Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Fuain Kemikaru, 54(5), p.53 - 60, 2025/05
no abstracts in English
 Pt
Pt Ga
Ga with a honeycomb structure using extended X-ray absorption fine structure
with a honeycomb structure using extended X-ray absorption fine structureMatsumoto, Yuji*; Watabe, Yuki*; Iesari, F.*; Osumi, Masakatsu*; Ota, Kyugo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Hatada, Keisuke*; Okajima, Toshihiko*
Metals, 15(4), p.436_1 - 436_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Yamada, Masako*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Bourgeois, D.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Langmuir, 40(46), p.24257 - 24271, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Microscopic structures in liquid-liquid extraction, such as structuration between extractants or extracted complexes in bulk organic phases and at interfaces, can influence macroscopic phenomena, such as the distribution behavior of solutes, including extraction efficiency, selectivity, and phase separation of the organic phase. In this study, we correlated the macroscopic behavior of the extraction of Zr(IV) ions from nitric acid solutions with microscopic structural information in order to understand at the molecular level the key factors contributing to the higher metal ion extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system comprising fluorous phosphate (TFP) in perfluorohexane as compared to the analogous organic extraction system comprising organic phosphate (THP) in n-hexane. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure, neutron reflectometry, and small-angle neutron scattering revealed the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion, the accumulation of extractant molecules at the interface, and the structuration of extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase, respectively. In the fluorous extraction system, extractant aggregates with were formed after contact with nitric acid. In contrast, in the organic extraction system, only extractant dimers were formed. We speculate that differences in the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion and the structuration of the extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase contribute to the high Zr(IV) extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system. In particular, the size of the aggregates hardly changed with increasing Zr(IV) concentration in the fluorous phase, which may be closely related to the absence of phase splitting in the fluorous extraction system.
Nankawa, Takuya
Kagaku, 79(8), p.48 - 52, 2024/08
Lacquer is a natural paint with excellent water and chemical resistance. It has long been known that adding a very small amount of iron into raw lacquer produces a very beautiful black color called Shikoku. However, the structure and reactions of lacquer are still largely unknown, and the reason of black color is also unclear. In this study, we analyzed the structure of raw lacquer and black lacquer films by using different kind of quantum beams. As a result, black lacquer has a completely different nanostructure from raw lacquer, and that the color changes depending on the difference in the structure. This result is the first successful analysis of the structure of the lacquer film, which had been a mystery for many years. This commentary describes this research and also explains how this research has been proceeded.
 -edge EXAFS and magnetic EXAFS studies on the halfmetallic ferromagnet Co
-edge EXAFS and magnetic EXAFS studies on the halfmetallic ferromagnet Co MnSi
MnSiKogo, Junya*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Saito, Yuji; Umetsu, Rie*; Niki, Kaori*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(3), p.034702_1 - 034702_12, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Ln
Ln O
O (Ln = Gd, Er) solid solution
(Ln = Gd, Er) solid solutionPham, V. M.*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153189_1 - 153189_9, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The crystal structure change was evaluated for (1-x)UO -xLnO
-xLnO (Ln=Gd or Er; x = 0 to 0.4) samples sintered at 1973 K for 8 h under Ar and Ar-10%H
(Ln=Gd or Er; x = 0 to 0.4) samples sintered at 1973 K for 8 h under Ar and Ar-10%H atmospheres. The effect of LnO
atmospheres. The effect of LnO doping on the crystal structure of UO
doping on the crystal structure of UO was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). LnO
was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). LnO doping into UO
doping into UO reduced the lattice parameter of UO
reduced the lattice parameter of UO -LnO
-LnO solid solutions up to 40mol% LnO
solid solutions up to 40mol% LnO . The lattice parameters of these samples were comparable to those of stoichiometric (U,Ln)O
. The lattice parameters of these samples were comparable to those of stoichiometric (U,Ln)O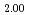 solid solutions, that is, the O/M ratios were close to 2.00. The U L
solid solutions, that is, the O/M ratios were close to 2.00. The U L -edge XANES analysis showed that higher U oxidation states of +5 or +6 formed, in addition to + 4. The EXAFS analysis indicated that the interatomic distances of U-O and Gd-O decreased with increasing x, whereas those of Er-O may not decrease monotonically.
-edge XANES analysis showed that higher U oxidation states of +5 or +6 formed, in addition to + 4. The EXAFS analysis indicated that the interatomic distances of U-O and Gd-O decreased with increasing x, whereas those of Er-O may not decrease monotonically.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Kanasashi, Tsutomu*; Takenaka, Chisato*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Science of the Total Environment, 755, Part 2, p.142598_1 - 142598_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.63(Environmental Sciences)In this study, we investigated coordination structures of Cs in  Cs-doped bark, sapwood, heartwood, needle, and branch samples of trees collected in Fukushima by extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. We examined four representative tree species in Fukushima,
Cs-doped bark, sapwood, heartwood, needle, and branch samples of trees collected in Fukushima by extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. We examined four representative tree species in Fukushima, 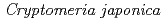 ,
, 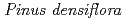 ,
, 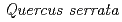 , and
, and 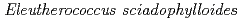 . EXAFS spectra suggested that Cs was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on all parts of the four species, with electrostatic binding to negatively charged functional groups in components of tree tissues. These results were supported by extraction experiments where most of the sorbed Cs was desorbed from all parts of each tree species using 1 M CH
. EXAFS spectra suggested that Cs was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on all parts of the four species, with electrostatic binding to negatively charged functional groups in components of tree tissues. These results were supported by extraction experiments where most of the sorbed Cs was desorbed from all parts of each tree species using 1 M CH COONH
COONH .
.
Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Okada, Makoto*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Hagura, Naoto*; Kada, Wataru*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 477, p.60 - 65, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Instruments & Instrumentation)IBIL and EXAFS analyses were applied on strucutral analysis of Eu complex formed in adsorbent developed for extraction chromatography. Those analyses revealed slight structural difference between adsorbent and solvent systems.
Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Ono, Shimpei; Nomura, Kazunori; Nakamura, Fumiya*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Seko, Noriaki*; Hoshina, Hiroyuki*; Hagura, Naoto*; Kubota, Toshio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 477, p.54 - 59, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)Narita, Hirokazu*; Nicolson, R. M.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ito, Fumiyuki*; Morisaku, Kazuko*; Goto, Midori*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Heller, W. T.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:75.49(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) As
As and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS analyses
and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS analysesLi, S.*; Toyoda, Masayuki*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Ito, Masayuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Otani, Akira*; Matsumura, Daiju; Asano, Shun*; Mizuki, Junichiro*; et al.
Physica C, 555, p.45 - 53, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.97(Physics, Applied) -dependence of local distortions in BaFe
-dependence of local distortions in BaFe As
As and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS methods. Although PDF data exhibit anomaly at the structure transition temperature, EXAFS data exhibit no anomaly. Data supporting the local orthorhombicity at 300 K in the tetragonal phase for BaFe
and LiFeAs by X-ray PDF and XAFS methods. Although PDF data exhibit anomaly at the structure transition temperature, EXAFS data exhibit no anomaly. Data supporting the local orthorhombicity at 300 K in the tetragonal phase for BaFe As
As . Arguments on the origins of the 4-fold symmetry breaking in the ground average structure of the tetragonal phase.
. Arguments on the origins of the 4-fold symmetry breaking in the ground average structure of the tetragonal phase.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Takano, Masahide
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.200 - 203, 2018/11
Chemical state of some simulated corium debris samples containing uranium (fuel), zirconium (fuel cladding), iron (structure material), calcium (cement) and lanthanides (fission products) was investigated by synchrotron radiation based extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis. The local structure of uranium for the simulated debris was classified into fluorite UO structure and C-type structure (stabilized cubic). The U
structure and C-type structure (stabilized cubic). The U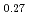 Zr
Zr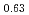 Fe
Fe Ca
Ca O
O sample, which consists of single phase (C-type), shows slightly shorter U-O distance. It can be concluded that the sample contains pentavalent uranium. The local structure of zirconium for U-Zr-O and U-Zr-Fe-O systems was very close to tetragonal ZrO
sample, which consists of single phase (C-type), shows slightly shorter U-O distance. It can be concluded that the sample contains pentavalent uranium. The local structure of zirconium for U-Zr-O and U-Zr-Fe-O systems was very close to tetragonal ZrO , while that of zirconium changed to CSZ (calcia stabilized cubic) by adding calcium.
, while that of zirconium changed to CSZ (calcia stabilized cubic) by adding calcium.
 -conjugated zig-zag chain of carbon atoms with sulfur-functional group
-conjugated zig-zag chain of carbon atoms with sulfur-functional groupIkeura, Hiromi*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Applied Physics Letters, 111(23), p.231605_1 - 231605_4, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Photo-oxidative doping processes were studied for the trans-polyacetylene (PA) backbone with the -SCH side group as a chemically representative of the S-functionalized zig-zag graphene nanoribbon edge. Sulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy indicates that photochemical reaction of S-CH
side group as a chemically representative of the S-functionalized zig-zag graphene nanoribbon edge. Sulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy indicates that photochemical reaction of S-CH with atmospheric O
with atmospheric O forms selectively oxidized products such as -S(O)CH
forms selectively oxidized products such as -S(O)CH and -SO
and -SO
 bound to the (PA) backbone. Using the correlation between the oxidation states of sulfur and the XANES peak positions, the partial charge distribution of CH
bound to the (PA) backbone. Using the correlation between the oxidation states of sulfur and the XANES peak positions, the partial charge distribution of CH S
S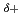 -PA
-PA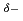 has been estimated. The results can provide some strategy for area-selective and controllable doping processes of atomic-scale molecular systems with the assistance of UV light.
has been estimated. The results can provide some strategy for area-selective and controllable doping processes of atomic-scale molecular systems with the assistance of UV light.
Sano, Yuichi; Watanabe, So; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Nagoshi, Kohei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(10), p.1058 - 1064, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)For effective recovery of radioactive elements by adsorbents using polymer-immobilized silica (SiO -P) supports, the microstructure of SiO
-P) supports, the microstructure of SiO -P particles impregnated with CMPO as extractants and their change with the crosslinking degree of polymer (CDP) were investigated using STXM and EXAFS analyses; further, their relation with adsorption/elution behavior was discussed. The adsorption/elution tests using adsorbents with a different CDP demonstrated that a higher CDP inhibited the elution of adsorbed metal ions from the adsorbent. The results of STXM and EXAFS analyses suggested that adsorption by CMPO proceeds through the entire area in the adsorbent and the local structure around adsorbed metal ions is similar irrespective of the CDP. Conversely, STXM analyses implied the capture of eluents such as H
-P particles impregnated with CMPO as extractants and their change with the crosslinking degree of polymer (CDP) were investigated using STXM and EXAFS analyses; further, their relation with adsorption/elution behavior was discussed. The adsorption/elution tests using adsorbents with a different CDP demonstrated that a higher CDP inhibited the elution of adsorbed metal ions from the adsorbent. The results of STXM and EXAFS analyses suggested that adsorption by CMPO proceeds through the entire area in the adsorbent and the local structure around adsorbed metal ions is similar irrespective of the CDP. Conversely, STXM analyses implied the capture of eluents such as H O by polymers with high CDP, which suppresses the prompt elution of adsorbed metal ions from the adsorbent.
O by polymers with high CDP, which suppresses the prompt elution of adsorbed metal ions from the adsorbent.
Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Ono, Shimpei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 404, p.202 - 206, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)Abe, Ryoji*; Nagoshi, Kohei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Takagi, Hideaki*; Shimizu, Nobutaka*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 404, p.173 - 178, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Hirao, Norie*
Applied Surface Science, 405, p.255 - 266, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.34(Chemistry, Physical)NEXAFS spectroscopy is applied to study orientation structures of polydimethylsilane (PDMS) films deposited on heteroatom-doped graphite substrates prepared by ion beam doping. The Si  -edge NEXAFS spectra of PDMS show opposite trends of polarization dependence for non irradiated and N
-edge NEXAFS spectra of PDMS show opposite trends of polarization dependence for non irradiated and N
 -irradiated substrates, and show no polarization dependence for an Ar
-irradiated substrates, and show no polarization dependence for an Ar -irradiated substrate. Based on a theoretical interpretation of the NEXAFS spectra via first-principles calculations, we clarify that PDMS films have lying, standing, and random orientations on the non irradiated, N
-irradiated substrate. Based on a theoretical interpretation of the NEXAFS spectra via first-principles calculations, we clarify that PDMS films have lying, standing, and random orientations on the non irradiated, N
 -irradiated, and Ar
-irradiated, and Ar -irradiated substrates, respectively. Furthermore, photoemission electron microscopy indicates that the orientation of a PDMS film can be controlled with microstructures on the order of
-irradiated substrates, respectively. Furthermore, photoemission electron microscopy indicates that the orientation of a PDMS film can be controlled with microstructures on the order of  m by separating irradiated and non irradiated areas on the graphite surface. These results suggest that surface modification of graphite using ion beam doping is useful for micro-orientation control of organic thin films.
m by separating irradiated and non irradiated areas on the graphite surface. These results suggest that surface modification of graphite using ion beam doping is useful for micro-orientation control of organic thin films.
Maeda, Motoki*; Narita, Hirokazu*; Tokoro, Chiharu*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Separation and Purification Technology, 177, p.176 - 181, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.11(Engineering, Chemical)Mayumi, Ren*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Saito, Yuichi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 42(1), p.9 - 14, 2017/02
AlCu binary alloys were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni or 4.5 MeV Al ions at room temperature. Changes in surface hardness and the local atomic structure around Cu atoms were examined by using the Vickers hardness measurement and the EXAFS measurements, respectively. Some specimens were aged at 453 K and Vickers hardness was measured. The computer simulation was also performed by using the rate equation method. The hardness of irradiated specimens increased much faster than that of the aged specimens and it became larger than the maximum value of the hardness for the aged specimens. The comparison of the experimental EXAFS result with that of FEFF simulation suggests that the ion irradiation produced small Cu precipitates in the specimens. The computer simulation visualized the growth process of Cu precipitates during the irradiation, and the result qualitatively corresponds to the experimental result.
 Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiation
Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiationKojima, Hiroshi*; Yoshizaki, Hiroaki*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 372, p.72 - 77, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:72.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au
Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni
ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni Al and Ni
Al and Ni V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.