Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuda, Norihiro; Izumi, Yuichi*; Yamanaka, Yoshiyuki*; Gando, Toshiyuki*; Yamada, Masaaki*; Oishi, Koji*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.07001_1 - 07001_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hotchi, Hideaki; Tani, Norio; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 19(1), p.010401_1 - 010401_11, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.97(Physics, Nuclear)In the J-PARC 3-GeV RCS, transverse injection painting is utilized not only to suppress space-charge induced beam loss but also to mitigate foil scattering beam loss during charge-exchange injection. The space-charge induced beam loss is well minimized by the combination of modest transverse painting and full longitudinal painting. But, for sufficiently mitigating the foil scattering beam loss, the transverse painting area has to be further expanded. However, such a wide-ranging transverse painting had not been realized until recently due to beta function beating caused by edge focusing of pulsed injection bump magnets. This beta function beating additionally excites random betatron resonances, causing significant extra beam loss when expanding the transverse painting area. To solve this issue, we newly installed pulse-type quadrupole correctors to compensate the beta function beating. This paper presents recent experimental results on this correction scheme, while discussing the beam loss and its mitigation mechanisms.
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Heavy Ion Accelerator Technology (HIAT 2015) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2015/09
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 767, p.372 - 378, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Okumura, Susumu; Ishibori, Ikuo; Yoshida, Kenichi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Nakamura, Yoshiteru
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.349 - 351, 2006/01
A flat-top acceleration system using fifth-harmonic frequency for the JAERI AVF cyclotron was developed to minimize the energy spread of an ion beam mainly for microbeam formation with a spot size of 1 micron in diameter by focusing with a set of quadrupole magnets. A single-turn extraction is an indispensable condition to reduce the energy spread without significant beam loss by the flat-top acceleration. In order to save time for the single-turn extraction tuning over measuring time distribution of the beam bunch, a deflector probe has been developed to observe the turn separation and the radial beam width. In this paper, we report the single-turn extraction technique with the deflector probe. As a result of beam developments, the single-turn extraction can be achieved in one or two hours and radioactivity of the deflector electrode can be also reduced in the acceleration of a high energy proton beam.
Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Okumura, Susumu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, P. 370, 2006/01
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Wataru; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sakai, Takuro; Okumura, Susumu; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.291 - 292, 2006/01
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Sakata, Shinya; Sueoka, Michiharu; Hosoyama, Hiroki*; Seki, Masami; JT-60 Team
AIP Conference Proceedings 787, p.279 - 286, 2005/09
A real-time control system of safety factor (q) profile was developed in JT-60. This system, for the first time, enables 1) real time evaluation of q profile using local magnetic pitch angle measurement by motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostic and 2) control of current drive (CD) location (rhoCD) by adjusting the parallel refractive index 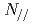 of lower-hybrid (LH) waves through the change of phase difference (dphi) of LH waves between multi-junction launcher modules. The method for q profile evaluation was newly developed, without time-consuming reconstruction of equilibrium, so that the method requires less computational time. The system evaluates q profile within every 10ms, which is much faster than current relaxation time, typically order of 1s. Safety factor profile by the real-time calculation agreed well with that by equilibrium reconstruction with MSE. From temporal evolution of q (or current) profile, we evaluate CD location in real-time, too. The control system controls rhoCD through
of lower-hybrid (LH) waves through the change of phase difference (dphi) of LH waves between multi-junction launcher modules. The method for q profile evaluation was newly developed, without time-consuming reconstruction of equilibrium, so that the method requires less computational time. The system evaluates q profile within every 10ms, which is much faster than current relaxation time, typically order of 1s. Safety factor profile by the real-time calculation agreed well with that by equilibrium reconstruction with MSE. From temporal evolution of q (or current) profile, we evaluate CD location in real-time, too. The control system controls rhoCD through 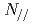 (or directly dphi) in such a way to minimize difference between the real-time evaluated q profile and its reference profile. The real-time control system was applied to positive shear plasmas (
(or directly dphi) in such a way to minimize difference between the real-time evaluated q profile and its reference profile. The real-time control system was applied to positive shear plasmas (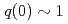 ), having plasma current of 0.6MA, toroidal field of 2.3T, and electron density of
), having plasma current of 0.6MA, toroidal field of 2.3T, and electron density of 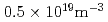 . In order to keep good coupling of LH waves to the plasma, gap between the launcher and the plasma surface was controlled to about 0.1m. The reference q profile was set to q(0)=1.3. The real-time q profile approached to the reference after application of real-time control; the controlled q profile was sustained for 3s, which was limited by injected LH power. RF experiments in JT-60U, such as stabilization of neo-classical tearing modes, plasma startup experiments, etc., are also presented.
. In order to keep good coupling of LH waves to the plasma, gap between the launcher and the plasma surface was controlled to about 0.1m. The reference q profile was set to q(0)=1.3. The real-time q profile approached to the reference after application of real-time control; the controlled q profile was sustained for 3s, which was limited by injected LH power. RF experiments in JT-60U, such as stabilization of neo-classical tearing modes, plasma startup experiments, etc., are also presented.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kubo, Shin*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(3), p.160 - 166, 2005/03
The local profile controls of electron temperature and current in fusion-oriented devices using the electron cyclotron (EC) wave is reviewed. Recent progress of the EC heating system that enabled those controls is briefly described. The specific feature of EC wave heating is local and high power density heating properties. Current drive and electron temperature profile control experiments using EC wave performed in order to improve and investigate plasma confinement properties are discussed.
Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Yokota, Wataru; Ishimoto, Takayuki*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Ishibori, Ikuo; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 76(3), p.033301_1 - 033301_6, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)A magnetic field drift, gradual decrease of the order of 10 in several tens of hours, was observed with the beam intensity decrease in an operation of an azimuthally-varying-field (AVF) cyclotron. From our experimental results, we show that the temperature increase of the magnet iron by the heat transfer from the excitation coils can induce such change of the magnetic field as to deteriorate the beam quality. The temperature control of the magnet iron was realized by thermal isolation between the main coil and the yoke and by precise control of the cooling water temperature of the trim coils attached to the pole surfaces in order to prevent temperature change of the magnet iron. The magnetic field stability of
in several tens of hours, was observed with the beam intensity decrease in an operation of an azimuthally-varying-field (AVF) cyclotron. From our experimental results, we show that the temperature increase of the magnet iron by the heat transfer from the excitation coils can induce such change of the magnetic field as to deteriorate the beam quality. The temperature control of the magnet iron was realized by thermal isolation between the main coil and the yoke and by precise control of the cooling water temperature of the trim coils attached to the pole surfaces in order to prevent temperature change of the magnet iron. The magnetic field stability of  5
5 10
10 and the beam intensity stability of
and the beam intensity stability of  2% have been achieved by this temperature control.
2% have been achieved by this temperature control.
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Okumura, Susumu; Chiba, Atsuya; Agematsu, Takashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Kaneko, Hirohisa; Nara, Takayuki; Saito, Yuichi; Ishii, Yasuyuki; et al.
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications (CYCLOTRONS 2004), p.208 - 210, 2005/00
A project to expand at TIARA (Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application) facilities of JAERI has been proposed to broaden applications in biotechnology and materials science. Heavy ions with energy more than 100 MeV/n are required for remarkable progress in breeding of plant and development of new materials. The magnet of a superconducting AVF cyclotron with a K number of 900 has been designed to cope with acceleration of both 150 MeV/n heavy ions and 300 MeV protons. The lower limit of energies has been investigated to overlap the energy region covered by the JAERI AVF cyclotron, required to increase beam time for present users. We have designed a beam transport system to satisfy requirements of the applications.
Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Okumura, Susumu; Yokota, Wataru; Yoshida, Kenichi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; et al.
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications (CYCLOTRONS 2004), p.157 - 159, 2005/00
The AVF cyclotron system at JAERI Takasaki has been smoothly operated for 13 years since 1991. This system continues to deliver various ion species with very frequent alterations of operational conditions. In order to provide a heavy ion beam with energy spread of 0.02 % required for microbeam production, we have developed a flat-top acceleration system, an additional buncher driven by saw-tooth wave, and improved the central region of the cyclotron. An old gradient corrector of passive type was replaced by a new gradient corrector with an active coil inside to obtain complete matching between the trunk beam line and extraction trajectory from the cyclotron. A compact ion source with a set of movable permanent magnet was designed to produce mainly light ions, which will be replaced the existing multi-cusp ion source in future.
Okumura, Susumu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Ishibori, Ikuo; Agematsu, Takashi; Nara, Takayuki; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Arakawa, Kazuo
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications (CYCLOTRONS 2004), p.410 - 412, 2005/00
A simple analyzing system has been developed to measure the energy spread of the beam extracted from the JAERI AVF cyclotron with an energy resolution of dE/E = 0.001%. The high analyzing power can be obtained with an existing deflecting magnet system in the transport line by installing three sets of slits with a minimum width of 0.01 mm and a beam intensity monitor with a Faraday cup and semiconductor detectors. These new instruments have been compactly designed to fulfill the geometrical condition of the existing beam diagnostic chambers, which are located at the object and image positions. Installation of the analyzing system was completed and a preliminary test has been carried out. This system will be used for optimization of the flat-top acceleration system to achieve the energy spread of dE/E = 0.02%, required for microbeam production.
Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sakai, Takuro; Okumura, Susumu; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Yokota, Wataru; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.207 - 210, 2004/10
A focused high-energy heavy ion scanning microbeam system with a spatial resolution of about 1 m is being developed at the AVF cyclotron of JAERI-Takasaki. It will provide microbeams to applications such as radiation tolerance testing of semiconductor devices and radio microsurgery in biomedical science with single ion hit technique. The main system components (slits, a beam scanner, quadrupole magnets and so on) had been installed in 2002. Test operations have been carried out since last year. We report the results obtained so far.
m is being developed at the AVF cyclotron of JAERI-Takasaki. It will provide microbeams to applications such as radiation tolerance testing of semiconductor devices and radio microsurgery in biomedical science with single ion hit technique. The main system components (slits, a beam scanner, quadrupole magnets and so on) had been installed in 2002. Test operations have been carried out since last year. We report the results obtained so far.
Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Okumura, Susumu; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Saito, Yuichi; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Agematsu, Takashi; Chiba, Atsuya; Sakai, Takuro; et al.
Proceedings of 1st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 29th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.643 - 645, 2004/08
A superconducting AVF cyclotron with a bending limit of 900 MeV and a focusing limit of 300 MeV is being designed to meet the requirements for the research in materials science and biotechnology at TIARA facility of JAERI. The spiral-sector shape of the cyclotron magnet has been optimized for acceleration of a 300 MeV proton to produce sufficient focusing forces in an extraction region. An energy range of the superconducting AVF cyclotron overlaps with that of the present K110 JAERI AVF cyclotron. Characteristics of a resonator for the superconducting AVF cyclotron have been investigated using the MAFIA code. An acceleration voltage in a frequency range of 24 to 64 MHz can be produced by the resonator with a  /2 excitation mode.
/2 excitation mode.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Ozeki, Takahisa
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(7), p.605 - 613, 2004/07
Neoclassical tearing mode stabilization by an electron cyclotron wave current drive (ECCD) has been studied by using the numerical model on the basis on the modified Rutherford eq. coupled with the 1.5D transport code and the EC code. Numerical model almost reproduces the JT-60U experimental results. Undetermined parameters in the modified Rutherford equation are estimated from JT-60U experiments. Sensitivity of stabilization to the EC current location is investigated. Low EC current and peaked EC current profile mitigates the sensitivity, while higher EC current and the peaked EC current profile moves the rational surface more largely through the background current modification by ECCD and intensify the sensitivity. High EC current and broad EC current profile also mitigates the sensitivity. EC current necessary for the full stabilization is studied. The necessary EC current much depends on the parameters of bootstrap current and ECCD terms in the modified Rutherford equation. Necessary ECCD power on ITER is evaluated on the basis of parameters estimated from JT-60U experiments.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Takizuka, Tomonori
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.477 - 487, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:72.41(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)NTM stabilization by ECCD has been numerically studied in order to evaluate the necessary EC power for the stabilization of NTM on ITER. The time evolution of an island width of NTM is calculated by the modified Rutherford equation. The modification of background current profile by the EC current is calculated by the current diffusion equation and the variation of the tearing stability index  ' is taken into account. When the EC power is higher than a threshold value, NTM with any island width can be fully stabilized. The dependence of the threshold power on parameters in the modified Rutherford equation is examined. The threshold power much depends on the parameters of the bootstrap current term in the modified Rutherford equation. The injected EC current decreases the value of
' is taken into account. When the EC power is higher than a threshold value, NTM with any island width can be fully stabilized. The dependence of the threshold power on parameters in the modified Rutherford equation is examined. The threshold power much depends on the parameters of the bootstrap current term in the modified Rutherford equation. The injected EC current decreases the value of  ' through the background current modification, which results in the reduction of the threshold power. The effects of the peakedness of EC current profile and the EC power modulation on the threshold power are investigated. When the width of the EC current profile becomes half, the threshold power is reduced to half or less. The EC power modulation is inessential for the threshold power reduction if the EC current profile can be peaked. Considering the maximum value of the threshold power in the range of the parameters, the EC power of about 25 MW is found to be sufficient for the simultaneous stabilization of both the
' through the background current modification, which results in the reduction of the threshold power. The effects of the peakedness of EC current profile and the EC power modulation on the threshold power are investigated. When the width of the EC current profile becomes half, the threshold power is reduced to half or less. The EC power modulation is inessential for the threshold power reduction if the EC current profile can be peaked. Considering the maximum value of the threshold power in the range of the parameters, the EC power of about 25 MW is found to be sufficient for the simultaneous stabilization of both the 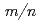 =3/2 and 2/1 mode NTM on ITER.
=3/2 and 2/1 mode NTM on ITER.
Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Okumura, Susumu; Yokota, Wataru; Arakawa, Kazuo; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; et al.
KEK Proceedings 2003-19, p.8 - 13, 2004/03
Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) facility at JAERI Takasaki was constructed to promote the various researches of wide field for materials science and biotechnology. The AVF cyclotron system, which is the one of four ion accelerators in TIARA, has been smoothly operated without any serious troubles since the first beam extraction in March 1991. The operation time for a year is about 3200 hours on an average through recent 8 years. In especial, the cyclotron system is needed the frequent alteration of operation condition according to many kinds of ion species required from the experimenters. On the other hand, because of the improvement of the beam quality, intensity and reliability, we have carried out continuously so far many reconstruction and development, several items of which are the renewal of a computer control system, reinforcement of the ion source, acceleration technique for some series of cocktail beams, stabilization of the cyclotron beam and design of a new gradient corrector including an active coil. Furthermore, now we are advancing various countermeasure to form the micro beam of 1mm size by means of focused type, such as the introduction of a flat-top acceleration system, reconstruction of the cyclotron center region, installation of a pair of precise micro slit systems in the trunk beam transport line, and so on.
Agematsu, Takashi; Arakawa, Kazuo; Okumura, Susumu; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Tajima, Satoshi
KEK Proceedings 2003-19, p.27 - 29, 2004/03
Cyclotron start-up operations require dozens of adjustable parameters to be tuned to maximize extracted beam current. Experienced operators perform this process through trial and error using their experience and intuition. However, the process is difficult for inexperienced operators because operator need to adjust parameters using little information such as measured beam data, alarm, status of components, and so on. We have developed a computer-based visual assistance system for JAERI AVF cyclotron. The system provides a CRT display: the cyclotron beam trajectories, feasible setting regions, search traces and the beam envelopes for external beam transport designed to optimize beam parameter adjustment. The evaluation experiment for the system was carried out and the operation time to reach required beam conditions of the injection region of the cyclotron was reduced by approximately 65%. Also the system is very useful to study the problems on the beam transport such as beam trajectory, envelope, beam profile, spot size and so on.
Fateh, B.; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Kume, Tamikazu; Sekine, Toshiaki*
JAERI-Review 2003-033, TIARA Annual Report 2002, p.259 - 261, 2003/11
no abstracts in English