Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Endo, Takashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Terashima, Motoki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(1), p.9 - 22, 2021/03
Evaluation method of colloid diffusion and filtration in compacted bentonites was developed using dendrimers. Diffusion and filtration behavior of PAMAM dendrimers with the size of 5.7 7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m
7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m and saturated with 0.005
and saturated with 0.005 0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Matsui, Hiroya
Proceedings of 8th Nordic Grouting Symposium, p.171 - 185, 2016/09
This paper presents the application of a durable liquid-type colloidal silica grout (CSG), to the great depth of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). The CSG had been invented decades ago in Japan for the purpose of the ground improvement. A post-grouting experiment with the CSG carried out in 300 m depth of MIU confirmed its applicability and good durability at a great depth more than 3 years. Furthermore, a comparison study of applying the CSG between this experiment and a Swedish project indicated good applicability of the Swedish theoretical design to MIU. The CSG with the Swedish design were applied to the post-grouting campaign in a gallery at 500 m depth for further reducing water ingress and for developing the latest grouting methodology. The grouting was successful in reducing the abundant inflow from the rock with many fractures. The conductivity of the grouted rock mass of the latter fans is estimated to be lower than 10 m/s.
m/s.
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Nagao, Seiya*; Ueno, Takashi; Takeda, Seiji; Amano, Hikaru; Tkachenko, Y.*
Applied Geochemistry, 19(10), p.1581 - 1599, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:55.52(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The association of dissolved  Sr,
Sr, 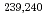 Pu and
Pu and  Am with natural colloids was investigated in surface waters in the Chernobyl nuclear accident area by means of ultrafiltration. Results suggest that Pu and Am isotopes were preferentially associated with dissolved humic substances (HS) of high molecular size. A model calculation of the complexation of Pu and Am with HS also supported the above. This study has expanded our understanding of the general role of natural organic colloids in dictating the chemical form of actinides in the surface aquatic environment.
Am with natural colloids was investigated in surface waters in the Chernobyl nuclear accident area by means of ultrafiltration. Results suggest that Pu and Am isotopes were preferentially associated with dissolved humic substances (HS) of high molecular size. A model calculation of the complexation of Pu and Am with HS also supported the above. This study has expanded our understanding of the general role of natural organic colloids in dictating the chemical form of actinides in the surface aquatic environment.
Kumata, Masahiro; Nakayama, Shinichi; Vandergraaf, T. T.*; Drew, D. J.*
JAERI-Conf 99-004, p.395 - 410, 1999/03
no abstracts in English

Dai, Z.*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Narumi, Kazumasa; Miyashita, Atsumi
1998 International Conference on Ion Implantation Technology Proceedings, Vol.2, p.1159 - 1162, 1998/06
no abstracts in English
; ;
JAERI-Research 94-024, 40 Pages, 1994/10
no abstracts in English
 sols suitable for gelation into microspheres in CCl
sols suitable for gelation into microspheres in CCl -ammonia media
-ammonia media;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 22(11), p.915 - 921, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:73.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 sols having colloid-size distribution suitable for gelation into microspheres
sols having colloid-size distribution suitable for gelation into microspheres; ; Shiba, Koreyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 21(7), p.528 - 537, 1984/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 84(2), p.269 - 275, 1984/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:56.88(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 Kernels by Sol-gel Process
Kernels by Sol-gel Process; ; ; Shiba, Koreyuki
JAERI 1271, 37 Pages, 1981/06
no abstracts in English
; ; Shiba, Koreyuki
JAERI-M 9477, 26 Pages, 1981/05
no abstracts in English
Journal of Radioanalytical Chemistry, 43(1), p.81 - 91, 1978/01
no abstracts in English
;
Radiochimica Acta, 24(1), P. 49, 1977/01
no abstracts in English
; Nakajima, Hayato; Takehisa, Masaaki; Machi, Sueo
Journal of Polymer Science; Polymer Letters Edition, 13(6), p.369 - 375, 1975/06
no abstracts in English
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 18(11), p.1703 - 1703, 1963/00
Times Cited Count:7no abstracts in English
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ohara, Shigeru*
no journal, ,
In the present study, a non-destructive technique using Particle Tracking Analysis (PTA) has been tested to determine size distribution and concentration of colloids in groundwater. The groundwaters were sampled from water-rings (4 samples) located in the vertical shafts and boreholes (6 samples) drilled in the drifts of the Horonobe URL. Results suggest that colloid particle concentrations range from 9.1 10
10  to 7.8
to 7.8 10
10  particle/mL (pt/mL) and the estimated colloid mass concentrations range from 3.4
particle/mL (pt/mL) and the estimated colloid mass concentrations range from 3.4 10
10  to 4.2 mg/L for the diameter of 1 to 1000 nm, respectively. Colloid concentrations of groundwater sampled from water-rings are generally higher than those sampled from boreholes due to differences in groundwater sampling conditions. For sizes
to 4.2 mg/L for the diameter of 1 to 1000 nm, respectively. Colloid concentrations of groundwater sampled from water-rings are generally higher than those sampled from boreholes due to differences in groundwater sampling conditions. For sizes  100 nm of particles, colloid stability was evaluated on the basis of DLVO theory. DLVO theory predicts that particle sizes
100 nm of particles, colloid stability was evaluated on the basis of DLVO theory. DLVO theory predicts that particle sizes  100 nm would be unstable (i.e., coagulation could occur). Particle and mass colloid concentrations in the groundwater were therefore reevaluated to obtain the reliable colloid particle concentrations range from 5.8
100 nm would be unstable (i.e., coagulation could occur). Particle and mass colloid concentrations in the groundwater were therefore reevaluated to obtain the reliable colloid particle concentrations range from 5.8 10
10  to 3.0
to 3.0 10
10  pt/mL and colloid mass concentrations range from 2.0
pt/mL and colloid mass concentrations range from 2.0 10
10  to 1.3
to 1.3 10
10  mg/L for the diameter range
mg/L for the diameter range  100 nm, respectively. Furthermore, the reevaluated results indicate a negative correlation between colloid concentrations and IS of groundwater.
100 nm, respectively. Furthermore, the reevaluated results indicate a negative correlation between colloid concentrations and IS of groundwater.
Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tanaka, Kazuya; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro
no journal, ,
When living Paramecium cells were exposed to a U(VI) aqueous solution, U was hardly detected in the cells, while U was clearly detected in the Paramecium cells that were pre-killed with a fixative before exposure to the U aqueous solution. The U in the liquid phase after the experiment was found to bound to a large soluble glycoprotein to form pseudocolloid. We discuss the relation between these results and the soluble glycoprotein covering the cell surface of Paramecium.