Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Endo, Akira
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 175(3), p.378 - 387, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.55(Environmental Sciences)The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) has been discussing to propose a new system of the operational quantities for external radiations based on protection quantities. The aim of this study is to provide a set of conversion coefficients for use in defining personal dose equivalent for individual monitoring. Fluence-to-effective dose conversion coefficients have been calculated for photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions and helium ions for various incident angles of radiations. The data sets comprise effective dose conversion coefficients for incident angles of radiations from 0  to 90
to 90  in steps of 15
in steps of 15 and at 180
and at 180 . Conversion coefficients for rotational, isotropic, superior hemisphere semi-isotropic and inferior hemisphere semi-isotropic irradiations are also included. The conversion coefficients are used to define the operational quantity personal dose equivalent which is being considered by ICRU and utilized for the design and calibration of dosemeters.
. Conversion coefficients for rotational, isotropic, superior hemisphere semi-isotropic and inferior hemisphere semi-isotropic irradiations are also included. The conversion coefficients are used to define the operational quantity personal dose equivalent which is being considered by ICRU and utilized for the design and calibration of dosemeters.
Yoshioka, Kenichi*; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Gunji, Satoshi*; Kumanomido, Hironori*; Mitsuhashi, Ishi*; Umano, Takuya*; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(2), p.282 - 293, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed a void reactivity evaluation method by using modified conversion ratio measurements in a light water reactor (LWR) critical lattice. Assembly-wise void reactivity is evaluated from the "finite neutron multiplication factor", 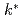 , deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and
, deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and 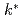 on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
Murakami, Hiroshi
Chemical Physics Letters, 417(4-6), p.550 - 554, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:15.45(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Onuki, Akira; Iwamura, Takamichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
Iwamura, Takamichi; Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakatsuka, Toru
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the matured Light Water Reactor (LWR) and coming LWR-Mixed Oxide (MOX) technologies, a concept of Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible Fuel Cycle (FLWR) has been investigated in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The concept consists of two parts in the chronological sequence. The first part realizes a high conversion type core concept, which is basically intended to keep the smooth technical continuity from current LWR without significant gaps in technical point of view. The second part represents the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) core concept, which realizes a high conversion ratio over 1.0 being useful for the long-term sustainable energy supply through plutonium multiple recycling based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The key point is that the two core concepts utilize the compatible and the same size fuel assemblies, and hence, the former concept can proceed to the latter in the same reactor system, based flexibly on the fuel cycle circumstances.
Shelley, A.; Kugo, Teruhiko; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Research 2004-002, 47 Pages, 2004/03
Neutronic study has been done for a PWR-type reduced-moderation water reactor with seed-blanket fuel assemblies to achieve a high conversion ratio, a negative void coefficient and a high burnup by using a MOX fuel. The results of the precise assembly burnup calculations show that the recommended numbers of seed and blanket layers are 15(S15) and 5(B5), respectively. By the optimization of axial configuration, the S15B5 assembly with the seed of 1000 2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400
2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400 2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500
2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500 2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO
2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO +ThO
+ThO ) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
Shelley, A.; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Kugo, Teruhiko; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 224(3), p.265 - 278, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Parametric studies have been done for a PWR-type reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) with seed-blanket fuel assembles to achieve a high conversion ratio, negative void reactivity coefficient and a high burnup. It was found that 50 to 60% of seed in a seed-blanket assembly has higher conversion ratio. The number of seed-blanket layers is 20, in which the number of seed layers is 15 and blanket layers is 5. The fuel assembly with the height of seed of 1000mm 2, internal blanket of 150 mm and axial blanket of 400mm
2, internal blanket of 150 mm and axial blanket of 400mm 2 is recommended. The conversion ratio is 1.0 and the average burnup in core region is 38.2 GWd/t. The enrichment of fissile Pu is 14.6 wt%. The void coefficient is +21.8 pcm/% void, however, it is expected that the void coefficient will be negative if the radial neutron leakage is taken into account. It is also possible to use this fuel assembly for a high core averaged burnup of 45GWd/t, however, the height of seed must be 500mm
2 is recommended. The conversion ratio is 1.0 and the average burnup in core region is 38.2 GWd/t. The enrichment of fissile Pu is 14.6 wt%. The void coefficient is +21.8 pcm/% void, however, it is expected that the void coefficient will be negative if the radial neutron leakage is taken into account. It is also possible to use this fuel assembly for a high core averaged burnup of 45GWd/t, however, the height of seed must be 500mm 2 to improve the void coefficient. The conversion ratio is 0.97 and void coefficient is +20.8 pcm/%void.
2 to improve the void coefficient. The conversion ratio is 0.97 and void coefficient is +20.8 pcm/%void.
Okubo, Tsutomu
Konsoryu, 17(3), p.228 - 235, 2003/09
The Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor is supposed to realize plutonium multiple recycling, and furthermore, plutonium breeding cycle, based on the well-established Light Water Reactor technologies. In the present paper, the overview of the design study is presented and the related R&D issues are introduced, especially focusing on the thermal hydraulic activities.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu
Proceedings of 2nd Asian Specialist Meeting on Future Small-Sized LWR Development, p.7_1 - 7_5, 2003/00
An innovative water-cooled reactor concept named Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) is under development at JAERI, aiming at effective fuel utilization through plutonium (Pu) multiple recycling based on the well-experienced water-cooled reactor technology. The reactor is able to achieve a high conversion ratio more than 1.0 with MOX fuel, to establish the sustainable Pu recycling. Such a high conversion ratio can be attained by reducing the moderation of neutrons, i.e. reducing the water fraction in the core. Detailed research and development activities have been performed on the core design, in conjunction with the other related studies such as on the thermal hydraulics in the tight-lattice core, the reactor physics and the fuel irradiation behavior, including the experimental activities. Also, for the total feasibility demonstration of the RMWR technologies, a design investigation for Reduced-Moderation Demonstration Reactor (RMDR) of 180MWt is being performed.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu*; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2002-021, 36 Pages, 2002/11
Silicon is a material which is easily oxidized like zirconium which is one of the LWR core materials. Also, its steam explosion behavior is a concern in semi-conductor industries where its melt is handled. In this study, steam explosion behavior of silicon melt and contribution of oxidation reaction in a steam explosion were investigated. Two cases of experiments were performed by dropping silicon melt into a water pool and both produced spontaneous steam explosions. Energy conversion ratio was 4--9% which was similar or slightly larger compared with previous experiments with thermite melt. Fragmentation of the melt was finer than previous experiments and the mass median diameter of the debris was 65--85 m. An oxide layer of about 5
m. An oxide layer of about 5 m thick was fond on the debris surface indicating possibility of oxidation of several % of the melt.
m thick was fond on the debris surface indicating possibility of oxidation of several % of the melt.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakatsuka, Toru; Takeda, Renzo*; Yamamoto, Kazuhiko*
Proceedings of 13th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC 2002) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2002/10
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in Japan, the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) has been developed by JAERI since 1998. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio. In order to establish negative void reactivity coefficient, the core should be short and flat to increase neutron leakage from the core. The core designs were accomplished to a large core with 1,356MWe and a small core with 330MWe. For both cores, negative void coefficient and natural circulation cooling of the core were realized. To confirm thermal-hydraulic feasibility, critical heat flux experiments were performed using 7-rod bundles with the gap width of 1mm and 1.3mm. The results indicated that enough cooling was assured for the tight lattice core. Further R&D studies, including large scale thermal-hydraulic experiments, reactor physics experiments, development of high burn-up fuel cladding material and simplified reprocessing technology, are necessary to realize commercial introduction of RMWR by 2020's for the replacement of current generation LWRs.
 O
O crystals
crystalsKiriyama, Hiromitsu; Inoue, Norihiro*; Yamakawa, Koichi
JAERI-Research 2002-020, 13 Pages, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
 O
O crystals
crystalsKiriyama, Hiromitsu; Inoue, Norihiro*; Yagi, Kenichi*; Nagai, Toru*; Aoyama, Makoto; Yamakawa, Koichi
Proceedings of Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics / Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference (CLEO/QELS 2002), p.CPDC6_1 - CPDC6_3, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Okubo, Tsutomu; Takeda, Renzo*; Iwamura, Takamichi; Yamamoto, Kazuhiko*; Okada, Hiroyuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Back-End of the Fuel Cycle: From Research to Solutions (GLOBAL 2001) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2001/09
An advanced water-cooled reactor concept named the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) has been proposed to attain a high conversion ratio more than 1.0 and to achieve the negative void reactivity coefficient. At present, several types of design concepts satisfying both the design targets have been proposed based on the evaluation for the fuel without fission products and minor actinides. In this paper, the feasibility of the RMWR core is investigated and confirmed for the plutonium multiple recycling under advanced reprocessing schemes with low decontamination factors as proposed for the FBR fuel cycle.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nakano, Fumihiko*; Yamakawa, Koichi
JAERI-Research 2001-030, 26 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Usui, Shuji*; Shirakawa, Toshihisa*; Nakatsuka, Toru; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Wada, Shigeyuki*
JAERI-Research 99-058, p.61 - 0, 1999/11
no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; ; Sekita, Kenji; ; Hino, Ryutaro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 40(1), p.59 - 64, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ando, Masaki; ; Nishina, Kojiro*;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 34(5), p.445 - 453, 1997/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 lattices
latticesNakajima, Ken;
Nuclear Technology, 113, p.375 - 379, 1996/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Ken; ; Suzaki, Takenori
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 119, p.175 - 181, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:54.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English