Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luu, V. N.; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steelIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Shibayama, Yuki; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Akiyama, Eiji*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 88, p.1010 - 1016, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.25(Chemistry, Physical)Higa, Ryota*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
Materials Transactions, 65(8), p.899 - 906, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)It is indispensable to suppress hydrogen embrittlement (HE) to develop the strength of the Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Because intergranular fracture (IGF) is mainly observed when HE occurs in the alloy, we need to understand the IGF initiation to suppress HE. In the present study, we investigated the stress, strain, and H concentration, which influence the IGF initiation, in actual fractured regions by simulation of a crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis in a 3D image-based model, which was created based on 3D polycrystalline microstructure data obtained from X-ray imaging technique. Combining the simulation and in-situ observation of the tensile test sample by X-ray CT, we examined the stress, strain, and H concentration, and discussed the IG crack initiation condition. As a result, it is revealed that stress normal to grain boundary induced by crystal plasticity dominates IG crack initiation while the accumulation of H due to stress has little impact on it.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 587, p.154736_1 - 154736_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Lu, K.; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 199, p.104706_1 - 104706_13, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:55.03(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Iwata, Keiko; Hata, Kuniki; Tobita, Toru; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(2), p.021505_1 - 021505_8, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.21(Engineering, Mechanical)Nagase, Fumihisa; Narukawa, Takafumi; Amaya, Masaki
JAEA-Review 2020-076, 129 Pages, 2021/03
Each light-water reactor (LWR) is equipped with the Emergency Core Cooling System (ECCS) to maintain the coolability of the reactor core and to suppress the release of radioactive fission products to the environment even in a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) caused by breaks in the reactor coolant pressure boundary. The acceptance criteria for ECCS have been established in order to evaluate the ECCS performance and confirm the sufficient safety margin in the evaluation. The limits defined in the criteria were determined in 1975 and reviewed based on state-of-the-art knowledge in 1981. Though the fuel burnup extension and necessary improvements of cladding materials and fuel design have been conducted, the criteria have not been reviewed since then. Meanwhile, much technical knowledge has been accumulated regarding the behavior of high-burnup fuel during LOCAs and the applicability of the criteria to the high-burnup fuel. This report provides a comprehensive review of the history and technical bases of the current criteria and summarizes state-of-the-art technical findings regarding the fuel behavior during LOCAs. The applicability of the current criteria to the high-burnup fuel is also discussed.
 and chromia-alumina additive fuels under simulated reactivity-initiated accidents; A Comparative analysis with FEMAXI-8
and chromia-alumina additive fuels under simulated reactivity-initiated accidents; A Comparative analysis with FEMAXI-8Udagawa, Yutaka; Mihara, Takeshi; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Amaya, Masaki
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 139, p.107268_1 - 107268_9, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nagase, Fumihisa; Fuketa, Toyoshi
NUREG/CP-0192, p.197 - 230, 2005/10
The Japanese regulatory criterion for a loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) is based on a threshold of fuel rod fracture during quenching, which was experimentally determined under simulated LOCA conditions. In order to evaluate the fracture threshold of high burn-up fuel rods, JAERI performs integral thermal shock tests simulating LOCA conditions. The tests have been performed with pre-hydrided, unirradiated claddings and high burn-up fuel claddings irradiated to 39 and 44 GWd/t at a PWR. It was shown that fracture/no-fracture threshold primarily depends on the oxidation amount and that the threshold decreases with increases in hydrogen concentration and axial restraint during the quench. It was also shown that fracture conditions of the tested high burn-up fuel claddings are consistent with the fracture threshold derived from unirradiated claddings with similar hydrogen concentrations.
Tachibana, Yukio; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Iyoku, Tatsuo
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 233(1-3), p.103 - 112, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tachibana, Yukio; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Iyoku, Tatsuo
Elevated Temperature Design and Analysis, Nonlinear Analysis, and Plastic Components, 2004 (PVP-Vol.472), p.39 - 44, 2004/07
The reactor pressure vessel (RPV) of the HTTR is 5.5m in inside diameter, 13.2m in inside height, and 122mm and 160mm in wall thickness of the body and the top head dome, respectively. Because the reactor inlet temperature of the HTTR is higher than that of LWRs, 2 1/4Cr-1Mo steel is chosen for the RPV material. Fluence of the RPV is estimated to be less than 1 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E 1 MeV), and so irradiation embrittlement is presumed to be negligible, but temper embrittlement is not. For the purpose of reducing embrittlement, content of some elements is limited on 2 1/4 Cr-1 Mo steel for the RPV using embrittlement parameters, J-factor and X-bar. In this paper design, fabrication procedure, and in-service inspection technique of the RPV for the HTTR are described.
1 MeV), and so irradiation embrittlement is presumed to be negligible, but temper embrittlement is not. For the purpose of reducing embrittlement, content of some elements is limited on 2 1/4 Cr-1 Mo steel for the RPV using embrittlement parameters, J-factor and X-bar. In this paper design, fabrication procedure, and in-service inspection technique of the RPV for the HTTR are described.
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.479 - 485, 2004/07
In the structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessel, fracture toughness values are estimated by assuming that the radiation effect on fracture toughness is equivalent to that on Charpy properties. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the correlation between both properties especially on irradiation embrittlement. In this paper, we present the fracture toughness data obtained by applying the master curve approach that was adopted recently in the ASTM test method. Materials used in this study are five ASTM A533B class 1 steels and one weld metal. Neutron irradiation for Charpy-size specimens as well as standard Charpy-v specimens was carried out at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor. The shifts of the reference temperature on fracture toughness due to neutron irradiation are evaluated. Correlation between the fracture toughness reference temperature and Charpy transition temperature is established. Based on the correlation, the optimum test temperature for fracture toughness testing and the method to determine a lower bound fracture toughness curve are discussed.
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Kato, Daisuke*; Li, Y.*
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.486 - 493, 2004/07
The probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAERI. This code can evaluate the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Based on the temperature and stress distributions in the vessel wall for four PTS sequences in a typical 3-loop PWR, parametric PFM analyses are performed using PASCAL on the variables such as pre-service inspection model, crack geometry, fracture toughness curve and irradiation embrittlement prediction equation. The results showed that the good perfomance inspection model had a significant effect on the fracture probability and reduced it by more than 3 orders of magnitude. The fracture probability calculated by the fracture toughness estimation method in Japan was about 2 orders of magnitude lower than that by the USA method. It was found that the treatment of a semi-elliptical crack in PASCAL reduced the conservatism in a conventional method that it is transformed into an infinite length crack.
 5 (012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary; A First-principles study
5 (012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary; A First-principles studyYamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(23), p.3933 - 3956, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:97 Percentile:93.73(Physics, Condensed Matter)A series of non-transition elements bound to the Ni  5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and the (012) free surface (FS) systems has been studied by first-principles calculation using WIEN2k code. The multilayer relaxations in presence/absence of the solutes are determined by the force minimization. The binding energies at some GB/FS/bulk sites including both interstitial and substitutional sites are calculated for all the non-transition elements between
5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundary (GB) and the (012) free surface (FS) systems has been studied by first-principles calculation using WIEN2k code. The multilayer relaxations in presence/absence of the solutes are determined by the force minimization. The binding energies at some GB/FS/bulk sites including both interstitial and substitutional sites are calculated for all the non-transition elements between  H and
H and 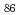 Rn. The GB/FS segregation energy is obtained by calculating the binding energy difference between the GB/FS site and the bulk site. The embrittling potency energy is obtained by calculating the difference between the GB and FS segregation energies based on Rice-Wang model. Our results show that most of the non-transition elements have negative GB/FS segregation energies. Here, this means that there exists a segregation site in the GB/FS. The embrittling potency energies are positive for most of the solutes. However, some exceptions like Be, B, C, and Si having negative and large embrittling potency can enhance the GB cohesion. Our results are found to be consistent with the experimental findings.
Rn. The GB/FS segregation energy is obtained by calculating the binding energy difference between the GB/FS site and the bulk site. The embrittling potency energy is obtained by calculating the difference between the GB and FS segregation energies based on Rice-Wang model. Our results show that most of the non-transition elements have negative GB/FS segregation energies. Here, this means that there exists a segregation site in the GB/FS. The embrittling potency energies are positive for most of the solutes. However, some exceptions like Be, B, C, and Si having negative and large embrittling potency can enhance the GB cohesion. Our results are found to be consistent with the experimental findings.
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Kato, Daisuke*; Li, Y.*
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2003/04
Probabilistic Fracture Mechanics (PFM) has been used in the fields of reliability analysis for important structural components. At JAERI, the PFM analysis code PASCAL has been developed. This code evaluates the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Four cases of PTS transients were selected based on the severity for a typical 3-loop PWR. Based on thermal stress analyses, PFM analyses were performed by using PASCAL code focusing on some important variables on the RPV fracture probability. The results showed that non-destructive examination methods had a significant effect on the fracture probability by more than three orders of magnitude. The comparisons of the results using fracture toughness estimation methods between in Japan and USA, and crack geometries between a semi-elliptical surface crack and an infinite surface crack are also made.
Ishii, Toshimitsu; Ooka, Norikazu; Hoshiya, Taiji; Kobayashi, Hideo*; Saito, Junichi; Niimi, Motoji; Tsuji, Hirokazu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part.1), p.240 - 244, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tobita, Toru; Suzuki, Masahide; Iwase, Akihiro; Aizawa, Kazuya
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 299(3), p.267 - 270, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:82.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kameda, Jun*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Bloomer, T. E.*
Surface and Interface Analysis, 31(7), p.522 - 531, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:28.36(Chemistry, Physical)This study describes intergranular segregation and embrittlement in several model ferritic alloys doped with Mn, P, S and/or Cu subjected to neutron irradiation, irradiation-equivalent thermal ageing (ETA) and post-irradiation annealing (PIA). Neutron irradiation produced a larger amount of intergranular P segregation than S segregation. Intergranular C segregation remained small in all the as-irradiated alloys. A PIA study has shown that the P segregation in P-doped alloys subjected to lower temperature PIA proceeds via mobile P-interstitial complexes while the S segregation is controlled by vacancy-enhanced diffusion. The mechanisms of non-equilibrium intergranular segregation induced by neutron irradiation are discussed in light of coupled fluxes of point defects and impurities, and changes in the segregation capacity of grain boundaries. Small punch tests demonstrated how the impurity segregation or desegregation and hardening or softening induced by the irradiation, ETA and PIA influence intergranular embrittlement in the various ferritic alloys.