Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Nunoshiba, Tatsuo*; Yamauchi, Ayako*; Iwata, Rika*; Sato, Katsuya; Ono, Yutaka; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 124, 2015/03

Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 18(3), p.134 - 135, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
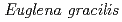
Hayashi, Hirotaka; Narumi, Issei; Wada, Seiichi; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Furuta, Masakazu*; Uehara, Kaku*; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Journal of Plant Physiology, 161(10), p.1101 - 1106, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:23.05(Plant Sciences)The resistance of 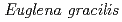 strains Z (wild type) and SM-ZK (chloroplast-deficient mutant) to ionizing radiation was investigated. The colony forming ability of
strains Z (wild type) and SM-ZK (chloroplast-deficient mutant) to ionizing radiation was investigated. The colony forming ability of 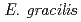 strain Z was higher than that of strain SM-ZK after
strain Z was higher than that of strain SM-ZK after  -irradiation. For both strains, the resistance of light-grown cells was higher than that of dark-grown cells, suggesting that the light conditions during the culture contribute to the radiation resistance of
-irradiation. For both strains, the resistance of light-grown cells was higher than that of dark-grown cells, suggesting that the light conditions during the culture contribute to the radiation resistance of 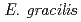 . The comet assay showed that the ability of rejoining DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) was much higher in the light-grown cells. These results suggest that
. The comet assay showed that the ability of rejoining DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) was much higher in the light-grown cells. These results suggest that 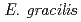 possesses a light-induced repair system to cope with DNA dsb.
possesses a light-induced repair system to cope with DNA dsb.

Battista, J. R.*; Cox, M. M.*; Daly, M. J.*; Narumi, Issei; Radman, M.*; Sommer, S.*
Science, 302(24), p.567 - 568, 2003/10
no abstracts in English

Narumi, Issei
Hoshasen To Chikyu Kankyo; Seitaikei Eno Eikyo O Kangaeru, p.113 - 122, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei
Iden, 57(5), p.57 - 62, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei
Trends in Microbiology, 11(9), p.422 - 425, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:89.95(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English

Hua, Y.*; Narumi, Issei; Gao, G.*; Tian, B.*; Sato, Katsuya; Kitayama, Shigeru; Shen, B.*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306(2), p.354 - 360, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:95.78(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have identified a unique deinococcal gene,  , as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which
, as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which  is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with
is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with  . In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of
. In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of  and
and  and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
Narumi, Issei
Science & Technology Journal, 12(5), p.50 - 51, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
 UV-endonuclease
UV-endonuclease 
Kitayama, Shigeru; Narumi, Issei; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 67(3), p.613 - 616, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.16(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Hiroshi
Bokin Bobai-Shi, 30(10), p.683 - 690, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
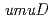 -encoded subunit of
-encoded subunit of  DNA polymerase V regulates its interactions with the
DNA polymerase V regulates its interactions with the  processivity clamp
processivity clampSutton, M. D.*; Narumi, Issei; Walker, G. C.*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(8), p.5307 - 5312, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:51.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The 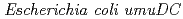 gene products (PolV) participate in both a DNA damage checkpoint control and translesion DNA synthesis. Interactions of the two
gene products (PolV) participate in both a DNA damage checkpoint control and translesion DNA synthesis. Interactions of the two 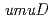 gene products, UmuD and UmuD' proteins, with components of the replicative DNA polymerase (PolIII), are important for determining which biological role the
gene products, UmuD and UmuD' proteins, with components of the replicative DNA polymerase (PolIII), are important for determining which biological role the 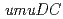 gene products will play. We have shown that UmuD possesses a higher affinity for PolIII
gene products will play. We have shown that UmuD possesses a higher affinity for PolIII  processivity clamp than does UmuD' because of the N-terminal arm of UmuD, much of which is missing in UmuD'. Futhermore, we identified specific amino acid residues of UmuD that crosslink to
processivity clamp than does UmuD' because of the N-terminal arm of UmuD, much of which is missing in UmuD'. Futhermore, we identified specific amino acid residues of UmuD that crosslink to  with a crosslinker,
with a crosslinker,  -azidoiodoacetanilide, defining the domain important for the interaction.
-azidoiodoacetanilide, defining the domain important for the interaction.

Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.172 - 184, 2002/03
 a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in
a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in  . By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in
. By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in  , LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in
, LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in  . This, in turn, led us to speculate that
. This, in turn, led us to speculate that  has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control
has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control  expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of
expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of  gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of
gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of  gene following
gene following  irradiation. Thus,
irradiation. Thus,  possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
 is not involved in RecA induction following
is not involved in RecA induction following  irradiation
irradiationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Journal of Bacteriology, 183(23), p.6951 - 6956, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:91 Percentile:84.2(Microbiology)The involvement of LexA in induction of RecA was investigated in  . As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following
. As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following  irradiation was detected in a
irradiation was detected in a 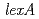 disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in
disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in  .
.
Kitayama, Shigeru*; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 461(3), p.179 - 187, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei
Advances in Space Research, 25(10), p.2103 - 2106, 2000/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:80.36(Engineering, Aerospace)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Hoshasen Kagaku, (67), p.35 - 39, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Sato, Katsuya
Hoshasen Seibutsu Kenkyu, 34(4), p.401 - 418, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Funayama, Tomoo; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 435, p.151 - 161, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 435(3), p.233 - 243, 1999/00
no abstracts in English