Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Materialia, 32, p.101934_1 - 101934_12, 2023/12
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Materialia, 32, p.101943_1 - 101943_8, 2023/12
Suzuki, Seiya; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Shiiki, Natsumi*; Nakayama, Yoshiko*; Takeguchi, Masaki*
Annalen der Physik, 535(9), p.2300122_1 - 2300122_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.2217_1 - 2217_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:89.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kawasaki, Takuro; Takahashi, Miwako*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi
Acta Crystallographica Section C; Structural Chemistry (Internet), 78(12), p.743 - 748, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Opletal, P.; Duverger-N dellec, E.*; Miliyanchuk, K.*; Malick, S.*; Hossain, Z.*; Custers, J.*
dellec, E.*; Miliyanchuk, K.*; Malick, S.*; Hossain, Z.*; Custers, J.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 927, p.166941_1 - 166941_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.92(Chemistry, Physical)Tsuda, Shuichi; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(17), p.1283 - 1291, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Spherical or cylindrical detectors superior to directional characteristic are commonly used to monitor dose rates in the environment to detect scattering gamma-rays emitted from radionuclides in soil or air. The authors have performed environmental dose rates measurements using various kinds of detectors to investigate the directional characteristics, and experimentally verified the variations in dose rates due to directional characteristics unique to each detector. Furthermore, a dose rate measured by a CsI(Tl) scintillation detector with cuboidal crystal agreed with that by a CsI(Tl) scintillation detector with cylindrical crystal. Simulations by PHITS under various CsI(Tl) crystal configurations revealed that there are certain aspect ratios of cuboidal CsI(Tl) crystal with less directional dependence. Since cubes are advantageous in terms of production cost, this result indicates the potential of CsI(Tl) scintillation detectors with cuboidal crystal for use in the environmental dose rate monitoring.
 and GeO
and GeO liquids
liquidsKawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Crystal Growth, 585, p.126590_1 - 126590_7, 2022/05
Phase-field mobility,  , and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO
, and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO and GeO
and GeO liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the
liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the  was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with
was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with 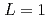 were confirmed to be proportional to a power of
were confirmed to be proportional to a power of 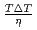 on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,
on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,  and
and  , of the
, of the 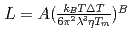 were
were 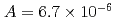 to
to 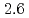 m
m J
J s
s and
and 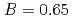 to
to 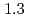 , which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined
, which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined  reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The
reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The  has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at
has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at 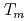 in a log-log graph. The
in a log-log graph. The  depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass,
depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass, 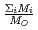 , in a compound. In
, in a compound. In 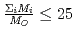 , the
, the  decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the
decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the  . Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the
. Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the  decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in
decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in 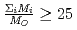 , the
, the  saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to
saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to 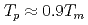 .
.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Yamazaki, Hayato*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Sando, Kazusa*; Imura, Takumi*; Ono, Takeshi*
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 226, p.105075_1 - 105075_9, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.83(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Simultaneous determination of the U-Pb age of zircon and concentration of titanium in a single analysis spot, using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with laser ablation sample introduction, produces paired age and temperature data of zircon crystallisation, potentially revealing time-temperature ( ) histories for evolved magma. The Kurobegawa granite, central Japan, contains abundant mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs). We applied this method to evaluate MMEs and their host (enclosing) granites. Cooling behaviour common to both MMEs and host rocks was found between 1.5 and 0.5 Ma. Rapid cooling from the zircon crystallisation temperature to the closure temperature of biotite K-Ar system was within
) histories for evolved magma. The Kurobegawa granite, central Japan, contains abundant mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs). We applied this method to evaluate MMEs and their host (enclosing) granites. Cooling behaviour common to both MMEs and host rocks was found between 1.5 and 0.5 Ma. Rapid cooling from the zircon crystallisation temperature to the closure temperature of biotite K-Ar system was within  1 million year. Combining the obtained
1 million year. Combining the obtained  paths of MMEs and host rocks with petrological information can provide insights into magma chamber processes. This suggests that MME flotation, migration, and spread through the magma chamber ceased at 1.5-0.5 Ma, indicating the emplacement age of the Kurobegawa granitic pluton, as no large-scale reheating episodes have occurred since then.
paths of MMEs and host rocks with petrological information can provide insights into magma chamber processes. This suggests that MME flotation, migration, and spread through the magma chamber ceased at 1.5-0.5 Ma, indicating the emplacement age of the Kurobegawa granitic pluton, as no large-scale reheating episodes have occurred since then.

Haga, Yoshinori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(17), p.175601_1 - 175601_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:89.04(Physics, Condensed Matter) sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden
Hard Rock Laboratory in SwedenTachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Gylling, B.*
Water Resources Research, 57(11), p.e2020WR029335_1 - e2020WR029335_20, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.48(Environmental Sciences)This paper focuses on the scaling approach for sorption and diffusion parameters from laboratory to in-situ conditions using the dataset of LTDE-SD experiment performed at the  sp
sp HRL. The near-surface heterogeneities at both fracture surface and rock matrix could be evaluated by conceptual model with high porosity and diffusivity, and sorption capacity, and their gradual change at the near-surface zones. The modelling results for non-sorbing Cl-36 and weak-sorbing Na-22 could validate the model concept and the parameter estimation of porosity and diffusivity, by considering the disturbed zone of 5 mm thickness with gradual parameter changes. The De values of these cationic and anionic tracers showed typical cation excess and anion exclusion effects. The modelling results for high sorbing tracers (Cs-137, Ra-226, Ni-63 and Np-237) with different sorption mechanism could confirm the validity of the scaling approaches of Kd values as a function of particle size and their relation to the near-surface disturbances.
HRL. The near-surface heterogeneities at both fracture surface and rock matrix could be evaluated by conceptual model with high porosity and diffusivity, and sorption capacity, and their gradual change at the near-surface zones. The modelling results for non-sorbing Cl-36 and weak-sorbing Na-22 could validate the model concept and the parameter estimation of porosity and diffusivity, by considering the disturbed zone of 5 mm thickness with gradual parameter changes. The De values of these cationic and anionic tracers showed typical cation excess and anion exclusion effects. The modelling results for high sorbing tracers (Cs-137, Ra-226, Ni-63 and Np-237) with different sorption mechanism could confirm the validity of the scaling approaches of Kd values as a function of particle size and their relation to the near-surface disturbances.
M ri, A.*; Mazurek, M.*; Ota, Kunio; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Eichinger, F.*; Leuenberger, M.*
ri, A.*; Mazurek, M.*; Ota, Kunio; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Eichinger, F.*; Leuenberger, M.*
Minerals (Internet), 11(10), p.1072_1 - 1072_17, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.7(Geochemistry & Geophysics) } polyoxo cluster U
} polyoxo cluster U O
O Cl
Cl (MeO)
(MeO)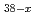 (x = 2.3, MeO = methoxide)
(x = 2.3, MeO = methoxide)Fichter, S.*; Radoske, T.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Acta Crystallographica Section E; Crystallographic Communications (Internet), 77(8), p.847 - 852, 2021/08
Liss, K.-D.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Aizawa, Kazuya; Xu, P. G.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 869, p.159232_1 - 159232_9, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.2(Chemistry, Physical)Sakurai, Yosuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Adachi, Nozomu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Todaka, Yoshikazu*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 11(11), p.5219_1 - 5219_17, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.11(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) B
BSato, Yoshiki*; Honda, Fuminori*; Maurya, A.*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Nakamura, Ai*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Li, D.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Aoki, Dai*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 5(3), p.034411_1 - 034411_9, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) *(10) dose rates measured in environment contaminated by radioactive caesium; Correction of directional dependence of scintillation detectors
*(10) dose rates measured in environment contaminated by radioactive caesium; Correction of directional dependence of scintillation detectorsTsuda, Shuichi; Tanigaki, Minoru*; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Okumura, Ryo*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 193(3-4), p.228 - 236, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.41(Environmental Sciences)Environmental dose rate monitoring has been performed with various scintillation detectors since the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Gamma-rays from caesium isotopes deposited in soil enter radiation detectors in any direction, but directional dependence of the detectors used for dose rate measurements are not always uniform and the dose rates vary even if measurement takes place at the same place. To investigate the influence of crystal configurations on dose rate, dose rate measurements using several scintillation detectors with different crystal configurations were conducted. By measuring pulse height spectra and multiplying them with spectrum - dose conversion operators (G(E) function), dose rates were deduced and compared. It was found that the dose rates varied within approximately 25% among six detectors. To reduce the differences, the dose rate using G(E) functions determined in rotational geometry were obtained and applied instead. The revised dose rates agreed with one another within uncertainties, but this was not the case of scintillation detector with flat crystal shape, and it means this method could not compensate its strong directional dependence. These experimental results reveal that detectors with superior directional characteristics should be used for environmental dose rate measurement since the compensation of directional dependence using a G(E) function determined in rotational geometry is not always available.
 O-2SiO
O-2SiO , Na
, Na O-2SiO
O-2SiO and K
and K O-2SiO
O-2SiO
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 128(10), p.832 - 838, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.23(Materials Science, Ceramics)This study developed phase-field method (PFM) technique in oxide melt system by using a new mobility coefficient ( ). The crystal growth rates (
). The crystal growth rates (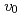 ) obtained by the PFM calculation with the constant
) obtained by the PFM calculation with the constant  were comparable to the thermodynamic driving force in normal growth model. The temperature dependence of the
were comparable to the thermodynamic driving force in normal growth model. The temperature dependence of the  was determined from the experimental crystal growth rates and the
was determined from the experimental crystal growth rates and the 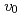 . Using the determined
. Using the determined  , the crystal growth rates (
, the crystal growth rates ( ) in alkali disilicate glasses, Li
) in alkali disilicate glasses, Li O-2SiO
O-2SiO , Na
, Na O-2SiO
O-2SiO and K
and K O-2SiO
O-2SiO were simulated. The temperature dependence of the
were simulated. The temperature dependence of the  was qualitatively and quantitatively so similar that the PFM calculation results demonstrated the validity of the
was qualitatively and quantitatively so similar that the PFM calculation results demonstrated the validity of the  . Especially, the
. Especially, the  obtained by the PFM calculation appeared the rapid increase just below the thermodynamic melting point (
obtained by the PFM calculation appeared the rapid increase just below the thermodynamic melting point (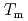 ) and the steep peak at around
) and the steep peak at around 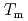 -100 K. Additionally, as the temperature decreased, the
-100 K. Additionally, as the temperature decreased, the  apparently approached zero ms
apparently approached zero ms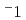 , which is limited by the
, which is limited by the  representing the interface jump process. Furthermore, we implemented the PFM calculation for the variation of the parameter
representing the interface jump process. Furthermore, we implemented the PFM calculation for the variation of the parameter  in the
in the  . As the
. As the  increased from zero to two, the peak of the
increased from zero to two, the peak of the  became steeper and the peak temperature of the
became steeper and the peak temperature of the  shifted to the high temperature side. The parameters
shifted to the high temperature side. The parameters  and
and  in the
in the  increased exponentially and decreased linearly as the atomic number of the alkali metal increased due to the ionic potential, respectively. This calculation revealed that the
increased exponentially and decreased linearly as the atomic number of the alkali metal increased due to the ionic potential, respectively. This calculation revealed that the  and
and  in the
in the  were close and reasonable for each other.
were close and reasonable for each other.
Miradji, F.; Suzuki, Chikashi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 136, p.109168_1 - 109168_9, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)