the coolant water, resulting in fuel-coolant interactions (FCIs). The explosive FCI, referred to as a steam explosion, has been identified as a significant safety assessment issue as it can compromise the integrity of the primary containment vessel. The JASMINE code is an analytical tool developed to evaluate the mechanical forces imposed by steam explosions in nuclear reactors. It performs numerical simulations of steam explosions in a mechanistic manner. The present report describes modeling concepts, basic equations, numerical solutions, and example simulations, as well as instructions for input preparation, code execution, and the use of supporting tools for practical purpose. The present report is the updated version of the "Steam Explosion Simulation Code JASMINE v.3 User's Guide, JAEA-Data/ Code 2008-014". The present report was compiled and updated based on the latest version of the code, JASMINE 3.3c, with corrections for minor errors of the distributed code JASMINE 3.3b, and conformance to recently widely used compilers on UNIX-like environments such as the GNU compiler. The numerical simulations described in the present report were obtained using the latest version JASMINE 3.3c. The latest parameter adjustment method for a model parameter proposed by the previous study is employed to conduct the numerical simulations.
Birkholzer, J. T.*; Graupner, B. J.*; Harrington, J.*; Jayne, R.*; Kolditz, O.*; Kuhlman, K. L.*; LaForce, T.*; Leone, R. C.*; Mariner, P. E.*; McDermott, C.*; et al.
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100685_1 - 100685_17, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Sugita, Yutaka; Ono, Hirokazu; Beese, S.*; Pan, P.*; Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Jove-Colon, C.*; Lopez, C. M.*; Liang, S.-Y.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100668_1 - 100668_21, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)The international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2023 focused on the Horonobe EBS experiment in the Task D, which was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (or thermo-hydro) interactions in bentonite based engineered barriers. One full-scale in-situ experiment and four laboratory experiments, largely complementary, were selected for modelling. The Horonobe EBS experiment is a temperature-controlled non-isothermal experiment combined with artificial groundwater injection. The Horonobe EBS experiment consists of the heating and cooling phases. Six research teams performed the THM or TH (depended on research team approach) numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws.
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Takei, Hayanori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45 Pages, 2025/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is working on the research and development of an accelerator-driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS) for transmuting minor actinides. This system combines a subcritical nuclear reactor with a high-power superconducting proton linear accelerator (JADS-linac). One of the factors limiting the advancement of the JADS-linac is beam trips, which often induce thermal cycle fatigue, thereby damaging the components in the subcritical core. The average beam current of the JADS-linac is 32 times higher than that of the linear accelerator (linac) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Therefore, according to the development stage, comparing the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac with the allowable beam trip frequency (ABTF) is necessary. Herein the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac was estimated through a Monte Carlo program using the reliability functions based on the operational data of the J-PARC linac. The Monte Carlo program afforded the distribution of the beam trip duration, which cannot be obtained using traditional analytical methods. Results show that the frequency of the beam trips with a duration exceeding 5 min must be reduced to 27% of the current J-PARC linac level to be below the ABTF.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Hayano, Akira; Ono, Hirokazu; Tachi, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
, 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched the Horonobe International Project (HIP) utilizing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The main objectives of this project are to develop and demonstrate advanced technologies to be used in repository design, operation and closure and a realistic safety assessment in deep geological disposal, and to encourage and train the next generation of engineers and researchers. In this review, an overview of the HIP is presented.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(6), p.1029 - 1043, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; Esaki, Nanse; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
Aoyama, Takahito; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Otani, Kyohei; Igarashi, Takahiro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111229_1 - 111229_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Mori, Airi; Johansen, M. P.*; McGinnity, P.*; Takahara, Shogo
Communications Earth & Environment (Internet), 6, p.356_1 - 356_11, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ono, Masato; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.235 - 242, 2025/05
Abe, Takumi; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.299 - 304, 2025/05
Currently, much research continues on stable energy sources that do not emit CO in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.195 - 198, 2025/05
Extraction chromatgraphy technology for trivalent minor actinide (MA(III) ; Am(III) and Cm(III)) recovery from the solution generated by an extraction process in reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel has been developed. A fine particle is generated in the solution. The fine particle must be removed before MA recovery operation, because that leads clogging of the extraction chlomatography column. In order to prevent clogging the column, filtration system utilizing porous silica beads packed column has been designed. In this study, a fine particle trapping system was developed and particle removal performance of the system was experimentally evaluated using alumina particles as simulated fine particle. Column experiments revealed that the fine particle with the particle size from 0.12 to 15  m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
Sato, Yuki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf046_1 - ncaf046_11, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences) hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH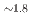 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH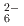 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH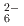 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (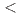 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.