Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2024-017, 208 Pages, 2025/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2023. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the temporal changes in the score were analyzed. A system to report the tritium concentration level in seawater to the Nuclear Regulation Authority was operated, and the variation of tritium concentration before and after the discharge of ALPS treated water to the ocean was analyzed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan until FY2023 was analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys. Representative life patterns that can be expected after the return to the evacuation-designated restricted area were set, and the cumulative exposure doses were evaluated for the local governments and residents in the area. The measurement results for FY2023 were published on the Web site and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
 at temperature range 170 - 290
at temperature range 170 - 290 C
CLuu, V. N.; Nakajima, Kunihisa
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 426, p.113402_1 - 113402_7, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Kawai, Hiromi*; Wakisaka, Shinji*; Nagase, Sota*; Nakamura, Kento*; Yaguchi, Hiroki*; Ishii, Toshiaki; Nakano, Yumi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-008, 23 Pages, 2024/07
Five people from three universities participated in the 2023 summer holiday practical training with the theme of "Technical development on HTTR". The participants practiced the analysis of HTTR core, the analysis of behavior on loss of forced cooling test, the analysis of Iodine deposition behavior in primary cooling system and the feasibility study of energy storage system for HTGRs. In the questionnaire after this training, there were impressions such as that it was useful as a work experience and some students found it useful for their own research. These impressions suggest that this training was generally evaluated as good.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2023-024, 176 Pages, 2024/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2022. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. The range of fluctuation of past tritium concentration data in seawater was determined, and the causes of the fluctuation were discussed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed in 2022 owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan was summarized, and temporal changes in cesium-137 were analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2022 were published on the "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(24), p.16321 - 16326, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.11(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We clarified the chemical state transformation of deposits following the reduction of uranyl ion (U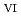 O
O
 ) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U
) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U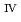 is formed by the disproportionation of U
is formed by the disproportionation of U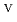 . (2) U
. (2) U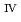 forms U
forms U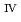 hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U
hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U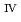 oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2022-026, 152 Pages, 2023/01
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2021. Car-borne surveys, a flat ground measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create air dose rate distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created for Fukushima Prefecture and the 80 km zone from the FDNPS, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan until 2020 was summarized, and temporal changes in cesium-137 were analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated the air dose rate distribution data obtained in this project with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2021 were published on the "Expansion Site of Distribution Map of Radiation Dose", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Villaret, F.*; Boulnat, X.*; Aubry, P.*; Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fabregue, D.*; de Carlan, Y.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 824, p.141794_1 - 141794_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.67(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Mikami, Satoshi; Tanaka, Hiroyuki*; Matsuda, Hideo*; Sato, Shoji*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Suzuki, Takeo*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Ando, Masaki; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105941_1 - 105941_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:63.21(Environmental Sciences)The deposition densities of radiocesium and the air dose rates were repeatedly measured in a large number of undisturbed fields within the 80km zone that surrounds the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant site between 2011 and 2016, and features of their temporal changes were clarified. The average air dose rate excluding background radiation in this zone decreased to about 20% of the initial value during the period from June 2011 to August 2016, which was essentially a result of the radioactive decay of  Cs with a half-life of 2.06y. The air dose rate reduction was faster than that expected from the decay of radiocesium by a factor of about two, with most of this reduction being attributed to the penetration of radiocesium into the soil. The average deposition densities of
Cs with a half-life of 2.06y. The air dose rate reduction was faster than that expected from the decay of radiocesium by a factor of about two, with most of this reduction being attributed to the penetration of radiocesium into the soil. The average deposition densities of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs in fields that were not decontaminated were found to have decreased nearly according to their expected radioactive decay, which indicated that the movement of radiocesium in the horizontal direction was relatively small. The effect of decontamination was apparently observed in the measurements of air dose rates and deposition densities. Nominally, the average air dose rates in the measurement locations were reduced by about 20% by decontamination and other human activities, of which accurate quantitative analysis is and continue to be a challenge.
Cs in fields that were not decontaminated were found to have decreased nearly according to their expected radioactive decay, which indicated that the movement of radiocesium in the horizontal direction was relatively small. The effect of decontamination was apparently observed in the measurements of air dose rates and deposition densities. Nominally, the average air dose rates in the measurement locations were reduced by about 20% by decontamination and other human activities, of which accurate quantitative analysis is and continue to be a challenge.
 gamma spectrometry intercomparison based on the information obtained through five intercomparisons during the Fukushima mapping project
gamma spectrometry intercomparison based on the information obtained through five intercomparisons during the Fukushima mapping projectMikami, Satoshi; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Matsuda, Hideo*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105938_1 - 105938_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.87(Environmental Sciences)Five intercomparisons of in situ  spectrometry by 6-7 participating teams have been conducted between December 2011 and August 2015 at sites in Fukushima prefecture which affected by the fallout of FDNPS accident occurred in March 2011. The evaluated deposition densities agreed within 5-6% in terms of coefficient of variation (CV) for radiocesium (
spectrometry by 6-7 participating teams have been conducted between December 2011 and August 2015 at sites in Fukushima prefecture which affected by the fallout of FDNPS accident occurred in March 2011. The evaluated deposition densities agreed within 5-6% in terms of coefficient of variation (CV) for radiocesium ( Cs and
Cs and  Cs), by our best achievement, and the ratio of
Cs), by our best achievement, and the ratio of  Cs/
Cs/ Cs in deposition density agreed within 1-2% in CV, through five intercomparisons. These results guarantee the accuracy of the measurements of the mapping project. Two different methods for intercomparison were conducted: (1) sequential measurements at an identical point; and (2) simultaneous measurements in a narrow area within 3 m radius. In a comparison between the two methods at a site, no significant difference was observed between the results. The standard protocols for the two different intercomparison methods were proposed based on our experience.
Cs in deposition density agreed within 1-2% in CV, through five intercomparisons. These results guarantee the accuracy of the measurements of the mapping project. Two different methods for intercomparison were conducted: (1) sequential measurements at an identical point; and (2) simultaneous measurements in a narrow area within 3 m radius. In a comparison between the two methods at a site, no significant difference was observed between the results. The standard protocols for the two different intercomparison methods were proposed based on our experience.
Saito, Kimiaki; Mikami, Satoshi; Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinase, Sakae; Tsuda, Shuichi; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Sato, Tetsuro*; Seki, Akiyuki; Yamamoto, Hideaki*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105878_1 - 105878_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:79.97(Environmental Sciences)Kato, Hiroaki*; Onda, Yuichi*; Gao, X.*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105996_1 - 105996_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:88.67(Environmental Sciences)Koizumi, Yasuo*; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Netsu Kogaku Konfuarensu 2019 Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 1 Pages, 2019/10
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Sentaro*; Kawashima, Shigeto*; Hidaka, Akihide; Tanaka, Sota*; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*
Nuclear Technology, 205(5), p.646 - 654, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)Horiguchi, Naoki; Miyahara, Naoya; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Osaka, Masahiko
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
For source term evaluation from reactor buildings (RBs) in LWR severe accidents, we have launched to develop an evaluation method of FP aerosol particle deposition onto surfaces of internal structures in an RB based on computational fluid dynamics (CFD). This paper describes development of a CFD simulation tool as the base part of the evaluation method. A preliminary simulation for a representative RB under a representative flow condition was conducted to confirm the tool performance by roughly grasping the deposition behaviors of FP aerosol particle and decontamination factor (DF) in the RB. Calculation results showed that most of aerosol particles were deposited along with gas flow formed by the internal structures in the RB, demonstrating the advantageous feature of the present CFD tool. The DFs from 4 to 14 were obtained with increase of the particle diameters from 0.1 to 10  m as expected in terms of the particle movement equation.
m as expected in terms of the particle movement equation.
 Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident; Simulations based on identical input data
Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident; Simulations based on identical input dataSato, Yosuke*; Takigawa, Masayuki*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kajino, Mizuo*; Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Uchida, Junya*; Goto, Daisuke*; Qu lo, D.*; et al.
lo, D.*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 123(20), p.11748 - 11765, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:84.51(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A model intercomparison of the atmospheric dispersion of  Cs emitted following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was conducted by 12 models to understand the behavior of
Cs emitted following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was conducted by 12 models to understand the behavior of  Cs in the atmosphere. The same meteorological data, horizontal grid resolution, and an emission inventory were applied to all the models to focus on the model variability originating from the processes included in each model. The multi-model ensemble captured 40% of the observed
Cs in the atmosphere. The same meteorological data, horizontal grid resolution, and an emission inventory were applied to all the models to focus on the model variability originating from the processes included in each model. The multi-model ensemble captured 40% of the observed  Cs events, and the figure-of-merit in space for the total deposition of
Cs events, and the figure-of-merit in space for the total deposition of  Cs exceeded 80. Our analyses indicated that the meteorological data were most critical for reproducing the
Cs exceeded 80. Our analyses indicated that the meteorological data were most critical for reproducing the  Cs events. The results also revealed that the differences among the models were originated from the deposition and diffusion processes when the meteorological field was simulated well. However, the models with strong diffusion tended to overestimate the
Cs events. The results also revealed that the differences among the models were originated from the deposition and diffusion processes when the meteorological field was simulated well. However, the models with strong diffusion tended to overestimate the  Cs concentrations.
Cs concentrations.
Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Mizuta, Naoki; Goto, Minoru; Fukaya, Yuji; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. Especially, a zirconium carbide (ZrC) coating is one of key technologies of the 3S-TRISO, which performs as an oxygen getter to reduce the fuel failure due to internal pressure during the irradiation. R&Ds on ZrC coating directly on the dummy CeO
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. Especially, a zirconium carbide (ZrC) coating is one of key technologies of the 3S-TRISO, which performs as an oxygen getter to reduce the fuel failure due to internal pressure during the irradiation. R&Ds on ZrC coating directly on the dummy CeO -YSZ kernel have been carried in the Japanese fiscal year 2017. As results of ZrC coating tests by the bromide chemical vapor deposition process, stoichiometric ZrC coatings with 3 - 18 microns of thicknesses were obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight.
-YSZ kernel have been carried in the Japanese fiscal year 2017. As results of ZrC coating tests by the bromide chemical vapor deposition process, stoichiometric ZrC coatings with 3 - 18 microns of thicknesses were obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Katata, Genki*; Kaneyasu, Naoki*; Nakanishi, Chika*; Urabe, Yoshimi*; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu*
Science of the Total Environment, 618, p.881 - 890, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:57.14(Environmental Sciences)Although the reconstruction of atmospheric deposition processes of radiocesium during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident is essential, the whole picture of the deposition mechanism in complex topography has not been well understood yet. To understand atmospheric deposition processes of aerosols over the complex mountainous topography, we analyzed altitudinal characteristics of radiocesium released during the accident. At five selected mountainous areas in the eastern Japan, altitudinal characters of air dose rate observed by our high-resolution airborne surveys after the accident was analyzed based on the results of three typical (dry, wet, and cloud water) deposition obtained from the latest atmospheric dispersion.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(49), p.29091 - 29100, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:53.01(Chemistry, Physical)The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen iodide in a membrane reactor using silica membranes derived from hexyltrimethoxysilane (HTMOS) was investigated for the production of hydrogen in the thermochemical water splitting iodine-sulfur process. The silica membranes were prepared by counter-diffusion chemical vapor deposition using porous alumina support tubes in both the absence and presence of a  -alumina layer. The silica membranes formed on
-alumina layer. The silica membranes formed on  -alumina-coated
-alumina-coated  -alumina tubes displayed a higher H
-alumina tubes displayed a higher H permeance than that formed directly on an
permeance than that formed directly on an  -alumina tube. A silica membrane based on a 1.5
-alumina tube. A silica membrane based on a 1.5  m-thick
m-thick  -alumina layer fabricated under deposition conditions of 450
-alumina layer fabricated under deposition conditions of 450 C, 1200 s, and a N
C, 1200 s, and a N carrier gas velocity of 0.044 m s
carrier gas velocity of 0.044 m s exhibited a high H
exhibited a high H permeance of 9.4
permeance of 9.4  10
10 mol Pa
mol Pa m
m s
s while maintaining an H
while maintaining an H /N
/N selectivity of over 80.0. The performance of a membrane reactor based on an HTMOS-derived silica membrane was evaluated at 400
selectivity of over 80.0. The performance of a membrane reactor based on an HTMOS-derived silica membrane was evaluated at 400 C by measuring the HI conversion and H
C by measuring the HI conversion and H flow rates. The conversion was approximately 0.48 when the HI flow rate was 9.7 mL min
flow rates. The conversion was approximately 0.48 when the HI flow rate was 9.7 mL min .
.
Ota, Masakazu; Kwamena, N.-O. A.*; Mihok, S.*; Korolevych, V.*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 178-179, p.212 - 231, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:46.91(Environmental Sciences)Environmental transfer models assume that organically-bound tritium (OBT) is formed directly from tissue-free water tritium (TFWT) in environmental compartments. Nevertheless, studies in the literature have shown that measured OBT/TFWT ratios are variable. The importance of soil-to-leaf HTO transfer pathway in controlling the leaf tritium dynamics is not well understood. A model inter-comparison of two tritium transfer models (CTEM-CLASS-TT and SOLVEG-II) was carried out with measured environmental samples from an experimental garden plot set up next to a tritium-processing facility. The garden plot received one of three different irrigation treatments - no external irrigation, irrigation with low tritium water and irrigation with high tritium water. The contrast between the results obtained with the different irrigation treatments provided insights into the impact of soil-to-leaf HTO transfer on the leaf tritium dynamics. Concentrations of TFWT and OBT in the garden plots that were not irrigated or irrigated with low tritium water were variable, responding to the arrival of the HTO-plume from the tritium-processing facility. In contrast, for the plants irrigated with high tritium water, the TFWT concentration remained elevated due to a continuous source of high HTO in the soil. Calculated concentrations of OBT in the leaves showed an initial increase followed by quasi-equilibration with the TFWT concentration. In this quasi-equilibrium state, concentrations of OBT remained elevated and unchanged despite the arrivals of the plume. These results from the model inter-comparison demonstrate that soil-to-leaf HTO transfer significantly affects OBT/TFWT ratio in the leaf regardless of the atmospheric HTO concentration, only if there is elevated HTO concentrations in the soil. The results of this work indicate that assessment models should be refined to consider the importance of soil-to-leaf HTO transfer to ensure that dose estimates are accurate and conservative.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
no abstracts in English