Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 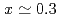
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
Higa, Ryota*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
Materials Transactions, 65(8), p.899 - 906, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)It is indispensable to suppress hydrogen embrittlement (HE) to develop the strength of the Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Because intergranular fracture (IGF) is mainly observed when HE occurs in the alloy, we need to understand the IGF initiation to suppress HE. In the present study, we investigated the stress, strain, and H concentration, which influence the IGF initiation, in actual fractured regions by simulation of a crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis in a 3D image-based model, which was created based on 3D polycrystalline microstructure data obtained from X-ray imaging technique. Combining the simulation and in-situ observation of the tensile test sample by X-ray CT, we examined the stress, strain, and H concentration, and discussed the IG crack initiation condition. As a result, it is revealed that stress normal to grain boundary induced by crystal plasticity dominates IG crack initiation while the accumulation of H due to stress has little impact on it.
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q. H.*; Fang, X.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tachi, Yukio
Sedimentary Geology, 465, p.106633_1 - 106633_14, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geology)Ito, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Watanabe, Nao; Yamashita, Susumu; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Nishihara, Kenji; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.3522 - 3534, 2023/08
Accelerator-driven system (ADS), the coolant of which is lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE), has been designed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Estimating corrosion rate at the wall surface of LBE channel is an important issue in considering safety and the life of the entire structure. The corrosion rate depends on state of oxygen layers forming at the material surface. Therefore, this study aims to develop a method to evaluate the corrosion rate in ADS for the design study by estimation of the oxide layer growth and dissolution (OLGD) rates by means of numerical analysis. The OLGD rates, mass transfer rates of oxygen and iron between the material and LBE and advection-diffusion rates of them in LBE depend on each other. Therefore, in order to estimate OLGD rates, the three numerical analysis models should be coupled. For the advection-diffusion calculation, to use CFD code should be reasonable approach to analyze complex flow in ADS, while for the OLGD and the mass transfer calculation, to use some correlation equations should be reasonable because their scales are much smaller than the advection-diffusion. The present work has developed the analysis method of OLGD rates by using JUPITER code, which is CFD code developed in JAEA. In terms of the correlation equations of OLGD and mass transfer rates, existing models used in a previous study were used with modified.
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1060218_1 - 1060218_18, 2022/12
 sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory (Sweden)
Hard Rock Laboratory (Sweden)Soler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
Geologica Acta, 20(7), 32 Pages, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:47.27(Geology)Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Soler, J. M.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; Svensson, U.*; Iraola, A.*; Ebrahimi, K.*; Trinchero, P.*; Molinero, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 208(6), p.1059 - 1073, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:62.34(Nuclear Science & Technology)The SKB Task Force is an international forum on modelling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing tracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A was the predictive modelling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modelling approaches and codes, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modelling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable.
 and GeO
and GeO liquids
liquidsKawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Crystal Growth, 585, p.126590_1 - 126590_7, 2022/05
Phase-field mobility,  , and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO
, and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO and GeO
and GeO liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the
liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the  was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with
was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with 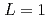 were confirmed to be proportional to a power of
were confirmed to be proportional to a power of 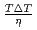 on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,
on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,  and
and  , of the
, of the 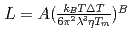 were
were 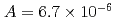 to
to 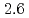 m
m J
J s
s and
and 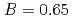 to
to 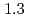 , which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined
, which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined  reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The
reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The  has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at
has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at 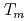 in a log-log graph. The
in a log-log graph. The  depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass,
depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass, 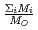 , in a compound. In
, in a compound. In 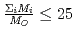 , the
, the  decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the
decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the  . Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the
. Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the  decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in
decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in 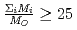 , the
, the  saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to
saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to 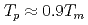 .
.
Hirooka, Shun; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Kato, Masato
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/04
Property studies on Am/Np-bearing MOX were carried out and how the properties influences on the irradiation behaviors was discussed. Both Am and Np inclusions increase the oxygen potential of MOX. Inter-diffusion coefficients obtained by using diffusion couple technique indicate that the inter-diffusion coefficient is larger in the order of U-Am, U-Pu and U-Np. Also, the inter-diffusion coefficients were evaluated to be larger at the O/M = 2 than those of O/M  2 by several orders. The increase of oxygen potential with Am/Np leads to higher vapor pressure of UO
2 by several orders. The increase of oxygen potential with Am/Np leads to higher vapor pressure of UO and the acceleration of the pore migration along temperature gradient during irradiation. The redistributions of actinide elements were also considered with the relationship of the pore migration and diffusion in solid state. Thus, the obtained inter-diffusion coefficients directly influence on the redistribution rate. The obtained properties were modelled and can be installed in a fuel irradiation simulation code.
and the acceleration of the pore migration along temperature gradient during irradiation. The redistributions of actinide elements were also considered with the relationship of the pore migration and diffusion in solid state. Thus, the obtained inter-diffusion coefficients directly influence on the redistribution rate. The obtained properties were modelled and can be installed in a fuel irradiation simulation code.
 -dispersed LATP by means of neutron radiography
-dispersed LATP by means of neutron radiographySong, F.*; Chen, H.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Yabutsuka, Takeshi*; Yao, Takeshi*; Takai, Shigeomi*
Solid State Ionics, 377, p.115873_1 - 115873_6, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.46(Chemistry, Physical)Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.121 - 125, 2022/04
The effect of solution layer thickness on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel was investigated using novel devices fabricated by a 3D printer. These novel devices allowed us to control the solution layer thickness precisely. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed under thickness-controlled solution layer, and oxygen diffusion limiting current density ( ) and anodic current density (
) and anodic current density ( ) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,
) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,  increased and
increased and  decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20
decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20 10
10 cm
cm s
s from the relationship between
from the relationship between  and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
Amemiya, Yutaro*; Nakada, Nobuo*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kosaka, Makoto*; Kato, Masaharu*
ISIJ International, 62(2), p.282 - 290, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.47(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 342, p.117580_1 - 117580_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.04(Chemistry, Physical)Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) and pulsed-field-gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFGNMR) analyses of a nanofluid composed of silicon dioxide (SiO ) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO
) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO
particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO nanofluids.
nanofluids.
 sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden
Hard Rock Laboratory in SwedenTachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Gylling, B.*
Water Resources Research, 57(11), p.e2020WR029335_1 - e2020WR029335_20, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.68(Environmental Sciences)This paper focuses on the scaling approach for sorption and diffusion parameters from laboratory to in-situ conditions using the dataset of LTDE-SD experiment performed at the  sp
sp HRL. The near-surface heterogeneities at both fracture surface and rock matrix could be evaluated by conceptual model with high porosity and diffusivity, and sorption capacity, and their gradual change at the near-surface zones. The modelling results for non-sorbing Cl-36 and weak-sorbing Na-22 could validate the model concept and the parameter estimation of porosity and diffusivity, by considering the disturbed zone of 5 mm thickness with gradual parameter changes. The De values of these cationic and anionic tracers showed typical cation excess and anion exclusion effects. The modelling results for high sorbing tracers (Cs-137, Ra-226, Ni-63 and Np-237) with different sorption mechanism could confirm the validity of the scaling approaches of Kd values as a function of particle size and their relation to the near-surface disturbances.
HRL. The near-surface heterogeneities at both fracture surface and rock matrix could be evaluated by conceptual model with high porosity and diffusivity, and sorption capacity, and their gradual change at the near-surface zones. The modelling results for non-sorbing Cl-36 and weak-sorbing Na-22 could validate the model concept and the parameter estimation of porosity and diffusivity, by considering the disturbed zone of 5 mm thickness with gradual parameter changes. The De values of these cationic and anionic tracers showed typical cation excess and anion exclusion effects. The modelling results for high sorbing tracers (Cs-137, Ra-226, Ni-63 and Np-237) with different sorption mechanism could confirm the validity of the scaling approaches of Kd values as a function of particle size and their relation to the near-surface disturbances.
Ito, Kanae; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shinohara, Akihiro*; Takata, Shinichi; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 125(39), p.21645 - 21652, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.54(Chemistry, Physical) sp
sp HRL LTDE-SD experiments
HRL LTDE-SD experimentsSoler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-20-17, 71 Pages, 2021/07
Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Fukuda, Kodai*; Honda, Yuki*; Tochio, Daisuke; Ho, H. Q.; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishii, Toshiaki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nakano, Yumi*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo
JAEA-Technology 2021-008, 23 Pages, 2021/06
The effect of mesh division around the burnable poison rod on the burnup calculation of the HTTR core was investigated using the SRAC code system. As a result, the mesh division inside the burnable poison rod does not have a large effect on the burnup calculation, and the effective multiplication factor is closer to the measured value than the conventional calculation by dividing the graphite region around the burnable poison rod into a mesh. It became clear that the mesh division of the graphite region around the burnable poison rod is important for more appropriately evaluating the burnup behavior of the HTTR core..