Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:96.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Okawa, Tomio*; Mori, Shoji*; Liu, W.*; Ose, Yasuo*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ono, Ayako
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(12), p.820 - 824, 2021/12
, 63(12), p.820 - 824, 2021/12
The evaluation method of the critical heat flux based on the mechanism is needed for the efficient design and development of fuel in reactors and the appropriate safety evaluation. In this paper, the current researches relating to the mechanism of the critical heat flux are reviewed, and the issue to be considered in the future are discussed.
Hironaka, Kota; Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a method for non-destructive measurement of nuclear material by using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. For NRTA system to carry out the short-distance TOF measurements with high resolutions, a short-pulsed neutron source is required. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) is very suitable as such a neutron source because of its short pulse width. Moreover, the compactness of the laser system is also expected due to the remarkable development of laser technology in recent years. In the present study, we have developed a technology for applying LDNS to the NRTA system and conducted the demonstration experiment using the LFEX laser at Osaka University to investigate the feasibility of the system. In this experiment, we successfully observed the neutron resonance peaks of indium and silver samples.
Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Hironaka, Kota; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
KURNS Progress Report 2020, P. 98, 2021/08
A compact Nuclear Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) system using a Laser Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been developed as a part of the development of nuclear non-proliferation technology supported by the MEXT. In NRTA, the neutron energy emitted from a pulsed neutron source is measured using the time-of-flight (TOF) method. LDNS is of interest because of its short pulse width, which is necessary for accurate TOF measurements over short flight distances. In the short-distance TOF measurement, there will be a large gamma-ray background event due to the coincidence of the timing of the arrival of 2.2 MeV gamma-rays due to neutron capture on hydrogen in the moderator and the timing of the arrival of neutrons around the resonance energy. Since the LDNS is still under development, the neutron flux is not sufficient and it is desirable to use a detector with high detection efficiency. For these reasons, we have developed a detector with low efficiency to gamma-rays and high efficiency to neutrons (multilayer neutron detector). As one of the results of this year's experiments, we confirmed that the multilayer neutron detector have low sensitivity to gamma-rays.
Yokokawa, Mitsuo; Saito, Minoru*; Ishihara, Takashi*; Kaneda, Yukio*
Hai Pafomansu Komputingu To Keisan Kagaku Shimpojium (HPCS2002) Rombunshu, p.125 - 131, 2002/01
With the advent of supercomputers, large-scale direct numerical simulations(DNS) of the Navier-Stokes equations are possible to carry out. However, larger scale DNS is required to make turbulence clear and to make a parameterization of turbulence. The Earth Simulator is a distributed memory parallel supercomputer whose peak speed is 40 Tflop/s and it is very useful to make a very large-scale DNS. Simulation codes named 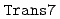 have been developed for the Earth Simulator and their correctness have been validated by compareing the simulation results by
have been developed for the Earth Simulator and their correctness have been validated by compareing the simulation results by 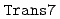 with ones by a conventinal code. The sustatined performance of 3.72Gflop/s is obtained in the execution of the serial version with the problem size of
with ones by a conventinal code. The sustatined performance of 3.72Gflop/s is obtained in the execution of the serial version with the problem size of 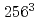 on an arithmetic processor(AP) of the Earth Simulator. Speedup of about 7 is achieved in 8APs by the parallelized code. Sppedup is degraded by the execution of 8 processor nodes, however, efficiency of 25% against the peak performance is obtained for the problem size of
on an arithmetic processor(AP) of the Earth Simulator. Speedup of about 7 is achieved in 8APs by the parallelized code. Sppedup is degraded by the execution of 8 processor nodes, however, efficiency of 25% against the peak performance is obtained for the problem size of 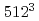 .
.
; ; ; ; ; ; Ogasawara, Shinobu*; Adachi, Masaaki*; Kume, Etsuo
JAERI-Data/Code 99-020, 168 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; ; Harada, Hiro; ; Kume, Etsuo;
JAERI-Data/Code 97-052, 160 Pages, 1997/12
no abstracts in English
Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Takahashi, Tone; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Hironaka, Kota; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
no journal, ,
We have been developing Nuclear Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) using Laser Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) as a part of nuclear non-proliferation technology development supported by the MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology) subsidy program "promotion of strengthening nuclear security and the like". An LDNS, which can generate short pulsed neutrons from a small volume, is considered to potentially have large benefits for the NRTA. In order to demonstrate the NRTA using the LDNS, the transmission measurements have been carried out by the TOF method using the LFEX laser at Osaka University. The results are reported here.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Hironaka, Kota; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hironaka, Kota; Lee, J.; Ito, Fumiaki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a method for non-destructive measurement of nuclear material by using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. For NRTA system to carry out the short-distance TOF measurements with high resolutions, a short-pulsed neutron source is required. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) is very suitable as such a neutron source because of its short pulse width. Moreover, the compactness of the laser system is also expected due to the remarkable development of laser technology in recent years. In the present study, we have developed a technology for applying LDNS to the NRTA system and conducted the demonstration experiment using the LFEX laser at Osaka University to investigate the feasibility of the system. In this experiment, we successfully observed the neutron resonance peaks of indium and silver samples.
Hironaka, Kota; Lee, J.; Ito, Fumiaki*; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a method for non-destructive measurement of nuclear material by using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. For NRTA system to carry out the short-distance TOF measurements with high resolutions, a short-pulsed neutron source is required. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) is very suitable as such a neutron source because of its short pulse width. Moreover, the compactness of the laser system is also expected due to the remarkable development of laser technology in recent years. In the present study, we have developed a technology for applying LDNS to the NRTA system and conducted the demonstration experiment using the LFEX laser at Osaka University to investigate the feasibility of the system. In this experiment, we successfully observed the neutron resonance peaks of indium and silver samples.