Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 (cr) at 318 K in the presence of iron
(cr) at 318 K in the presence of ironYoshida, Yasushi*; Kitamura, Akira; Shibutani, Sanae*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.900 - 910, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lobzenko, I.; Tsuru, Tomohito; 2 of others*
Computational Materials Science, 219, p.112010_1 - 112010_9, 2023/02
Katano, Ryota; Yamanaka, Masao*; Pyeon, C. H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(2), p.169 - 176, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)We proposed the linear combination method as a subcriticality measurement method which estimates the prompt neutron decay constant ( ) correlated with the subcriticality using measurement results obtained at multiple detector positions. In the previous study, we confirmed applicability of the linear combination method through the pulsed neutron experiment with DT neutron source at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). In this study, we conduct the pulsed neutron source experiment with spallation neutrons at KUCA and confirm the robustness of the linear combination to neutron sources.
) correlated with the subcriticality using measurement results obtained at multiple detector positions. In the previous study, we confirmed applicability of the linear combination method through the pulsed neutron experiment with DT neutron source at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). In this study, we conduct the pulsed neutron source experiment with spallation neutrons at KUCA and confirm the robustness of the linear combination to neutron sources.
Katano, Ryota; Yamanaka, Masao*; Pyeon, C. H.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 193(12), p.1394 - 1402, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:46.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)The author proposed the linear combination method as a subcriticality measurement method which estimates the prompt neutron decay constant (alpha) correlated with the subcriticality using measurement results obtained at multiple detector positions. In this study, we conduct the pulsed neutron experiment at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA) and measure alpha by the linear combination method using measured neutron counts. Through experiment, we experimentally show that the linear combination method can reduce the higher-mode effect compared to the conventional method. In addition, experimentally show that the linear combination has capability of the different mode extraction.
Nishioka, Shunichiro; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(11), p.988 - 995, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:76.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to contribute to improvement of Cs chemisorption model used in severe accident analysis codes, the influence of chemical factors (temperature, atmosphere, concentration of affecting chemical elements etc.) on the Cs chemisorption behaviour onto stainless steel was investigated experimentally. It was found that the surface reaction rate constant used in the current Cs-chemisorption model was influenced by not only temperature, as already known, but also atmosphere, cesium hydroxide (CsOH) concentration in the gas phase and silicon content in SS304. Such chemical factors should be considered for the construction of the improved Cs-chemisorption model. Another important finding is that the chemisorption behavior at lower temperatures, around 873 K, could differ from those above 1073 K. Namely, Cs-Fe-O compounds would form as the main Cs-chemisorbed compounds at 873 K while Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds at more than 1073 K.
Katano, Ryota
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 193(4), p.431 - 439, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:46.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)We proposed "linear combination method" to reduce the higher order mode effect on the prompt neutron decay constant measured by the pulsed neutron experiment. When the spatial higher order mode effect is taken into account, the time evolution of the neutron counts after the pulsed neutron injection is given by linear combination of multiple exponential functions. However, the measurement results by the conventional method include the systematic error derived from the higher order mode effect because the conventional method fit the neutron counts with a single exponential function. The proposed method extract the single exponential function of the fundamental mode by linear combination of the neutron counts at multiple detectors, thus the proposed method reduces the higher order mode effect. As the verification, we applied the proposed method to the numerical simulation. The results indicate that the proposed method can reduce the higher order mode effect by linear combination.
Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(2), p.228 - 240, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:61.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to improve LWR source term under severe accident conditions, the first version of a fission product (FP) chemistry database named "ECUME" was developed. The ECUME is intended to include major chemical reactions and their effective kinetic constants for representative SA sequences. It is expected that the ECUME can serve as a fundamental basis from which FP chemical models in the SA analysis codes can be elaborated. The implemented chemical reactions in the first version were those for representative gas species in Cs-I-B-Mo-O-H system. The chemical reaction kinetic constants were evaluated from either literature data or calculated values using ab-initio calculations. The sample chemical reaction calculation using the presently constructed dataset showed meaningful kinetics effects at 1000 K. Comparison of the chemical equilibrium compositions by using the dataset with those by chemical equilibrium calculations has shown rather good consistency for the representative Cs-I-B-Mo-O-H species. From these results, it was concluded that the present dataset should be useful to evaluate FP chemistry in Cs-I-B-Mo-O-H system under LWA SA conditions.
 (am) solubility at 25
(am) solubility at 25 C in the Ca
C in the Ca -Na
-Na -H
-H -Cl
-Cl -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; A Critical review
O system; A Critical reviewRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Altmaier, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 47(5), p.855 - 891, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:10.73(Chemistry, Physical)We have critically reviewed experimental data for Zr hydrolysis constant values for formation of several mononuclear and polynuclear species and a solubility product value for ZrO (am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
(am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH) (aq), Zr(OH)
(aq), Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH)
 and Ca
and Ca Zr(OH)
Zr(OH)
 , and the solubility product for ZrO
, and the solubility product for ZrO (am) after the critical review.
(am) after the critical review.

Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.356 - 362, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The sound speeds of longitudinal and transverse waves in the uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) pellets were measured as functions of porosity, oxygen-to-metal ratio (O/M) and plutonium content. The effect of each parameter was well fitted by a linear function and the equations were obtained to calculate the sound speeds. Mechanical properties were evaluated with the sound speeds and the result of Young's modulus showed that porosity was the most important factor to decrease Young's modulus. Temperature dependence on Young's modulus was also evaluated with previously reported thermal expansion. Decrease of Young's modules with increasing temperature was in good agreement with available literature.
Rai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 114, p.135 - 143, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:20.39(Thermodynamics)Isosaccharinic acid is a cellulose degradation product that can form in low-level nuclear waste repositories and is known to form strong complexes with many elements, including actinides, disposed of in these repositories. We (1) reviewed the available data for deprotonation and lactonisation constants of isosaccharinic acid, and the isosaccharinate binding constants for Ca, Fe(III), Th, U(IV), U(VI), Np(IV), Pu(IV), and Am(III), (2) summarized complexation constant values for predicting actinide behavior in geologic repositories in the presence of isosaccharinate, and (3) outlined additional studies to acquire reliable thermodynamic data where the available data are inadequate.
 (am) in the aqueous K
(am) in the aqueous K - HCO
- HCO
 - CO
- CO
 - OH
- OH - H
- H O system
O systemRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K.*
Radiochimica Acta, 105(8), p.637 - 647, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.11(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility of HfO (am) was determined as a function of KHCO
(am) was determined as a function of KHCO concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg
concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg to 0.1 mol.kg
to 0.1 mol.kg . The solubility of HfO
. The solubility of HfO (am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO
(am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO
concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-)
concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-) (CO
(CO )
)
 and Hf(CO
and Hf(CO )
)
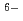 . The log
. The log K
K values for the reactions [Hf
values for the reactions [Hf + 2 CO
+ 2 CO
 +2 OH
+2 OH
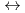 Hf(OH)
Hf(OH) (CO
(CO )
)
 ] and [Hf
] and [Hf + 5 CO
+ 5 CO

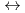 Hf(CO
Hf(CO )
)
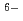 ], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53
], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53  0.46 and 41.53
0.46 and 41.53  0.46, respectively.
0.46, respectively.
Mukai, Satoru*; Umehara, Ryuji*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Kasahara, Shigeki; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Water Chemistry of Nuclear Reactor Systems (NPC 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2016/10
In Japanese PWR, the concentration of dissolved hydrogen in the primary coolant is controlled in the range from 25 cc/kg-H O to 35 cc/kg-H
O to 35 cc/kg-H O for suppression of water decomposition. However this concentration is desired to reduce for the purpose of radiation source reduction in Japan. So, the concentration due to water radiolysis in primary coolant was evaluated at lower hydrogen concentration by the water radiolysis model in consideration of
O for suppression of water decomposition. However this concentration is desired to reduce for the purpose of radiation source reduction in Japan. So, the concentration due to water radiolysis in primary coolant was evaluated at lower hydrogen concentration by the water radiolysis model in consideration of  ray, fast neutron and alpha ray due to the reaction
ray, fast neutron and alpha ray due to the reaction  B(n,
B(n, )
) Li. The results of evaluation showed that the water radiolysis was suppressed even if the hydrogen concentration was decreased to 5 cc/kg-H
Li. The results of evaluation showed that the water radiolysis was suppressed even if the hydrogen concentration was decreased to 5 cc/kg-H O. The effects of the different G-value and the rate constants of major reaction on the concentration of H
O. The effects of the different G-value and the rate constants of major reaction on the concentration of H O
O and O
and O were studied under hydrogen addition. We also focused on the effect of the alpha radiolysis in boron acid water.
were studied under hydrogen addition. We also focused on the effect of the alpha radiolysis in boron acid water.
Iwai, Yasunori
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1796 - 1799, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hydrophobic platinum catalysts have been widely applied in the field of nuclear fusion for the exchange reactions of hydrogen isotopes between hydrogen and vapor in the water detritiation system, and for the oxidation of tritium on the atmospheric detritiation system. Hydrophobic platinum catalysts are hardly susceptible to water mist and water vapor. Hydrophobic platinum catalysts are produced by supporting platinum directly on hydrophobic polymer beads. For the hydrophobic polymer, styrene - divinyl benzene (SDB) has been applied in Japan. It can be pointed out that the upgrade in catalytic activity of hydrophobic catalyst is expected to downsize the catalytic reactor based on a hard look at a large increase in flow rate in future. The upgrade in catalytic activity of two types of commercial Pt/SDB catalysts was found when they were irradiated with electron beams. After irradiation with electron beams, the catalytic activity was evaluated by means of overall reaction rate constant for the oxidation of tritium. The overall reaction rate constant increased as increase in dose. The constant showed the peak value in the dose between 500 to 1000 kGy. After the peak, the constant decreased as increase in dose. The overall reaction rate constant at the peak was 6 times larger than that evaluated with unirradiated. The mechanical strength of irradiated Pt/SDB kept sound until 1500 kGy. The irradiation is a promising method to the upgrading in catalytic activity of Pt/SDB catalyst.
Nagaya, Yasunobu
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and the Monte Carlo Method (M&C + SNA + MC 2015) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/04
A new method to calculate the prompt neutron decay constant ( ) with the Monte Carlo method is proposed. It is based on the conventional
) with the Monte Carlo method is proposed. It is based on the conventional  -
- search algorithm but no iteration is required for the
search algorithm but no iteration is required for the  value search. The
value search. The  eigenvalue is expressed in the truncated Taylor series with regard to
eigenvalue is expressed in the truncated Taylor series with regard to  ; the differential coefficients are calculated with the differential operator sampling, which is one of the Monte Carlo perturbation techniques. In order to examine the applicability of the proposed method, verification has been performed for simple geometries of a bare fast system (Godiva) and an unreflected thermal system (STACY). Comparisons has been done with the pulsed neutron source (PNS) simulation and the direct calculation from the definition of the
; the differential coefficients are calculated with the differential operator sampling, which is one of the Monte Carlo perturbation techniques. In order to examine the applicability of the proposed method, verification has been performed for simple geometries of a bare fast system (Godiva) and an unreflected thermal system (STACY). Comparisons has been done with the pulsed neutron source (PNS) simulation and the direct calculation from the definition of the  value. The results with the proposed method show good agreement with the reference PNS simulation.
value. The results with the proposed method show good agreement with the reference PNS simulation.
 system
systemKurosaki, Yuzuru; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*
Chemical Physics Letters, 406(1-3), p.121 - 125, 2005/04
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Moriai, Atsushi; Minakawa, Nobuaki*; Morii, Yukio
Zairyo, 54(3), p.339 - 345, 2005/03
In a conventional method of a neutron stress measurement, it is required to know the stress-free lattice constant accurately. A new stress measurement method, which does not need the lattice constant of the strain-free material, was applied to evaluate the residual stress distributions in welded sample. The lattice constant distribution which was measured by using our proposed method showed an increase as close to the weld zone, and the absolute value of the lattice constant almost agreed with the lattice constant which was measured using coupons cut from welded sample. Therefore, it is possible to predict the lattice constant by using our proposed method. The residual stress distributions were evaluated by using conventional method and our proposed method. As a result, the residual stress distributions decided by our proposed method almost agreed with those measured by conventional method. This proposed method can be applied to determination of the residual stress states in the samples with the complex residual stress states.
Nojiri, Naoki; Fujimoto, Nozomu; Mori, Tomoaki; Obata, Hiroyuki*
JAERI-Data/Code 2004-012, 65 Pages, 2004/10
DELIGHT code is a fuel cell burnup analysis code which can produce the group constants necessary for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGR) core analyses. Collision probability method is used to the lattice calculation. The lattice calculation model is a cylinder type fuel or a ball type fuel of the HTGR. This code characterizes the burnup calculation considering the double heterogeneity caused by coated fuel particles of the HTGR fuel. DELIGHT code has updated its nuclear data library to the latest JENDL-3.3 data, and included new burnup chain models in order to calculate high burnup HTGR cores. The material regions of the periphery burnable poisons (BPs) were divided into details in order to improve calculation accuracy of the BP lattice calculation. This report presents the revised points of the DELIGHT-8 and can be used as user's manual.
Lis, S.*; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; But, S.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 380(1-2), p.173 - 176, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.17(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Hamada, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Matsui, Kunihiro; Kato, Takashi; Okuno, Kiyoshi
Cryogenics, 44(1), p.45 - 52, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:60.21(Thermodynamics)In the ITER Central Solenoid Model Coil (CSMC) and a CS Insert Coil (CSIC) experiment, a pressure drop of the CSIC decreased by about 12% at 40 kA, 10 T and coupling losses indicated an transport current dependence. As a result of pressure drop analysis, an electromagnetic force causes a compressive deformation of cable in a jacket and a new flow passage was generated as a gap between cable and jacket. The cable deformation causes a decrease of a contact electrical resistance between strands and an increase of coupling losses. Taking account of the electromagnetic force dependency of a coupling time constant, calculated coupling losses show a good agreement with measured coupling losses at a pulsed operation of CSMC and CSIC.
 potential energy surfaces for the lowest three doublet states (1
potential energy surfaces for the lowest three doublet states (1 A', 2
A', 2 A', and 1
A', and 1 A") of the BrH
A") of the BrH system
systemKurosaki, Yuzuru; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 119(15), p.7838 - 7856, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:62.73(Chemistry, Physical)Adiabatic potential energy surfaces of the lowest three doublet states (1 A', 2
A', 2 A', and 1
A', and 1 A") for the BrH
A") for the BrH system have been calculated globally using the MRCI+Q method with the aug-cc-pVTZ basis set. Spin-orbit effects were considered on the basis of Breit-Pauli Hamiltonian. The calculated adiabatic energies were fitted to the analytical functional form of many-body expansion. The barrier heights of the abstraction and exchange reactions on the ground-state PES were calculated to be 1.28 and 11.71 kcal mol
system have been calculated globally using the MRCI+Q method with the aug-cc-pVTZ basis set. Spin-orbit effects were considered on the basis of Breit-Pauli Hamiltonian. The calculated adiabatic energies were fitted to the analytical functional form of many-body expansion. The barrier heights of the abstraction and exchange reactions on the ground-state PES were calculated to be 1.28 and 11.71 kcal mol , respectively, at the MRCI+Q/aug-cc-pVTZ level of theory. The fits for the three PESs were successful within the accuracy of 0.1 kcal mol
, respectively, at the MRCI+Q/aug-cc-pVTZ level of theory. The fits for the three PESs were successful within the accuracy of 0.1 kcal mol . Thermal rate constants for the abstraction and exchange reactions and their isotopic variants were calculated with the fitted 1
. Thermal rate constants for the abstraction and exchange reactions and their isotopic variants were calculated with the fitted 1 A' PES using the ICVT/LAG method. The calculated rate constants for the abstarction reactions agree fairly well with experiment but those for the exchange reactions were much smaller than experiment, which suggests that the reliable experimental data are still insufficient.
A' PES using the ICVT/LAG method. The calculated rate constants for the abstarction reactions agree fairly well with experiment but those for the exchange reactions were much smaller than experiment, which suggests that the reliable experimental data are still insufficient.