Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
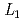 -edge XAFS measurement
-edge XAFS measurementTsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Kobayashi, Toru
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(4), p.214 - 217, 2023/08
no abstracts in English
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.36(Engineering, Civil) Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Takei, Akihiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:71.43(Chemistry, Physical)The identification of adsorption sites of Cs on clay minerals has been studied in the fields of environmental chemistry. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments allow direct observations of the local structures of adsorbed Cs. The NMR parameters of  Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The
Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The  Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(1), p.15 - 18, 2023/02
no abstracts in English
Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-022, 40 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption behavior of radionuclides (RNs) in buffer materials, rocks and cementitious materials is one of the key processes in a safe geological disposal. This report focuses on updating of JAEA sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as a basis of integrated approach for the performance assessment (PA)-related distribution coefficient (K ) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K
) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K
data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K
setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K data from 60 references were added and the total number of K
data from 60 references were added and the total number of K values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K
values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K data reached about 72% for all K
data reached about 72% for all K data in JAEA-SDB.
data in JAEA-SDB.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Sato, Hisao*; Arthur, R. C.*
Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 188, p.318 - 325, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.30(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Ammonium is potentially an important constituent of deep groundwater under reducing condition. The retention of cesium by sorption in geological formations may have an important role ensuring the long-term safety of high-level radioactive waste. Cesium sorption will be affected by competing effects due to dissolve cation likely ammonium in groundwater, however. In the present study, a possible reaction to control of ammonium in deep groundwater was evaluated based on the data selected in the Horonobe as a test case in Japan. Results of investigation of mineralogy, thermodynamic evaluation of groundwaters and the Electron Probe Micro Analysis (EPMA) to identify nitrogen distribution on minerals suggest that the clay minerals bearing potassium, particularly smectite, illite and interstratified illite/smectite, appear to control the ammonium concentration in groundwaters by ion exchange reactions. Additionally, the selected groundwaters in the Horonobe seem to resemble to the gas and oil fields groundwater in the screened dataset in Japan in terms of ammonium distribution.
Hirao, Norie; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Izumi, Toshinori; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi
Bunseki Kagaku, 65(5), p.259 - 266, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.85(Chemistry, Analytical)After the Fukushima nuclear plant accident, radiocesium was strongly fixed to clay minerals in the soil. Some dry methods with heating are being developed to remove radiocesium from the soil. In this work, we propose a new dry method that combines heat treatment in vacuum and molten salts to reduce the processing temperature in dry methods. Vermiculite saturated with non-radioactive Cs was heated in vacuum, and Cs contents in the vermiculite were compared before and after heating using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Approximately 40% of cesium were removed by heating at 800 C for three minutes when only vermiculite was heated. Approximately 70% of cesium were removed by heating at 450
C for three minutes when only vermiculite was heated. Approximately 70% of cesium were removed by heating at 450 C for three minutes when vermiculite was heated with NaCl/CaCl
C for three minutes when vermiculite was heated with NaCl/CaCl mixed salts. Based on these results, this method is expected to reduce temperature and increase efficiency on dry methods for cesium removal from clay minerals.
mixed salts. Based on these results, this method is expected to reduce temperature and increase efficiency on dry methods for cesium removal from clay minerals.
Ikeda, Takashi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 119(30), p.8369 - 8375, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:67.86(Chemistry, Physical)Adsorption states of alkali metal ions in three kinds of 2:1 type clay minerals are systematically investigated via first-principles-based metadynamics. Our reconstructed free energy surfaces in a two dimensional space of coordination numbers specifically employed as collective variables for describing the interlayer cations show that an inner-sphere (IS) complex is preferentially formed for Cs in the 2:1 type trioctahedral clay minerals with saponitelike compositions, where lighter alkali ions show a tendency to form an outer-sphere one instead. The strong preference for an IS complex observed for Cs
in the 2:1 type trioctahedral clay minerals with saponitelike compositions, where lighter alkali ions show a tendency to form an outer-sphere one instead. The strong preference for an IS complex observed for Cs is found to result partially from the capability of recognizing selectively Cs
is found to result partially from the capability of recognizing selectively Cs ions at basal O atoms with the Lewis basicity significantly enhanced by the isomorphic substitution in tetrahedral sheets.
ions at basal O atoms with the Lewis basicity significantly enhanced by the isomorphic substitution in tetrahedral sheets.
 -Fe
-Fe and Ca
and Ca -Mn
-Mn exchange selectivity of kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illite
exchange selectivity of kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illiteSaeki, Kazutoshi*; Wada, Shinichiro*; Shibata, Masahiro
Soil Science, 169(2), p.125 - 132, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:26.74(Soil Science)The Gains-Thomas ion exchange selectivity coefficients, KGT of Fe and Mn
and Mn on three types of Ca
on three types of Ca -saturated clay minerals (kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illite) were determined in an oxygen-free condition (O
-saturated clay minerals (kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illite) were determined in an oxygen-free condition (O
 0.0001 %) in order to understand better the behaviors of these ions in anaerobic soils. The results indicate that KGT values for Ca
0.0001 %) in order to understand better the behaviors of these ions in anaerobic soils. The results indicate that KGT values for Ca -Fe
-Fe , Ca
, Ca -Mn
-Mn exchange reactions on kaolinite and montmorillonite are close to unity. The KGT value for Ca
exchange reactions on kaolinite and montmorillonite are close to unity. The KGT value for Ca -Fe
-Fe exchange on illite were markedly higher than those for on the other clay minerals. The organic carbon contained in the illite specimen may have affected the results. The present study showed that Fe
exchange on illite were markedly higher than those for on the other clay minerals. The organic carbon contained in the illite specimen may have affected the results. The present study showed that Fe and Mn
and Mn are adsorbed on the surface of layered silicate clay minerals, with selectivity similar to Ca
are adsorbed on the surface of layered silicate clay minerals, with selectivity similar to Ca . Thus, Fe
. Thus, Fe and Mn
and Mn behave like alkaline-earth cations such as Ca
behave like alkaline-earth cations such as Ca in soils, sediments and aquifers dominated by layered silicate clay minerals.
in soils, sediments and aquifers dominated by layered silicate clay minerals.
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta
no journal, ,
A low aqueous-phase diffusion in low-permeable clay barrier materials has been accepted as a critical process in the long-term performance evaluation of nuclear waste repository. Low-permeable clay materials whose pores are poorly interconnected are known to have anomalous diffusion properties that strongly impact long-term net diffusion. Related research works with mudrocks of Wakkanai formation of Horonobe URL in Japan, Opalinus clay of Mt. Terri URL in Switzerland, as well as various shale and clay mineral, utilizes a complementary suite of pore structure characterization approaches (e.g., mercury intrusion porosimetry, small angle neutron scattering) and tracer experiments followed with micro-scale mapping with laser ablation-ICP-MS. These results presents the relationship between pore connectivity and anomalous diffusion in clay materials. Pore size is not the major contributor to slow fluid flow and radionuclide transport, the anomalous behavior appears to be caused by low pore connectivity.
Ikeda, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yin, X.; Koma, Yoshikazu; Inaba, Yusuke*; Takeshita, Kenji*
no journal, ,
Ikeda, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English