Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
Seki, Takeshi*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(33), p.333001_1 - 333001_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.04(Physics, Condensed Matter) No
NoBronis, A.*; He berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Andel, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Andel, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(1), p.014602_1 - 014602_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:69.45(Physics, Nuclear)Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Motoyama, Mizuki*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Ishii, Toshiaki; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 135, p.12 - 18, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.66(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Takeishi, Minoru; Shibamichi, Masaru; Malins, A.; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Murakami, Mitsuhiro*; Saegusa, Jun; Yoneya, Masayuki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 177, p.1 - 12, 2017/10
By convention radiation measurements from vehicle-borne surveys are converted to the dose rate at 1 m above the ground in the absence of the vehicle. To improve the accuracy of the converted results from vehicle-borne surveys, we investigated combining measurements from two detectors mounted on the vehicle at different heights above the ground. A dual-detector setup was added to a JAEA monitoring car and compared against hand-held survey meter measurements in Fukushima Prefecture. The dose rates obtained by combining measurements from two detectors were within  20% of the hand-held reference measurements. The combined results from the two detectors were more accurate than those from either the roof-mounted detector, or the detector inside the vehicle, taken alone. When radiocesium is deficient on a road compared to the adjacent land, mounting detectors high on vehicles yields dose rates closer to the values adjacent to the road. We also investigated mounting heights for vehicle-borne detectors using Monte Carlo
20% of the hand-held reference measurements. The combined results from the two detectors were more accurate than those from either the roof-mounted detector, or the detector inside the vehicle, taken alone. When radiocesium is deficient on a road compared to the adjacent land, mounting detectors high on vehicles yields dose rates closer to the values adjacent to the road. We also investigated mounting heights for vehicle-borne detectors using Monte Carlo  -ray simulations.
-ray simulations.
Endo, Akira
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 175(3), p.378 - 387, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:66.74(Environmental Sciences)The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) has been discussing to propose a new system of the operational quantities for external radiations based on protection quantities. The aim of this study is to provide a set of conversion coefficients for use in defining personal dose equivalent for individual monitoring. Fluence-to-effective dose conversion coefficients have been calculated for photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions and helium ions for various incident angles of radiations. The data sets comprise effective dose conversion coefficients for incident angles of radiations from 0  to 90
to 90  in steps of 15
in steps of 15 and at 180
and at 180 . Conversion coefficients for rotational, isotropic, superior hemisphere semi-isotropic and inferior hemisphere semi-isotropic irradiations are also included. The conversion coefficients are used to define the operational quantity personal dose equivalent which is being considered by ICRU and utilized for the design and calibration of dosemeters.
. Conversion coefficients for rotational, isotropic, superior hemisphere semi-isotropic and inferior hemisphere semi-isotropic irradiations are also included. The conversion coefficients are used to define the operational quantity personal dose equivalent which is being considered by ICRU and utilized for the design and calibration of dosemeters.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamichi, Hideo; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Nishimura, Kazuaki; Fujisaku, Sakae; Tanaka, Hideki; Isomae, Hidemi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Kurita, Tsutomu; Iida, Masayoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/04
TRP has stored the plutonium in solution state for long-term since the last PCDF operation in 2007 was finished. After the great east Japan earthquake in 2011, JAEA had investigated the risk against potential hazard of these solutions which might lead to make hydrogen explosion and/or boiling of the solution accidents with the release of radioactive materials to the public when blackout. To reduce the risk for storing Pu solution (about 640 kg Pu), JAEA planned to perform the process operation for the solidification and stabilization of the solution by converted into MOX powder at PCDF in 2013. In order to perform PCDF operation without adaption of new safety regulation, JAEA conducted several safety measures such as emergency safety countermeasures, necessary security and safeguards (3S) measures with understanding of NRA. As a result, the PCDF operation had stared on 28th April, 2014, and successfully completed to convert MOX powder on 3rd August, 2016 for about 2 years as planned.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 166(Part 3), p.419 - 426, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:71.83(Environmental Sciences)Air dose rate monitoring in the environment has been performed since the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident happened. In the measurement, NaI(Tl) and CsI(Tl) scintillation detectors are used, which are usually used in nuclear power plants and calibrated in a uniform irradiation condition in a radiation calibration field. In general, however, the detector responses are dependent on incident direction and in reality, the incident direction of the photons is not uniform in the environment. In this study, to evaluate the dependence of dose on the photon incident direction, the spectrum - dose conversion operator (G(E) function) for air kerma in a semi-infinite radiation field were obtained using the PHITS code for commonly used NaI(Tl) and CsI(Tl) scintillation detectors. The results indicate that the commonly used scintillation detectors overestimate the doses by a maximum of 40% for mono-energetic photons but under the real environment, one could obtain the dose in the semi-infinite radiation field within 20%.
Fukaya, Yuji
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 81, p.301 - 305, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Development of a simple method to incorporate the out-of-core cooling effect on the thorium conversion in multi-pass fueled reactors and investigation on characteristics of the effect have been performed. For multi-pass fueled reactors, such as Molten Salt Breeder Reactor (MSBR) and Pebble-Bed Modular Reactor (PBMR), fuel moves in the core and exits from the core. The nuclides decay also out of the core, and it should be also considered if it is important for core characteristics. In the present study,  Pa is considered to evaluate the thorium conversion accurately. To take the effect into account, in the present study, an effective decay constant is proposed to make equilibrium concentration of
Pa is considered to evaluate the thorium conversion accurately. To take the effect into account, in the present study, an effective decay constant is proposed to make equilibrium concentration of  Pa without out-of-core cooling equal to that of out-of-core cooling. With the effective decay constant, the out-of-core cooling effect can be incorporated even with the code system using macroscopic cross sections generated by cell burn-up calculations without any code modification. In addition, the characteristic of out-of-core cooling effect for the thorium conversion is evaluated for thorium fueled reactors of MSBR and PBMR. It is concluded that the out-of-core cooling effect is suitable for MSBR to enhance thorium conversion because of the fast flow rate of fuel salt. On the other hand, the effect is not important and not realistic to employ for PBMR because the in-core residence time of approximately 100 days is longer than the half-life of
Pa without out-of-core cooling equal to that of out-of-core cooling. With the effective decay constant, the out-of-core cooling effect can be incorporated even with the code system using macroscopic cross sections generated by cell burn-up calculations without any code modification. In addition, the characteristic of out-of-core cooling effect for the thorium conversion is evaluated for thorium fueled reactors of MSBR and PBMR. It is concluded that the out-of-core cooling effect is suitable for MSBR to enhance thorium conversion because of the fast flow rate of fuel salt. On the other hand, the effect is not important and not realistic to employ for PBMR because the in-core residence time of approximately 100 days is longer than the half-life of  Pa of 27.0 days, and the effect cannot improve the conversion ratio drastically.
Pa of 27.0 days, and the effect cannot improve the conversion ratio drastically.
Yoshioka, Kenichi*; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Gunji, Satoshi*; Kumanomido, Hironori*; Mitsuhashi, Ishi*; Umano, Takuya*; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(2), p.282 - 293, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed a void reactivity evaluation method by using modified conversion ratio measurements in a light water reactor (LWR) critical lattice. Assembly-wise void reactivity is evaluated from the "finite neutron multiplication factor", 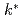 , deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and
, deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and 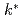 on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
Cheng, S.; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2015, p.964327_1 - 964327_14, 2015/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.92(Nuclear Science & Technology) rays and the exposure doses
rays and the exposure dosesSaito, Kimiaki; Endo, Akira
Radioisotopes, 63(12), p.585 - 602, 2014/12
The article provides the fundamental information necessary for the appropriate evaluation of exposure doses in the environment. The basic characteristics of environmental  rays from typical environmental sources are introduced; then, the dose conversion coeffcients for the public at different ages are summarized which were obtained from the simulation considering the basic characteristics of environmental
rays from typical environmental sources are introduced; then, the dose conversion coeffcients for the public at different ages are summarized which were obtained from the simulation considering the basic characteristics of environmental  rays. Further, the variations of environmental exposure doses due to a variety of factors, and the relation of exposure doses to measured air dose rates are discussed.
rays. Further, the variations of environmental exposure doses due to a variety of factors, and the relation of exposure doses to measured air dose rates are discussed.
Murakami, Hiroshi
Chemical Physics Letters, 417(4-6), p.550 - 554, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:15.32(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Nakatsuka, Toru; Misawa, Takeharu; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
R&D project to investigate thermal-hydraulic performance in tight-lattice rod bundles for Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) is started at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute in collaboration with power company, reactor vendors, universities since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured LWR technologies. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight-lattice configuration. In this paper, we will show the R&D plan and describe some advances on experimental and analytical studies. Steady-state and transient critical power experiments have been conducted with two 37-rod bundle test facilities (Gap width between rods: 1.3mm and 1.0mm) and the experimental data reveal the feasibility of RMWR.
Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Onuki, Akira; Iwamura, Takamichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
 No and its
No and its  -decay daughter
-decay daughter 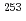 Fm
FmAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Osa, Akihiko; Oura, Yasuji*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 95(10), p.102502_1 - 102502_4, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:87.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excited states in 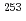 Fm fed by the
Fm fed by the  decay of
decay of  No have been established through
No have been established through  -
- and
and  -electron coincidence spectroscopy using a gas-jet transport system and an on-line isotope separator. The spin-parity of the 124.1 keV level in
-electron coincidence spectroscopy using a gas-jet transport system and an on-line isotope separator. The spin-parity of the 124.1 keV level in 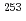 Fm has been identified on the basis of the measured internal conversion coefficients. The
Fm has been identified on the basis of the measured internal conversion coefficients. The ![$$nu 3/2^{+}[622]$$](/search/images/EROG23JAGMXTEXT1FN4VWNRSGJOSI.gif) configuration has been assigned to the ground state of
configuration has been assigned to the ground state of  No as well as to the 124.1 keV level. It was found that the ground state configuration of
No as well as to the 124.1 keV level. It was found that the ground state configuration of  No is different from that of lighter
No is different from that of lighter 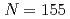 isotones.
isotones.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Nakatsuka, Toru; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
R&D project to investigate thermal-hydraulic performance in tight-lattice rod bundles for Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) is started at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute in collaboration with power company, reactor vendors, universities since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured LWR technologies. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight-lattice configuration. In this paper, we will show the R&D plan and describe some advances on experimental and analytical studies. The experimental study is performed mainly using large-scale (37-rod bundle) test facility and the analytical one aims to develop a predictable technology for geometry effects such as gap between rods etc. using advanced 3-D two-phase flow simulation methods. Steady-state and transient critical power experiments are conducted with the test facility (Gap width between rods: 1.3mm and 1.0mm) and the experimental data reveal the feasibility of RMWR.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakatsuka, Toru
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the matured Light Water Reactor (LWR) and coming LWR-Mixed Oxide (MOX) technologies, a concept of Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible Fuel Cycle (FLWR) has been investigated in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The concept consists of two parts in the chronological sequence. The first part realizes a high conversion type core concept, which is basically intended to keep the smooth technical continuity from current LWR without significant gaps in technical point of view. The second part represents the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) core concept, which realizes a high conversion ratio over 1.0 being useful for the long-term sustainable energy supply through plutonium multiple recycling based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The key point is that the two core concepts utilize the compatible and the same size fuel assemblies, and hence, the former concept can proceed to the latter in the same reactor system, based flexibly on the fuel cycle circumstances.
Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Iwamura, Takamichi
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the matured LWR technologies, a concept of Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible Fuel Cycle (FLWR) has been investigated in JAERI. The concept consists of two parts in the chronological sequence. The first part realizes a high conversion type core concept, which is basically intended to keep the smooth technical continuity from current LWR technologies without significant gaps in technical point of view. The second part represents the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) core concept, which realizes a high conversion ratio more than and around 1.0 being useful for the long-term sustainable energy supply through plutonium multiple recycling based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The key point is that the two core concepts utilize the compatible and the same size fuel assemblies, and hence, the former concept can proceed to the latter in the same reactor system based flexibly on the fuel cycle circumstances during the reactor operation period around 60 years.
Tran, V. H.; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Tsuda, Shuichi; Endo, Akira; Saito, Kimiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Tech 2004-079, 37 Pages, 2005/02
no abstracts in English